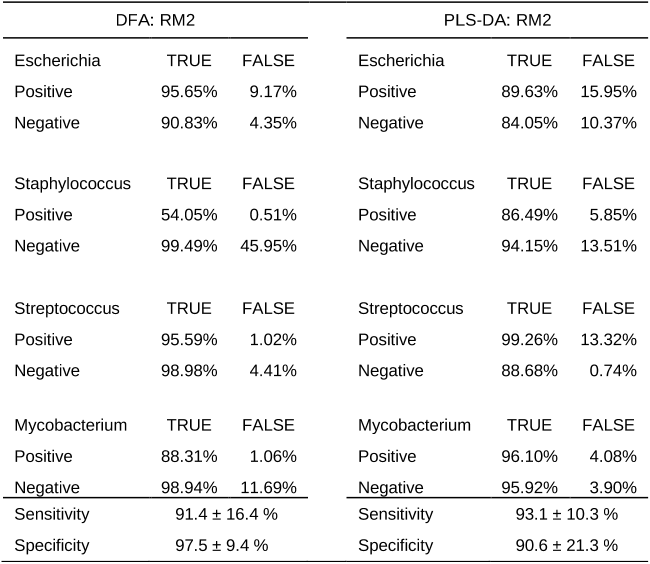
Q2. What have the authors stated for future works in "A comparison of multivariate analysis techniques and variable selection strategies in a laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy bacterial classification" ?
Such a confirmation will need to be investigated in future work.