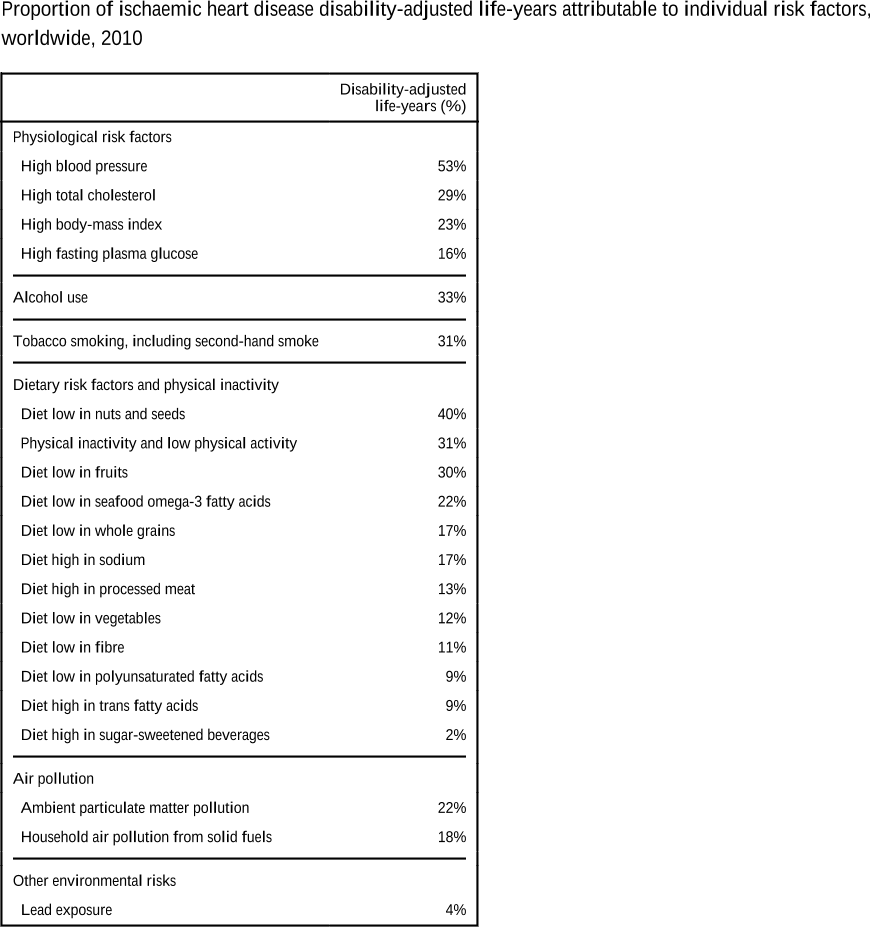
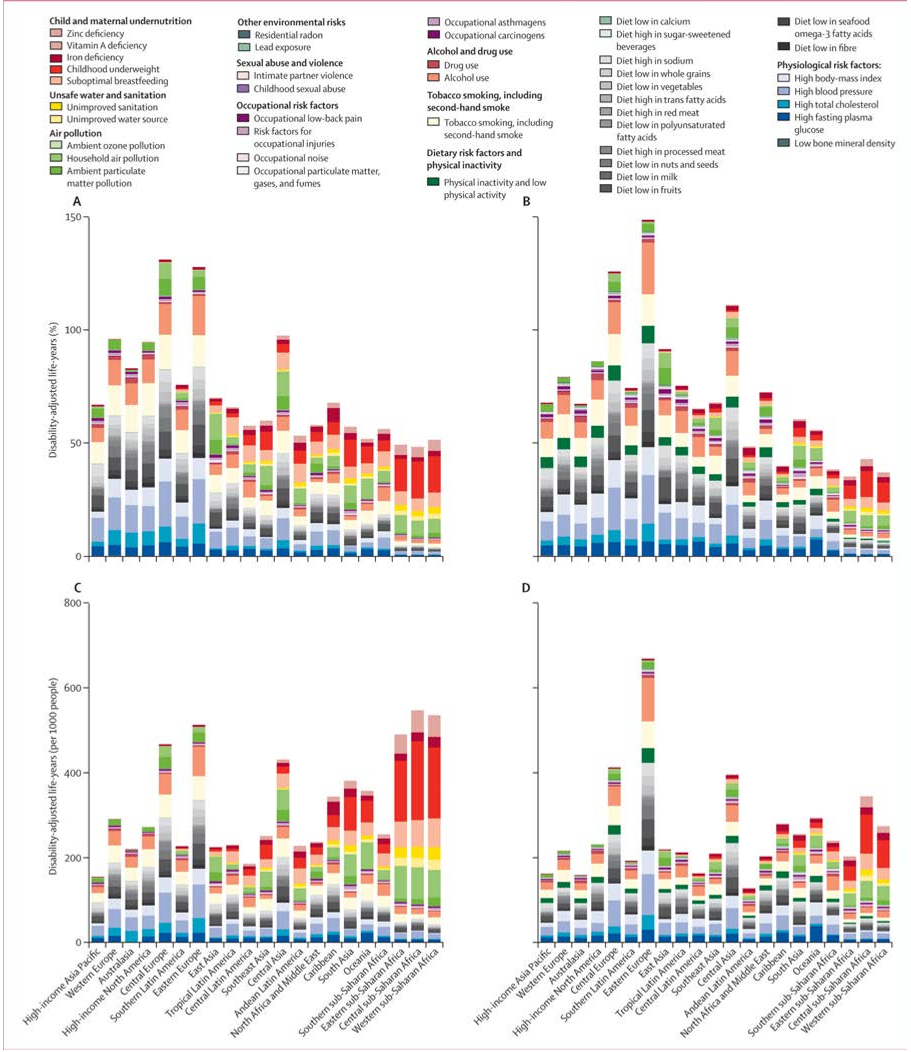
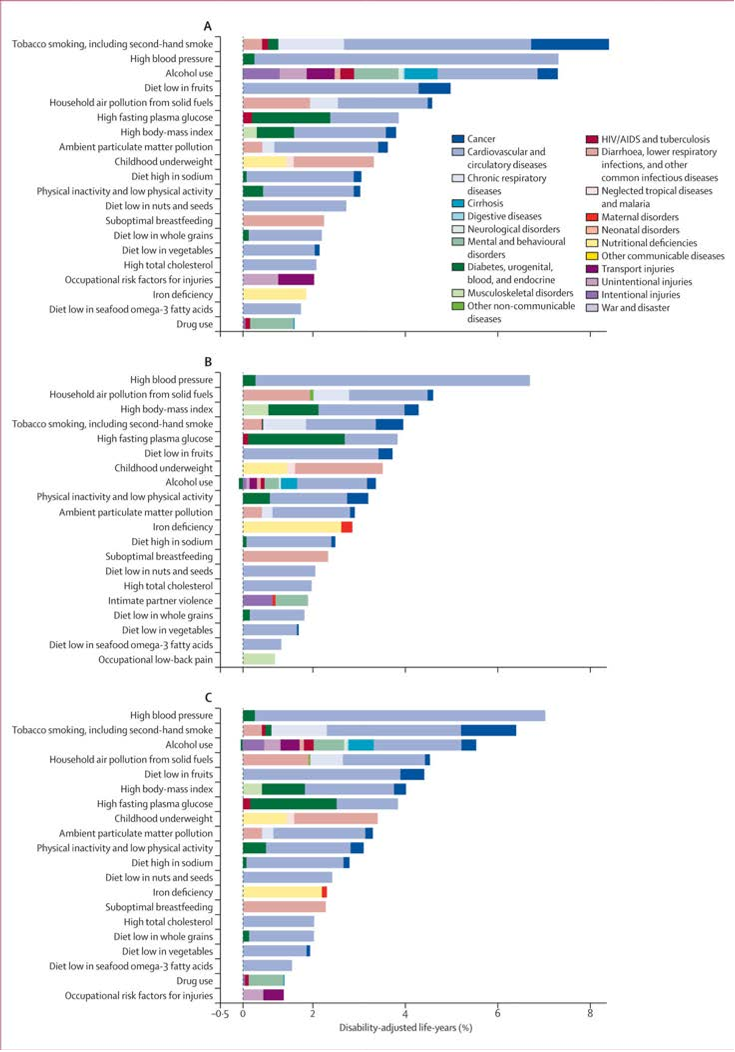
Abstract: Background Type 2 diabetes affects approximately 8 percent of adults in the United States. Some risk factors — elevated plasma glucose concentrations in the fasting state and after an oral glucose load, overweight, and a sedentary lifestyle — are potentially reversible. We hypothesized that modifying these factors with a lifestyle-intervention program or the administration of metformin would prevent or delay the development of diabetes. Methods We randomly assigned 3234 nondiabetic persons with elevated fasting and post-load plasma glucose concentrations to placebo, metformin (850 mg twice daily), or a lifestyle modification program with the goals of at least a 7 percent weight loss and at least 150 minutes of physical activity per week. The mean age of the participants was 51 years, and the mean body-mass index (the weight in kilograms divided by the square of the height in meters) was 34.0; 68 percent were women, and 45 percent were members of minority groups. Results The average follow-up was 2.8 years. The incidence of diabetes was 11.0, 7.8, and 4.8 cases per 100 person-years in the placebo, metformin, and lifestyle groups, respectively. The lifestyle intervention reduced the incidence by 58 percent (95 percent confidence interval, 48 to 66 percent) and metformin by 31 percent (95 percent confidence interval, 17 to 43 percent), as compared with placebo; the lifestyle intervention was significantly more effective than metformin. To prevent one case of diabetes during a period of three years, 6.9 persons would have to participate in the lifestyle-intervention program, and 13.9 would have to receive metformin. Conclusions Lifestyle changes and treatment with metformin both reduced the incidence of diabetes in persons at high risk. The lifestyle intervention was more effective than metformin.