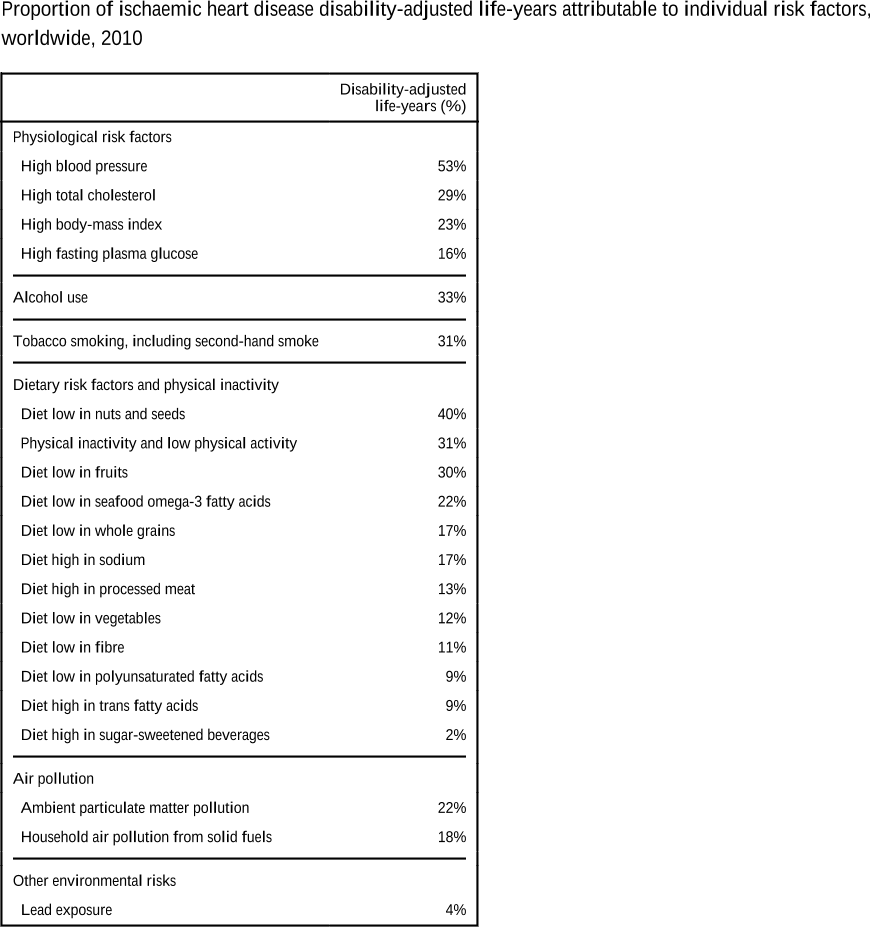
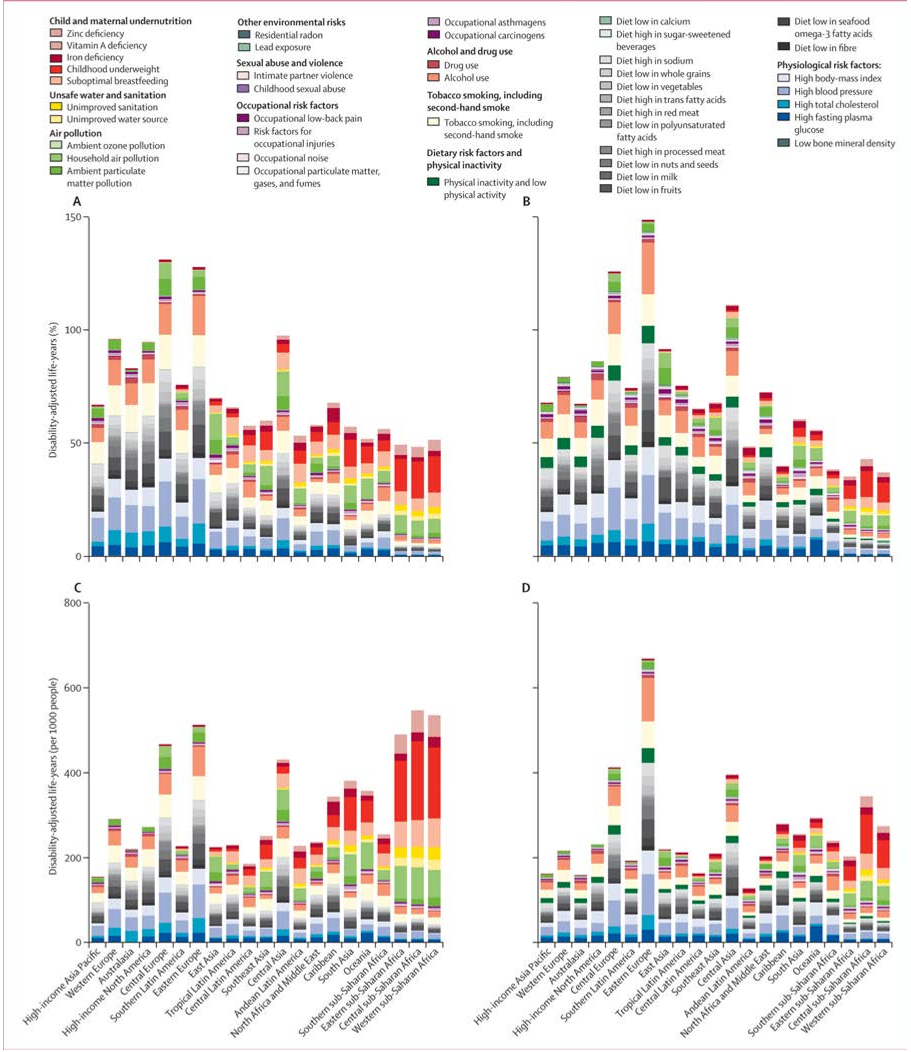
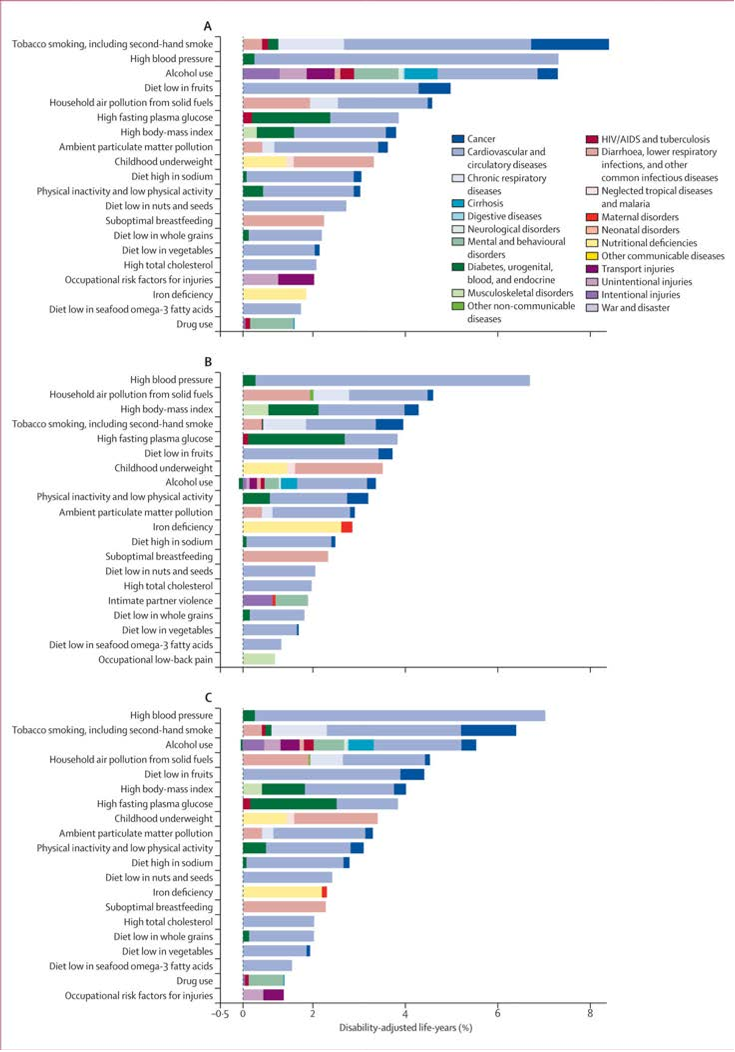
Abstract: Reported associations between preparing and eating home cooked food, and both diet and health, are inconsistent. Most previous research has focused on preparing, rather than eating, home cooked food; used small, non-population based samples; and studied markers of nutrient intake, rather than overall diet quality or health. We aimed to assess whether frequency of consuming home cooked meals was cross-sectionally associated with diet quality and cardio-metabolic health. We used baseline data from a United Kingdom population-based cohort study of adults aged 29 to 64 years (n = 11,396). Participants self-reported frequency of consuming home cooked main meals. Diet quality was assessed using the Mediterranean Diet Score, Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) score, fruit and vegetable intake calculated from a 130-item food frequency questionnaire, and plasma vitamin C. Markers of cardio-metabolic health were researcher-measured body mass index (BMI), percentage body fat, haemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), cholesterol and hypertension. Differences across the three exposure categories were assessed using linear regression (diet variables) and logistic regression (health variables). Eating home cooked meals more frequently was associated with greater adherence to DASH and Mediterranean diets, greater fruit and vegetable intakes and higher plasma vitamin C, in adjusted models. Those eating home cooked meals more than five times, compared with less than three times per week, consumed 62.3 g more fruit (99% CI 43.2 to 81.5) and 97.8 g more vegetables (99% CI 84.4 to 111.2) daily. More frequent consumption of home cooked meals was associated with greater likelihood of having normal range BMI and normal percentage body fat. Associations with HbA1c, cholesterol and hypertension were not significant in adjusted models. Those consuming home cooked meals more than five times, compared with less than three times per week, were 28% less likely to have overweight BMI (99% CI 8 to 43%), and 24% less likely to have excess percentage body fat (99% CI 5 to 40%). In a large population-based cohort study, eating home cooked meals more frequently was associated with better dietary quality and lower adiposity. Further prospective research is required to identify whether consumption of home cooked meals has causal effects on diet and health.