4"
"
protein precursor has been observed in male fish exposed to E2 concentrations as low as 25 ng L
-
62"
1
.
[12]
Drinking water contaminated with estrogens could pose health risk to humans.
[7,12]
63"
64"
Bacteria that can degrade E2 in soil and human waste products include the genera Aminobacter, 65"
Escherichia, Pseudomonas, Sphingomonas (Proteobacteria), Corynebacterium, Microbacterium, 66"
Nocardioides, Rhodococcus (Actinobacteria), and Flavobacterium (Bacteroidetes).
[13-19]
67"
Microbial degradation is a main path of estrogen degradation
[20-22]
, hence antimicrobial toxicity 68"
towards these bacteria may result in increased E2 persistence in soil and human waste products. 69"
For example, chlortetracycline, sulfamethazine and tylosin applied to soil at concentrations as 70"
low as 2 mg kg
-1
significantly reduced the transformation of E2 to estrone (E1).
[23]
71"
Antimicrobials affect bacterial compositions with the impact on specific species being depended 72"
on the types and concentrations of antimicrobial present, as well as the duration of exposure and 73"
the level of bacterial resistance to the antibiotics.
[24]
74"
75"
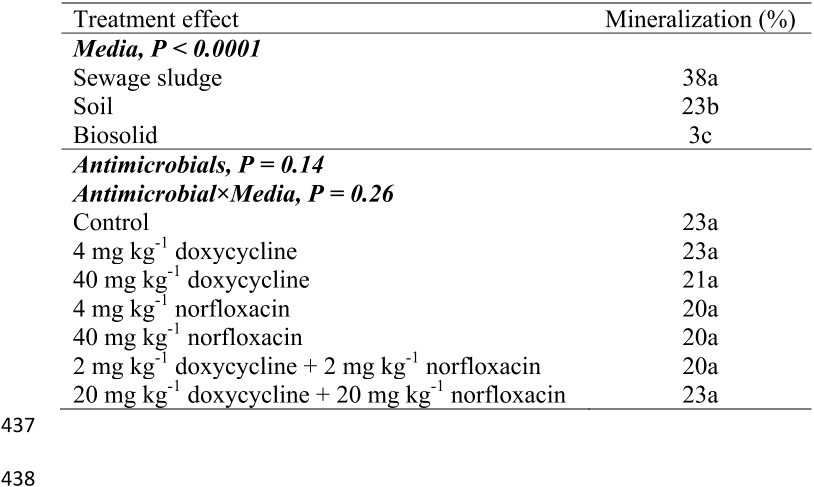
E2 mineralization can be quantified by using radiolabeled [4-
14
C] E2 in microcosm experiments 76"
[21,25,26]
, whereby the recovery of
14
CO
2
indicates that the steroid molecule has been inactivated 77"
because of ring cleavage.
[27]
Antimicrobial additions to soil and other media has shown to 78"
reduce reduced E2 mineralization in some cases.
[20,23,26]
For example, the addition of 40 mg kg
-1
79"
tetracycline to manure decreased total E2 mineralization by 14% relatively to manure without 80"
antibiotics added, but E2 mineralization in soils was not impacted.
[26]
81"
82"
"In this study, we examine the impact of the antimicrobials doxycycline and norfloxacin on E2 83"
mineralization in media. Doxycycline, which selectively inhibits the 30S ribosomal subunit in 84"