




Did you find this useful? Give us your feedback








567 citations
337 citations
292 citations
147 citations
138 citations
270 citations
...At present, one of the most important gaps and uncertainties in tree line research appears on intermediate (10–10,000 km2) spatial scales (Holtmeier & Broll, 2007; Kullman & Öberg, 2009) at which feedbacks to the climate system are significant (Harding et al., 2002), yet studies on the causes of…...
[...]
...On a global scale, heat deficiency may be the dominant factor controlling tree line dynamics, but regional studies have shown that tree line position rarely changes in parallel with the shift of any isotherm (Holtmeier & Broll, 2007)....
[...]
...Projecting future tree line dynamics The extreme discrepancy that exists between model projections of the tree line position and in situ observations is a world-wide phenomenon (Holtmeier & Broll, 2007; Van Bogaert et al., 2007)....
[...]
242 citations
...At the tree line, disturbance by reindeer (Rangifer tarandus L.) may be significant (Cairns & Moen, 2004)....
[...]
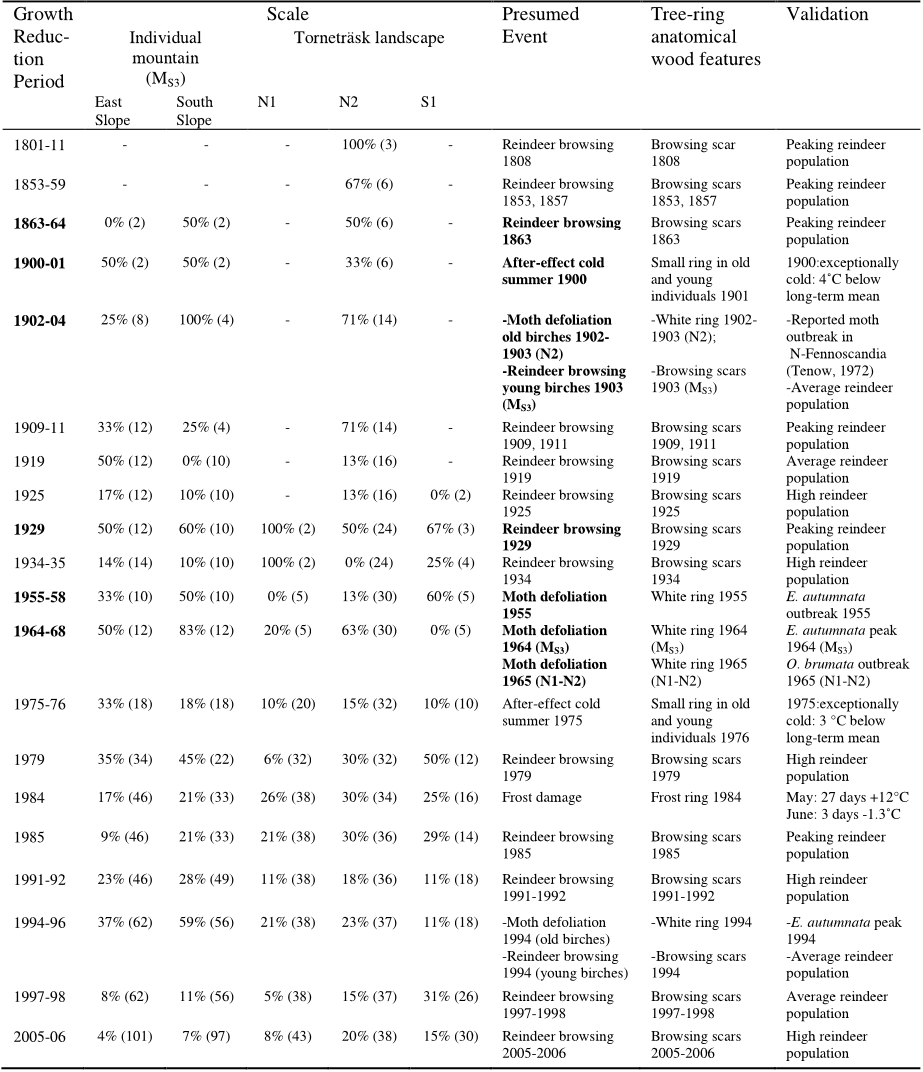
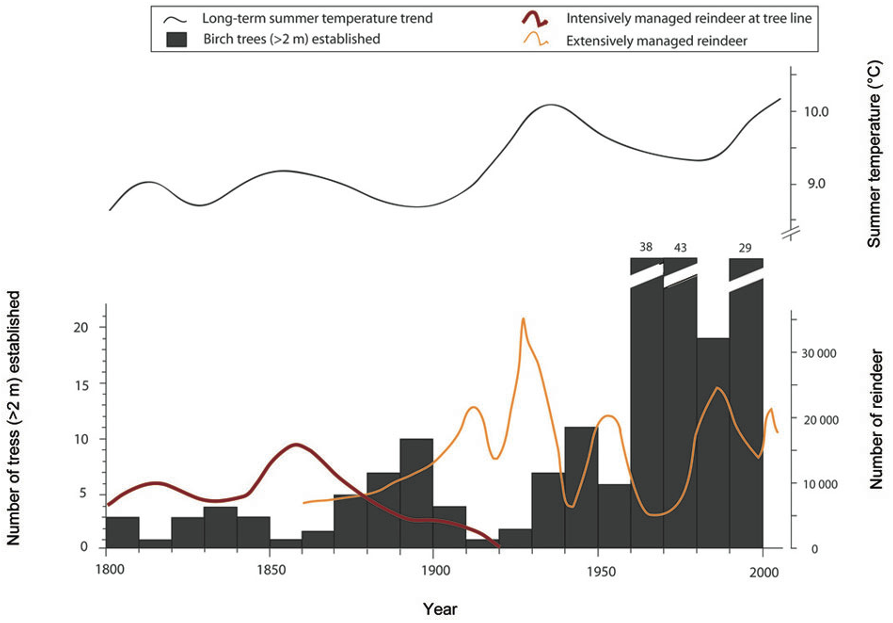
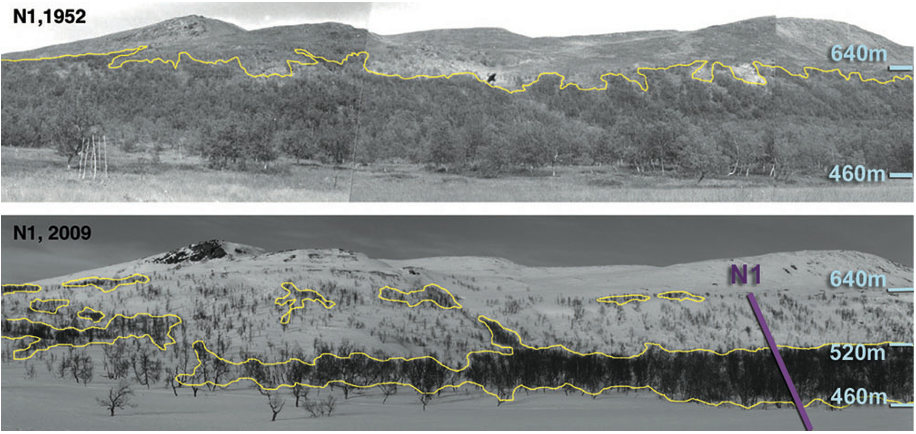
...We confirmed the hypothesis of Emanuelsson (1987) and Cairns & Moen (2004) that the impacts of humans and semidomesticated herbivores have significantly determined the elevational shifts of the tree line boundary (Table 1)....
[...]
229 citations
...The importance of an ample snow cover for mountain birch, providing insulation in winter and moisture in spring, has been elucidated in previous tree line studies (Dalen & Hofgaard, 2005; Kullman & Öberg, 2009)....
[...]
...In contrast to other studies (Danby & Hik, 2007; Kullman & Öberg, 2009), slope aspect and inclination were not correlated with elevational shifts of the tree line ecotone....
[...]
...Indeed, modern evidence for such relocations exists and these have been explicitly or implicitly related to recent climate warming (Shiyatov et al., 2007; Kullman & Öberg, 2009)....
[...]
...…of the most important gaps and uncertainties in tree line research appears on intermediate (10–10,000 km2) spatial scales (Holtmeier & Broll, 2007; Kullman & Öberg, 2009) at which feedbacks to the climate system are significant (Harding et al., 2002), yet studies on the causes of tree line…...
[...]
...However, the fastest upslope shifts of tree lines recorded during 20th century warming are in the range of 1 to 2 m year)1 (Shiyatov et al., 2007; Kullman & Öberg, 2009)....
[...]
212 citations
...Daily temperature and precipitation measurements are available since 1913 (Callaghan et al., 2010), human impact has been described in detail since 1600 (Emanuelsson, 1987), reindeer population numbers since 1750 (Emanuelsson, 1987) and moth outbreaks on birch have been reported since 1862 (Tenow,…...
[...]
...Daily temperature and precipitation measurements are available since 1913 (Callaghan et al., 2010), human impact has been described in detail since 1600 (Emanuelsson, 1987), reindeer population numbers since 1750 (Emanuelsson, 1987) and moth outbreaks on birch have been reported since 1862 (Tenow, 1972)....
[...]
...The Torneträsk area has an exceptionally long-term record of climatic and other environmental data offering a powerful instrument for validation of measurements (Callaghan et al., 2010)....
[...]
...The Torneträsk area has an exceptionally long-term record of climatic and other environmental data offering a powerful instrument for validation of measurements (Callaghan et al., 2010)....
[...]
...5 C increase in temperature over the period 1913– 2006 (Callaghan et al., 2010)....
[...]
163 citations
...In the next 100 years, alpine and polar tree lines are projected to shift upslope by 2 to 6 m year)1 (Moen et al., 2004) and northwards by 7.4–20 km year)1 (Kaplan & New, 2006) if climate warming continues....
[...]