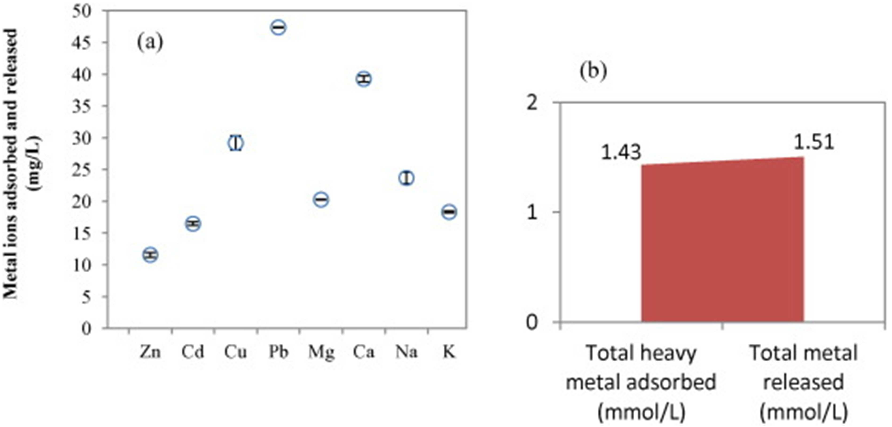
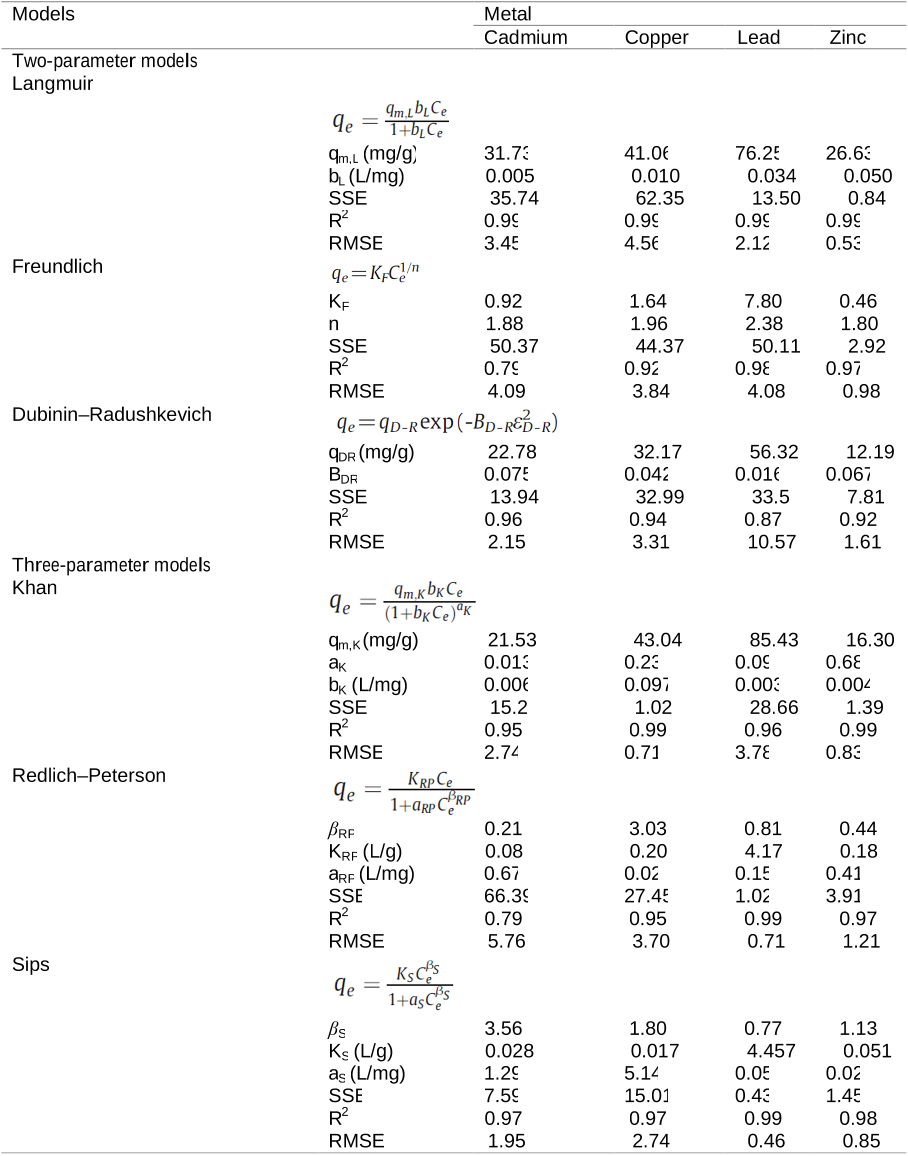
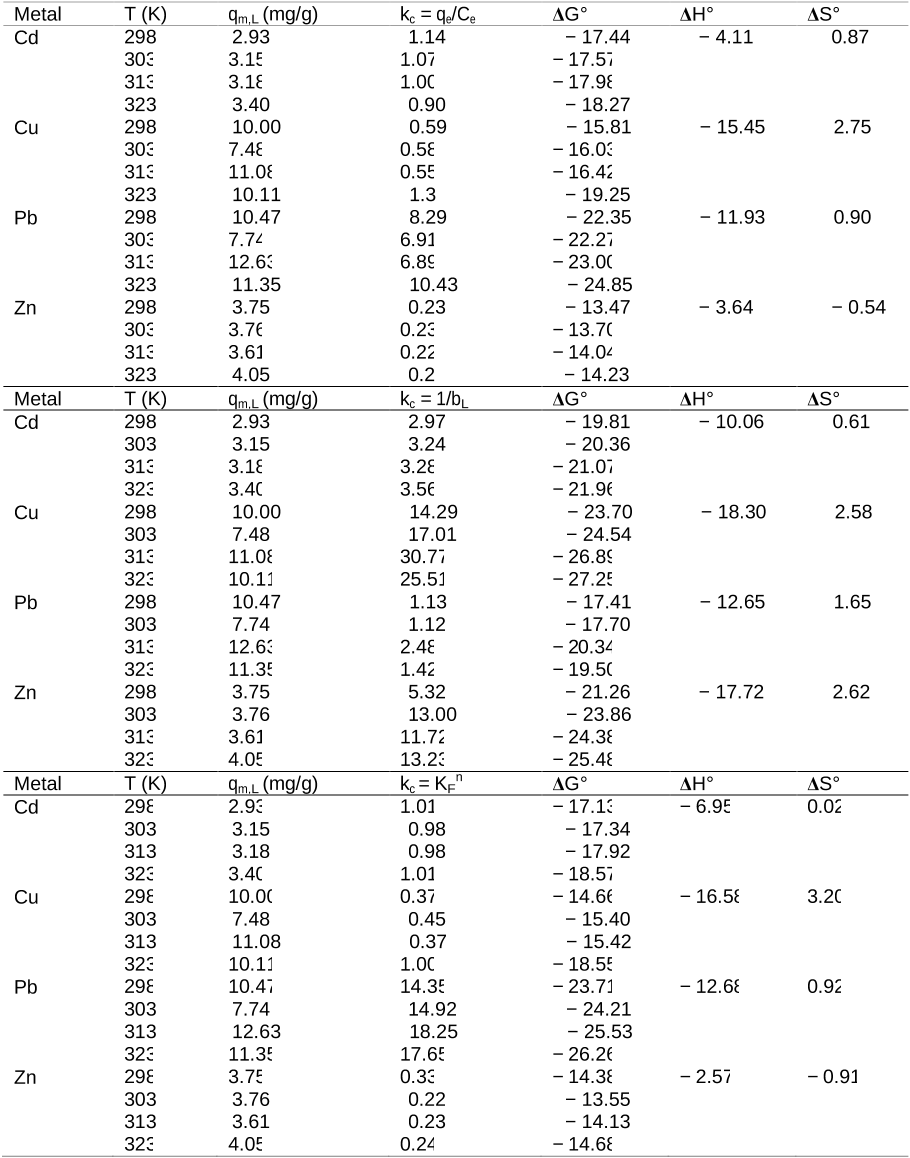
Abstract: Biosorption may be simply defined as the removal of substances from solution by biological material. Such substances can be organic and inorganic, and in gaseous, soluble or insoluble forms. Biosorption is a physico-chemical process and includes such mechanisms as absorption, adsorption, ion exchange, surface complexation and precipitation. Biosorption is a property of both living and dead organisms (and their components) and has been heralded as a promising biotechnology for pollutant removal from solution, and/or pollutant recovery, for a number of years, because of its efficiency, simplicity, analogous operation to conventional ion exchange technology, and availability of biomass. Most biosorption studies have carried out on microbial systems, chiefly bacteria, microalgae and fungi, and with toxic metals and radionuclides, including actinides like uranium and thorium. However, practically all biological material has an affinity for metal species and a considerable amount of other research exists with macroalgae (seaweeds) as well as plant and animal biomass, waste organic sludges, and many other wastes or derived bio-products. While most biosorption research concerns metals and related substances, including radionuclides, the term is now applied to particulates and all manner of organic substances as well. However, despite continuing dramatic increases in published research on biosorption, there has been little or no exploitation in an industrial context. This article critically reviews aspects of biosorption research regarding the benefits, disadvantages, and future potential of biosorption as an industrial process, the rationale, scope and scientific value of biosorption research, and the significance of biosorption in other waste treatment processes and in the environment. Copyright © 2008 Society of Chemical Industry