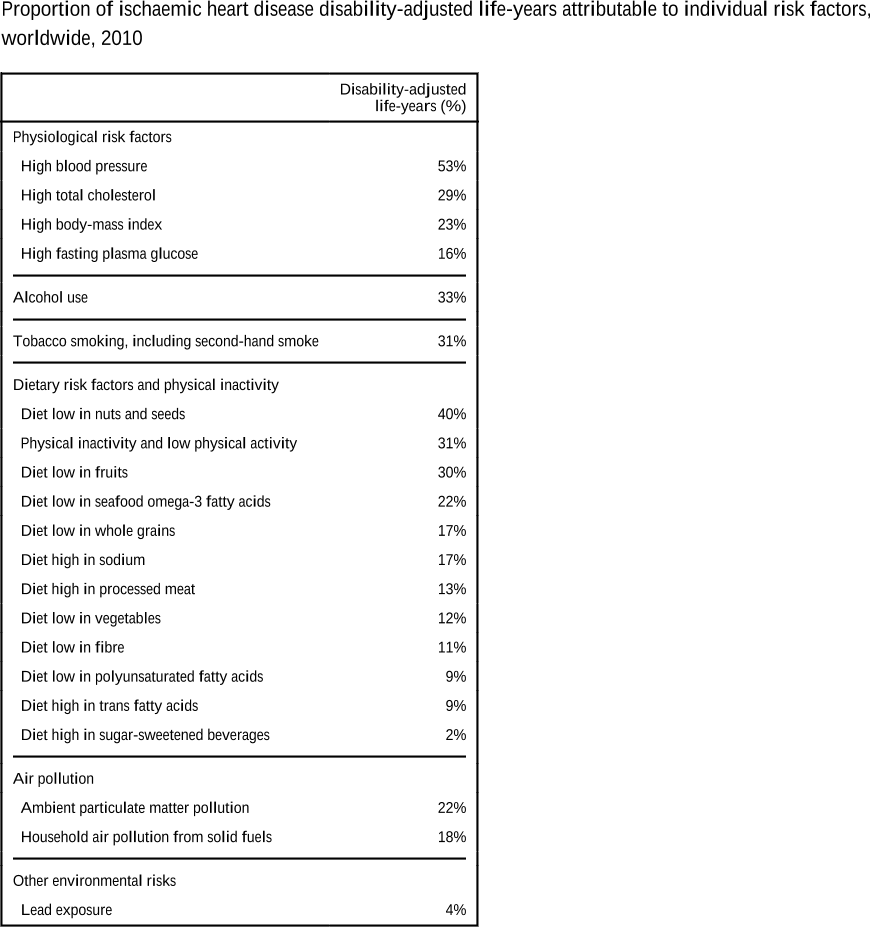
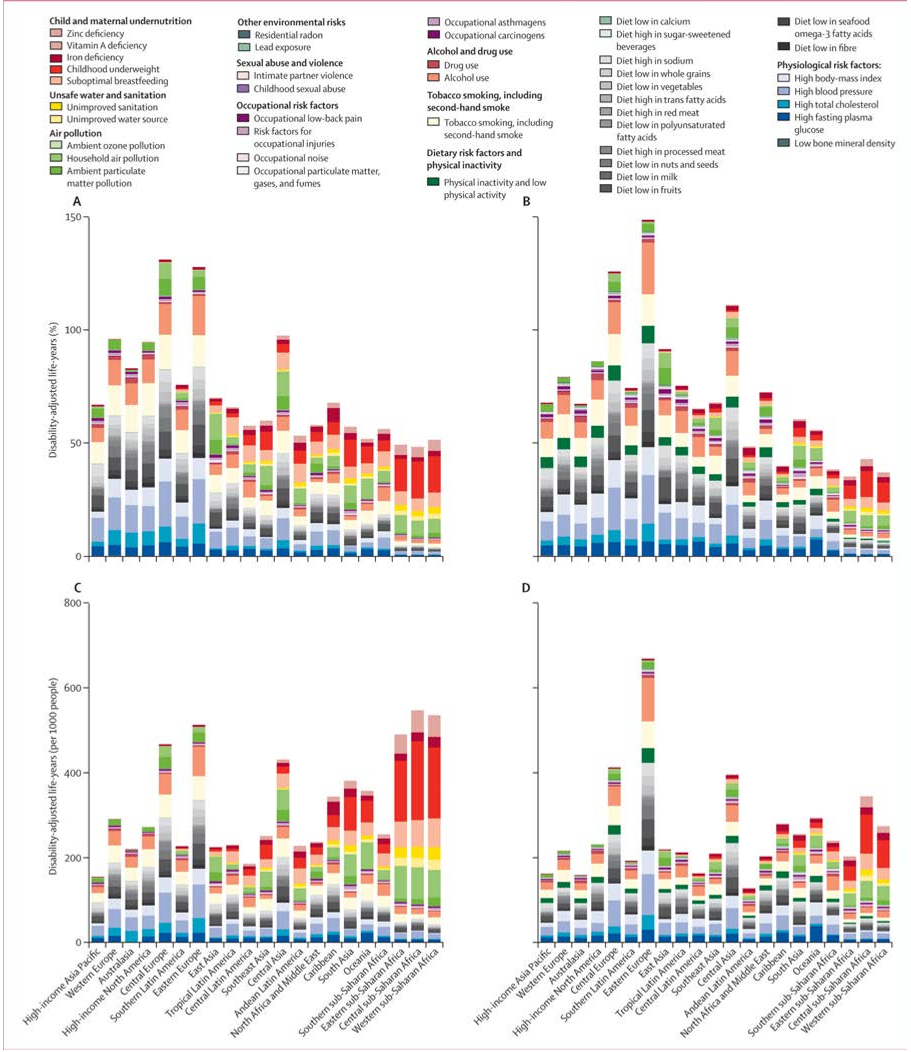
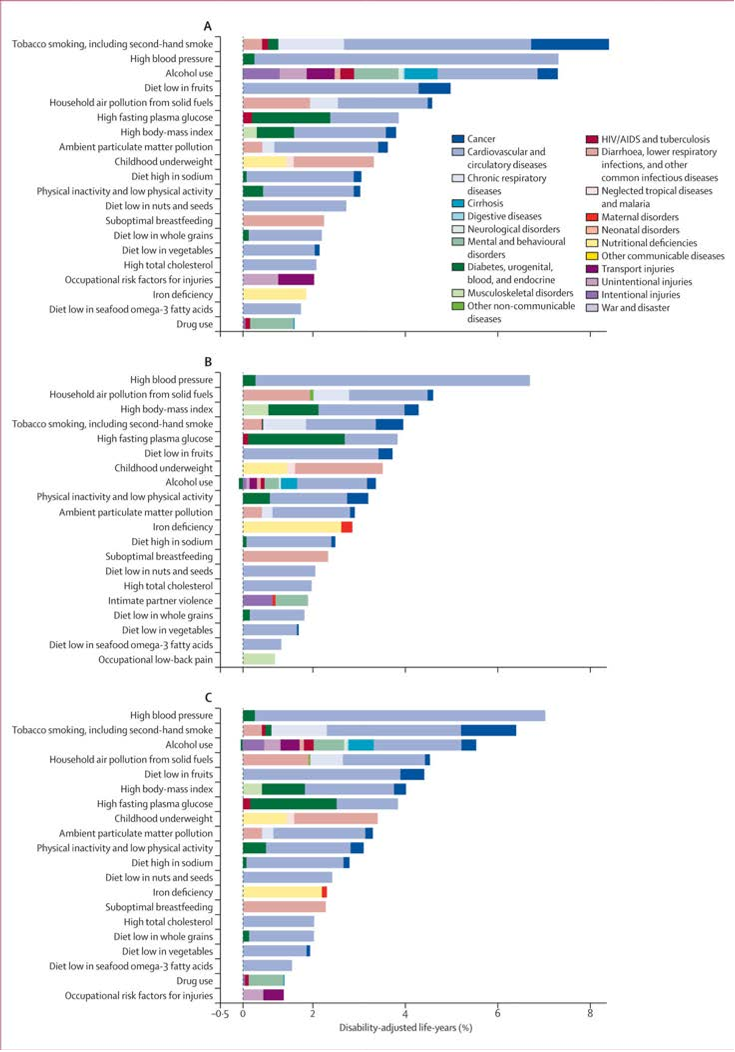
Abstract: Although obesity was only introduced in the 1950s into the International Classification of Diseases (currently ICD-10 code E66, though EASO thinks that this categorization requires revision and is committed to propose novel criteria for ICD-11), it had already reached epidemic proportions by the end of the century, becoming one of the leading causes of death and disability worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) the prevalence of obesity has tripled since the 1980s in many countries of the WHO European Region, with overweight and obesity affecting 50% of the population in the majority of European countries [1]. In 2008, 1.5 billion adults, 20 years and older, were overweight with an estimated 500 million adults worldwide being obese (over 200 million men and nearly 300 million women); approximately 65% of the world's population inhabit countries where overweight and obesity kill more people than underweight [2,3]. The figures of affected individuals rage on unabated, and more than 40 million children under the age of 5 years were overweight in 2010 [3]. Noteworthy, severe obesity (i.e., a BMI > 35 kg/m2) is a rapidly growing segment of the obesity epidemic in which the detrimental effects are particularly evident and harsh. Moreover, obesity not only disproportionately affects the disadvantaged segments of the population, but these groups experience the most important increases in obesity prevalence. Thus, the WHO has declared obesity as the largest global chronic health problem in adults, which is emerging as a more serious world health problem than malnutrition. In fact, obesity has become a truly global problem that has led to coin the term ‘globesity' to describe the escalating global pandemia affecting both developed and developing countries [2]. In this sense, it has been estimated that 60% of the world's population, i.e., 3.3 billion people, could be overweight (2.2 billion) or obese (1.1 billion) by 2030 if recent trends continue [4]. In spite of these preoccupying facts, obesity is frequently not even thought of as a frequent, serious, complex and chronic disease and is often even dismissed or neglected as a clinical entity.