




Did you find this useful? Give us your feedback





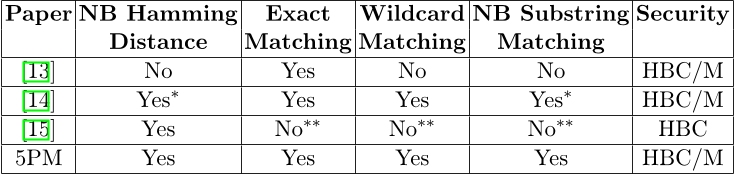

![Table 2. Detailed comparison with [14] and [16] for single-character wildcards and substring matching in malicious model with text length=n, pattern length=m, security parameter=k, rounds=Rds.](/figures/table-2-detailed-comparison-with-14-and-16-for-single-xf61t5xw.png)
![Table 3. Detailed comparison with [15] for non-binary substring matching in HBC model with text length=n, pattern length=m, security parameter=k, rounds=Rds.](/figures/table-3-detailed-comparison-with-15-for-non-binary-substring-2o93ac7o.png)


![Table 13. Performance results for 1024 and 2048 bit key length in seconds for different settings of the alphabet Σ, the pattern p and the text T using fast-decryption Paillier [40].](/figures/table-13-performance-results-for-1024-and-2048-bit-key-juynvcjx.png)





130 citations
...5PM [3] O((k + )λ) 2 (semi-honest) practical in using exact, approximate, (MPC-based) O((k + )λ(2)) 8 (malicious) k ≤ 1000 ∼ 10000 wildcards, substring FHE O( ) 2 impractical any Our work O( /n ) 2 faster than 5PM exact, approximate (SHE scheme)...
[...]
...in [3] presented an efficient twoparties protocol of secure pattern matching for more expressive search queries including single character wildcards and substring pattern matching....
[...]
77 citations
...These works take the approach of considering a specific type of query and identifying a data structure that allows efficient evaluation of those queries in an unencrypted setting....
[...]
67 citations
...Finally, the work of [6] studies pattern matching with wildcards in the malicious setting and achieves similar costs to our protocols but for larger alphabets....
[...]
...[6] studies the problem of pattern matching with wildcards in a more general sense of non-binary alphabet, implementing a different algorithm based on linear algebra formulation and additive homomorphic encryption....
[...]
35 citations
...(A) integer comparison based pattern matching [41], (B) fast Fourier transform based protocol [48], (C) matrix multiplication-based pattern matching [49] and (D) garbled circuit-based text processing [43]....
[...]
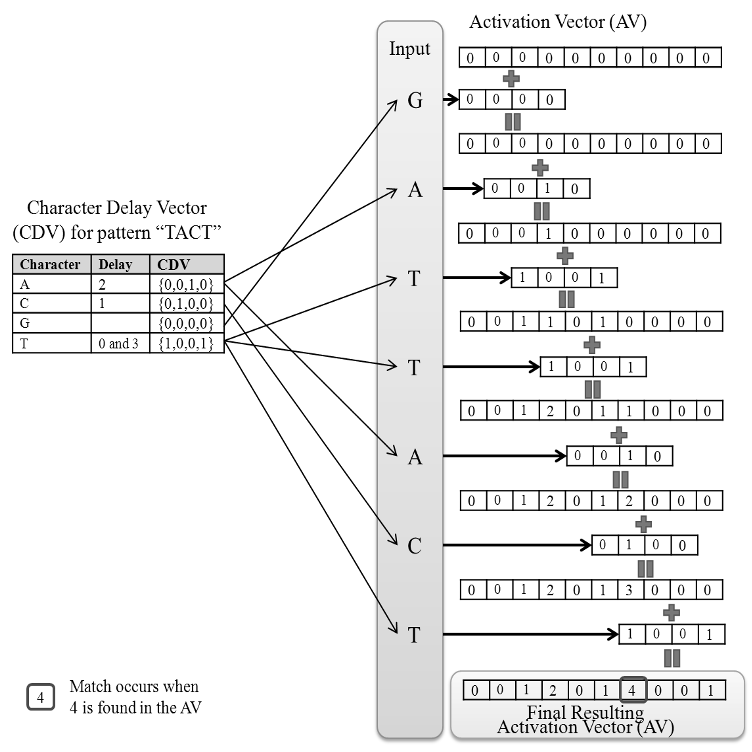
...The authors in [49] call their work on (C) “5PM (5ecure Pattern Matching),” and they propose the notion of a Character Delay Vector (CDV), which enables to efficiently compute the position where a matching pattern could possibly end....
[...]
...5PM [49] Paillier scheme O((k + `) ) bandwidth 670 ms for k = 1, 000 and ` = 100 Our work Polynomial LWE scheme O(d`/ne) bandwidth 12....
[...]
...Unfortunately, only implementation results of H 5PM has been reported in the full version paper of [49]....
[...]
...The protocol H 5PM requires only two rounds of communication between two parties (see Table 5 in the full version paper of [49]), which is the same as ours in the matching phase of Section 5....
[...]
31 citations
...To evaluate the matching degree between 𝑠𝑖 and 𝑠𝑝, we introduce a metric called weighted Euclidean distance that can compare the fingerprint of two strings....
[...]
...There are some works [9]–[15] that use secure multi-party computation to achieve string pattern matching without revealing each party’s own information to others....
[...]
1,226 citations
1,088 citations
897 citations
895 citations
635 citations