HAL Id: hal-02383394
https://hal.laas.fr/hal-02383394
Submitted on 27 Nov 2019
HAL is a multi-disciplinary open access
archive for the deposit and dissemination of sci-
entic research documents, whether they are pub-
lished or not. The documents may come from
teaching and research institutions in France or
abroad, or from public or private research centers.
L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est
destinée au dépôt et à la diusion de documents
scientiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non,
émanant des établissements d’enseignement et de
recherche français ou étrangers, des laboratoires
publics ou privés.
6D interaction control with aerial robots: The ying
end-eector paradigm
Markus Ryll, Giuseppe Muscio, Francesco Pierri, Elisabetta Cataldi, Gianluca
Antonelli, Fabrizio Caccavale, Davide Bicego, Antonio Franchi
To cite this version:
Markus Ryll, Giuseppe Muscio, Francesco Pierri, Elisabetta Cataldi, Gianluca Antonelli, et al.. 6D
interaction control with aerial robots: The ying end-eector paradigm. The International Journal
of Robotics Research, SAGE Publications, 2019, 38 (9), pp.1045-1062. �10.1177/0278364919856694�.
�hal-02383394�

6D Interaction Control with Aerial
Robots: The Flying End-Effector
Paradigm
Accepted for The International Journal of
Robotics Research 2019
Preprint version,
final version at
https://journals.sagepub.com/loi/ijra
Markus Ryll
1
, Giuseppe Muscio
2
, Francesco Pierri
2
, Elisabetta Cataldi
3
, Gianluca
Antonelli
3
, Fabrizio Caccavale
2
, Davide Bicego
1
and Antonio Franchi
1
Abstract
This paper presents a novel paradigm for physical interactive tasks in aerial robotics allowing to increase reliability and
decrease weight and costs compared to state of the art approaches. By exploiting its tilted propeller actuation, the robot
is able to control the full 6D pose (position and orientation independently) and to exert a full-wrench (force and torque
independently) with a rigidly attached end-effector. Interaction is achieved by means of an admittance control scheme
in which an outer loop control governs the desired admittance behavior (i.e., interaction compliance/stiffness, damping,
and mass) and an inner loop based on inverse dynamics ensures full 6D pose tracking. The interaction forces are
estimated by a IMU-enhanced momentum based observer. An extensive experimental campaign is performed and four
case studies are reported. Firstly, a hard touch and slide on a wooden surface, named sliding surface task. Secondly, a
tilted peg-in-hole task, i.e., the insertion of the end-effector in a tilted funnel. Then an admittance shaping experiment in
which it is shown how the stiffness, damping and apparent mass can be modulated at will. Finally, the fourth experiment
is in charge of showing the effectiveness of the approach also in the presence of time-varying interaction forces
Keywords
Aerial robotics, Aerial physical interaction, Aerial Manipulation
INTRODUCTION
Direct physical interaction of a robot with its environment
is a vast and continuously growing field of research with
several relevant applications. Industrial case studies have
been object of massive research, see, e.g., Villani and
De Schutter (2008) for an introductory reading. Recently,
the use of aerial robotic platforms, possibly equipped with
an arm, came prominently into focus. Aerial robots offer
a nearly unlimited motion space and can be exposed in
dangerous or poisonous environments. Along this line,
aerial robots have been recently exploited in operations
such as, e.g., transportation (Fink et al. (2011)), structure
assembly, object grasping (Augugliaro et al. (2014)), and
wall inspection (Fumagalli et al. (2012)), requiring both
autonomous flight competences and physical interaction
capabilities; the latter being a particularly challenging task
due to the complexity of aerodynamics – especially when
the vehicle is close to surfaces – and intrinsic instability of
almost all the aerial robotic platforms.
To perform physical interaction, aerial robots are either
equipped with a rigid tool or an n degree of freedom (DoF)
robotic arm. In the first case, the tool is rigidly fixed to
the airframe, see, e.g., Gioioso et al. (2014b); Augugliaro
et al. (2014); Y
¨
uksel et al. (2014b); Nguyen and Lee (2013);
Gioioso et al. (2014a). A drawback of this solution is that
typical aerial platforms are underactuated and therefore it is
impossible to independently control the 6D (position plus
orientation) dynamics of the end-effector. This limits the
potential use cases and also creates stability issues. In fact, it
has been shown that in the presence of interaction with points
of the airframe different from the vehicle’s center of mass
(CoM) the internal dynamics of underactuated multi-rotors
is not guaranteed to be stable, and it is, in general, neither
easy to stabilize nor practical for real applications (Nguyen
and Lee (2013)).
The second possibility is to attach an n-DoF robotic arm
to the aerial platform (Muscio et al. (2016, 2017); Baizid
et al. (2016); Kim et al. (2013); Tognon et al. (2017)),
a solution which aims at overcoming the underactuation
of the end-effector dynamics by exploiting the increased
number of actuators provided by the arm. In this way, a fully
actuated 6D force control at the end-effector side becomes
possible (Yang and Lee (2014)). However, this solution
comes with several drawbacks as well, which are mentioned
in the following:
i) a robotic arm strongly decreases the payload and flight
time due to its own weight;
ii) the system is much more complex from a mechanical
point of view than a single airframe with a rigid tool and,
thus, it is more expensive to build and also requires more
maintenance and repairing costs across its operational life;
1
LAAS-CNRS, Universit
´
e de Toulouse, CNRS, Toulouse, France,
2
University of Basilicata, School of Engineering, via dell’Ateneo Lucano,
10, Potenza, Italy,
3
University of Cassino and Southern Lazio, Via Di Biasio 43, 03043
Cassino, Italy
Corresponding author:
Antonio Franchi, LAAS-CNRS, Universit
´
e de Toulouse, CNRS, Toulouse,
France.
Email: antonio.franchi@laas.fr
Preprint, final version at https://journals.sagepub.com/loi/ijra

2 Accepted for The International Journal of Robotics Research 2019
iii) lateral forces in body frame, which cannot be provided
by the aerial platform itself, have to be generated through the
dynamical/inertial coupling between the arm and the aerial
robot: the proper mastering of the dynamical coupling is
something that has to be necessarily exploited in order to
get the sought benefits in terms of 6D force control. This, in
turn, requires the knowledge of the precise dynamical model
and a very accurate measurement of the system inputs and
states (position, orientation, linear and angular velocities).
As a matter of fact, these requirements are extremely hard to
achieve in real world conditions (especially the former). For
this reason, kinematic-only approaches have been preferred
for real world validations, see e.g., Muscio et al. (2016,
2017), at the expense of losing the main benefits for which
the manipulator was introduced.
As a byproduct, the use of such complex systems has
been exploited in real world so far only for basic interaction
tasks such as, e.g., pick and place, vertical insertion,
and pull/pushing of constrained objects like drawers (Kim
et al. 2015). At the best of our knowledge, more complex
interactions required in real world like: a) peg in-hole
with non-vertical orientation, b) position-force control for
sliding on surfaces, and, more in general, c) an accurate
shaping of the full 6D force/moment interaction of the end-
effector with the environment; have not yet been successfully
demonstrated in real world in state-of-the-art systems.
Summarizing, standard flying platforms are underactuated
and, thus, incapable of 6D end-effector force control. On the
other side, using a full manipulator up in the air to perform
the sought 6D end-effector force control is often excessively
complex and may introduce more problems than benefits.
To solve all these problems at once and finally achieve
the sought full 6D force control of the aerial interaction,
we propose a novel paradigm which we named the Flying
End-Effector. The concept is based on the ascertainment
that the overall mission goal is to achieve 6D interaction
with an end-effector. While in ground robotics the end-
effector must be actuated by a manipulator with at least six
degrees of freedom (DoF), in the aerial robotics case there
is no necessity to bring up to the air a full manipulator
together with the end-effector. What is instead needed is
that the aerial robot possesses the minimal requirements
to perform such interaction with a rigidly attached end-
effector. In order to achieve such requirements, we propose
to use a multi-rotor robot with non-collinear fixedly-tilted
propellers (NCFTP) instead of the more common collinear
fixedly-tilted propeller (CFTP) architectures (Ryll et al.
(2016)). In NCFTP platforms, which appeared in the robotics
literature only recently (see, e.g., Rajappa et al. (2015);
Voyles and Jiang (2014); Brescianini and D’Andrea (2016);
Park et al. (2016)), the full-actuation is achieved by a more
general propeller position and orientation. The difference
between the underactuated platform and NCFTP platforms
is that, in the former approach, all the propellers have
the same orientation while, in the latter approach, every
propeller orientation is different. The NCFTP approach is,
thus, able to control independently the translational and
angular acceleration when unconstrained, or any of the six
components of the exerted wrench when in contact, thus
allowing full and dexterous 6D force control, which makes
them much more suited for physical interaction tasks than
standard CFTP platforms.
Another solution to obtain full-actuation consists of
actively tilting the whole propeller groups (Ryll et al. (2016,
2015); Long and Cappelleri (2013)), a solution which is
called thrust vectoring or tilting propeller. This solution
however is subject to the same drawbacks of the solutions
employing a manipulator arm, since they require extra
actuation, mechanical complexity, and weight. Furthermore,
they cannot in general guarantee instantaneous disturbance
rejection or fast force exertion since the propellers might
have to be re-oriented, which again takes some non-
negligible time.
A critical issue for aerial robot interaction control is the
measurement of the interaction wrench. A reliable solution
is the adoption of force/torque sensors, such as in Antonelli
et al. (2016) where the wrench measurement of a wrist
mounted sensor of an aerial manipulator is fed to an
admittance filter. Use of force/torque sensor increases the
cost and the weight of the aerial platform, thus alternative
solutions based on wrench estimators have been proposed
in the last years. In Y
¨
uksel et al. (2014a) a Lyapunov-
based nonlinear observer is proposed for estimating the
external wrenches applied on a quadrotor, while in Tomic
and Haddadin (2014) a hybrid estimation is proposed, using
the linear acceleration for directly computing the interaction
forces and a momentum based observer for estimating
the interaction torques. In Tomic et al. (2017) the same
authors propose a more refined hybrid estimation, where
the estimated forces are not simply computed by the model
but are obtained via a first-order stable filter, similar to
the solution proposed in Y
¨
uksel et al. (2014a). In Rajappa
et al. (2017), the authors, by exploiting both a wrench
estimation and a ring of eight contact sensors, proposed
a control able to separate human interaction forces from
additional disturbances as wind and parameter uncertainties.
In Tagliabue et al. (2016) as well an admittance control
framework is used for collaborative transportation of objects
by using underactuated aerial robots, an approach which is
theoretically analyzed and refined in Tognon et al. (2018) by
demonstrating its stability and the fundamental role of the
internal force in such control scheme.
A preliminary (6-pages long) version of this work has been
presented in a conference version (Ryll et al. (2017)). With
respect to Ryll et al. (2017), in this paper i) we provide much
more details for all considered aspect; ii) we consider an
improved solution for the wrench estimate that exploits also
the linear acceleration measurements provided by the IMU;
iii) the position and force tracking quality has been largely
improved; iv) the physical property shaping capabilities of
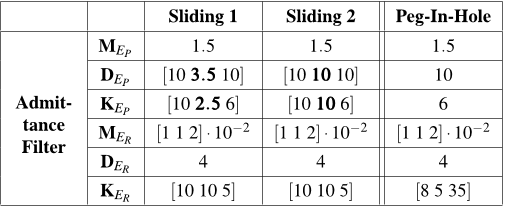
the admittance filter are thoroughly tested and explained
and v) a very broad range of experiments is performed and
discussed; in particular, the case of sliding on a surface
with a tilted orientation, the peg-in-hole experiment, and the
admittance shaping tests and sliding in contact with two
ledges have been conducted.
Concluding this introduction, in the following we
summarize the main contributions (but not all) of this work:
1) we propose and show the practicability through real
experiments, of a completely new aerial physical interaction
paradigm: the 6D flying end-effector. We believe that this
Preprint, final version at https://journals.sagepub.com/loi/ijra Accepted for The International Journal of Robotics Research 2019

6D Interaction Control with Aerial Robots: The Flying End-Effector Paradigm 3
Figure 1. The Tilt-Hex (NCFTP aerial platform with tilted
propellers in-house developed at LAAS-CNRS) with the rigidly
attached end-effector. Notice how the interaction takes place far
away and off-centered from the vehicle CoM. The picture is
taken right after a Peg-In-Hole task was successfully performed.
paradigm will pave the way to a novel aerial system concept
which outperforms currently adopted solutions for aerial
manipulation and physical interaction in terms of capability,
reliability, complexity and costs.
2) we propose a specific integration of known robotic
algorithms, achieving both motion and interaction control
as well as external wrench estimation, in a thoroughly
conceived architecture and show how the integrated system
can work with a minimal sensor suite (pose sensor plus IMU)
not even needing a force sensor in its basic configuration
– the addition of more sensors, if available, being anyway
straightforward.
3) in support of the aforementioned features, we show
experiments that are the first of their kind in aerial robotics:
fully impedance shaping in 6D, peg-in-hole with tilted
holes, sliding on tilted surfaces. Moreover, in order to
show the effectiveness of the wrench estimate, a forth
experiment, consisting on sliding in contact with two ledges
on a surface mounted on an ATI45 force/torque sensor, has
been conducted in such a way to exert variable forces and
torques on the end-effector. The wrench estimator results
are compared with the measures obtained by the sensor. The
experiments are designed to clearly show the versatility and
the robustness of the proposed approach to the environmental
uncertainties.
The paper is organized as follows. First a generic model
for NCFTP aerial systems is introduced and afterwards we
model the proposed NCFTP platform, named Tilt-Hex. Then
the complete admittance control framework is presented as
well as its components, namely the inner loop geometric pose
controller, the wrench observer and the outer loop admittance
filter. Then we present the hard-/software architecture and the
experimental evaluation. Finally, we conclude the paper with
a summary of the results and an outline of future works.
Remark It is important to mention that the theory and the
architecture proposed in this paper is very general and works
seamlessly with any NCFTP platform other than the one used
in particular here.
System Modeling
We consider as aerial robot a fully actuated aerial vehicle
equipped with an arbitrarily mounted end-effector tool. The
presented physical interaction framework is generic for any
fully actuated system able to track a full-pose trajectory
with the end-effector. We shall start with the generic parts
of the modeling and present afterwards the instantiation of
this general model for the NCFTP hexarotor used in the
experiments.
General Modeling Let us consider the following coordinate
frames (see Figure 2):
• Inertial world frame F
W
, whose axes (unit vectors)
and origin are indicated with {x
W
,y
W
,z
W
} and O
W
,
respectively;
• Body frame F
R
: O
R
−{x
R
,y
R
,z
R
}, attached to the
robot and with origin O
R
in the CoM of the aerial
vehicle with the end-effector;
• End-effector frame F
E
: O
E
−{x
E
,y
E
,z
E
}, attached to
the robot end effector and with origin in the interaction
point O
E
.
For a generic vector υ, the notation υ
?
(with ? = R,E)
denotes that the vector υ is expressed in frame F
?
. If the
superscript is omitted it means that the vector is expressed in
inertial frame.
The position of O
R
expressed in F
W
is denoted by p
R
∈
R
3
, while the position of O
E
in F
W
and in F
R
are denoted by
p
E
∈R
3
and p
R
E
∈R
3
, respectively, where p
R
E
is constant over
time. Analogously, let us denote with R
R
∈ SO(3) and R
E
∈
SO(3) (where SO(3) = {A ∈ R
3×3
|AA
T
= I ∧ det A = 1})
the rotation matrices expressing, respectively, the orientation
of frame F
R
and F
E
with respect to the inertial frame F
W
.
Moreover, R
R
E
∈ SO(3) denotes the constant rotation matrix
expressing the orientation of F
E
with respect to F
R
. Finally
let us denote as ω
ω
ω
R
R
∈R
3
and ω
ω
ω
E
E
∈R
3
the angular velocities
of F
R
and F
E
with respect to F
W
expressed, respectively,
in frame F
R
and F
E
. Thus, the orientation kinematics of the
robot and the end effector are then expressed by
˙
R
R
= R
R
[ω
ω
ω
R
R
]
×
(1)
˙
R
E
= R
E
[ω
ω
ω
E
E
]
×
, (2)
respectively, where [•]
×
∈ SO(3) represents the skew
symmetric matrix (Siciliano et al. (2009)) associated to
vector •∈ R
3
.
Using the Newton-Euler formalism, the equation of
motion of the aerial robot can be expressed as
m
¨
p
R
J
˙
ω
ω
ω
R
R
= −
mge
3
ω
ω
ω
R
R
×Jω
ω
ω
R
R
| {z }
g(ω
ω
ω
R
R
)
+
f
τ
τ
τ
R
+
f
R
τ
τ
τ
R
R
(3)
where m and J ∈R
3×3
represent the robot mass and its inertia
matrix with respect to O
R
and expressed in F
R
, respectively,
g is the gravitational acceleration, f ∈ R
3
and τ
τ
τ
R
∈ R
3
are
force and torque inputs, while f
R
and τ
τ
τ
R
R
are the external force
and torque on the robot CoM due to the force and torque
exerted by the environment on the end-effector.
Preprint, final version at https://journals.sagepub.com/loi/ijra Accepted for The International Journal of Robotics Research 2019

4 Accepted for The International Journal of Robotics Research 2019
Figure 2. Schematic view of important frames and vectors of
the Tilt-Hex with the rigidly attached end-effector. The zoomed
propeller group shows further vectors needed to model the
system.
Remark It is worth noticing that, as usual in aerial robotics
field, in (3) the translational dynamics is expressed in the
frame F
W
, while the rotational dynamics is expressed in the
frame F
R
.
Tilt-Hex Without loss of generality for any fully actuated
aerial platform, we will now derive (3) for the NCFTP
platform used in the later presented experiments. The
NCFTP platform is based on a hexarotor structure, with
propellers equally-spaced and equidistant from O
R
in the
x-y-plane of F
R
. Full actuation is achieved by rigid
adapters, tilting every single motor-propeller combination
(see Figure 1 and 2). Let us consider 6 frames F
P
i
, i = 1 ...6
where O
P
i
coincides with the center of rotation of the i-th
propeller group (see Figure 2). The orientation of F
P
i
with
respect to F
B
is represented by the rotation matrix
R
R
P
i
= R
z
((i −1)
π
3
)R
x
((−1)
i−1
α)R
y
(β ), i = 1...6. (4)
The inclination of the i-th motor-propeller group with
respect to F
R
is defined by the constant parameters α and
β . The selection of α and β decides the maximum lateral
forces with the cost that higher lateral forces result in higher
internal forces and therefore a waste of energy (Rajappa et al.
(2015)). Selecting an alternating sign of α for every other
propeller in (4) allows for the full actuation of the aerial
vehicle.
The i-th motor-propeller group’s position with respect to
O
R
can be defined as
p
R
P
i
= R
z
((i −1)
π
3
)l +R
x
((−1)
i−1
α)R
y
(β )d, i = 1 ...6
(5)
where d is the vector from the center of the tilting rotation to
the center of the motor-propeller group O
P
i
, and l is the vector
from O
R
to the center of the tilting rotation (see Figure 2).
As well known, a spinning propeller generates a thrust
force and a drag moment in O
P
i
. In a good approximation
both can be modeled by utilizing the signed squared of the
spinning velocity as
f
R
i
= c
f
u
i
R
R
P
i
e
3
, i = 1 . . . 6 (6)
and
τ
τ
τ
R
i
= (−1)
i−1
c
τ
u
i
R
R
P
i
e
3
, i = 1 . . . 6 (7)
Table 1. Overview of most symbols used in this paper. If
constant through all experiments a value is presented as well.
Definition Symbol Value
Inertial world frame with origin O
W
and axes {x
W
,y
W
,z
W
} F
W
Robot body frame with origin O
R
and axes {x
R
,y
R
,z
R
} F
R
End effector frame with origin O
E
and axes {x
E
,y
E
,z
E
} F
E
Symbols that can assume the values W,R, or E ?, ◦
Position of O
◦
in F
W
p
◦
Velocity of O
◦
in F
W
v
◦
Rotation matrix expressing the orientation of F
◦
w.r.t. F
?
R
?
◦
Rotation matrix expressing the orientation of F
◦
w.r.t. F
W
R
◦
Angular velocity of F
◦
w.r.t. F
W
, expressed in F
◦
ω
ω
ω
◦
Reference position expressed in F
W
p
R,r
Reference rotation matrix R
R,r
Desired position expressed in F
W
p
R,d
Desired rotation matrix R
R,d
Actuation wrench expressed in F
W
w
Real external wrench on the EE in F
W
w
E
Observed (estimated) external wrench on the EE in F
W
ˆ
w
E
Observed (estimated) external wrench on the robot in F
W
ˆ
w
R
Tilting angle (around x
P
i
) of the i
th
prop. group α
i
35
◦
Tilting angle (around y
P
i
) of the i
th
prop. group β
i
10
◦
i
th
propeller blade spinning frequency about z
P
i
(in Hz)
√
u
i
Mass of the whole aerial robot m 2.4 Kg
Gravity acceleration constant g 9.81 m/s
2
Gain matrix of the wrench observer K
I
Mechanical impedance inertia matrix M
E
Mechanical impedance damping matrix D
E
Mechanical impedance stiffness matrix K
E
with c
f
and c
τ
being constant parameters linking the
propeller spinning velocity
√
u
i
to the generated thrust force
and drag moment. The term (−1)
i−1
in (7) represents the
effect of counter spinning rotors for all even propellers.
We can now express the total force applied on O
R
in F
W
as
f(u) = R
R
6
∑
i=1
f
R
i
= R
R
F
1
u (8)
with F
1
∈ R
3×6
incorporating the geometrical and physical
properties of the aerial robot (i.e., dimensions, tilting angles,
thrust coefficients) and with u = [u
1
...u
6
]
T
being the vector
collecting the 6 squared propeller spinning velocities.
In the same manner we can incorporate the total torque due
to the thrust contribution and the drag moment expressed in
F
B
utilizing (6) and (7) as
τ
τ
τ
R
(u) =
6
∑
i=1
(p
R
P
×f
R
i
+ τ
τ
τ
R
i
) = F
2
u (9)
where F
2
∈R
3×6
again includes the geometrical and physical
properties. A detailed derivation of the model and of F
1
and
F
2
and its necessary conditions for full actuation can be
found in Rajappa et al. (2015) and Michieletto et al. (2017).
By replacing (8) and (9) in (3) we obtain
m
¨
p
R
J
˙
ω
ω
ω
R
R
= g(ω
ω
ω
R
) +
R
R
F
1
F
2
u +
f
R
τ
τ
τ
R
R
(10)
as a reliable dynamical model under slow flight conditions
(< 0.5 m/s). We neglect any aerodynamic effects like the
well known first order-effects rotor drag, fuselage drag and
H-force as these effects linearly depend on the vehicle’s
velocity and can therefore be neglected for the slow velocity
aerial interaction considered in this paper (Faessler et al.
(2018); Kai et al. (2017)).
Preprint, final version at https://journals.sagepub.com/loi/ijra Accepted for The International Journal of Robotics Research 2019