Q1. What have the authors contributed in "A bacteriophage detection tool for viability assessment of salmonella cells" ?
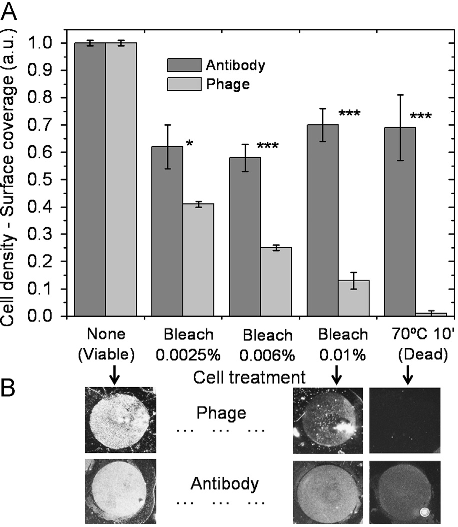
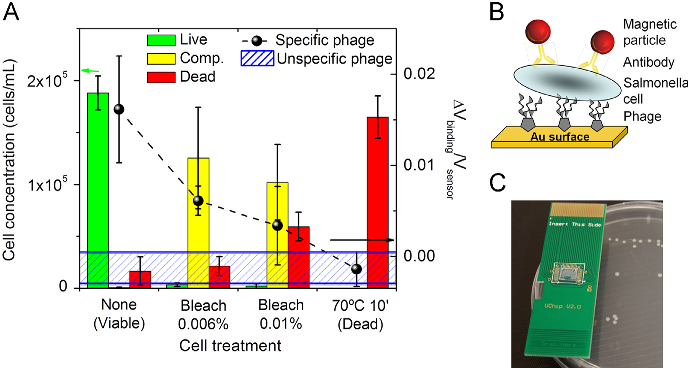
This work presents and validates a novel bacteriophage ( phage ) -based microbial detection tool to detect and assess Salmonella viability. This ability was confirmed for immobilized phages on gold surfaces, where the phage detection signal follows the same trend of the concentration of viable plus VBNC cells in the sample. Salmonella Enteritidis cells in a VBNC physiological state were evaluated by cell culture, flow-cytometry and epifluorescence microscopy, and further assayed with a biosensor platform.