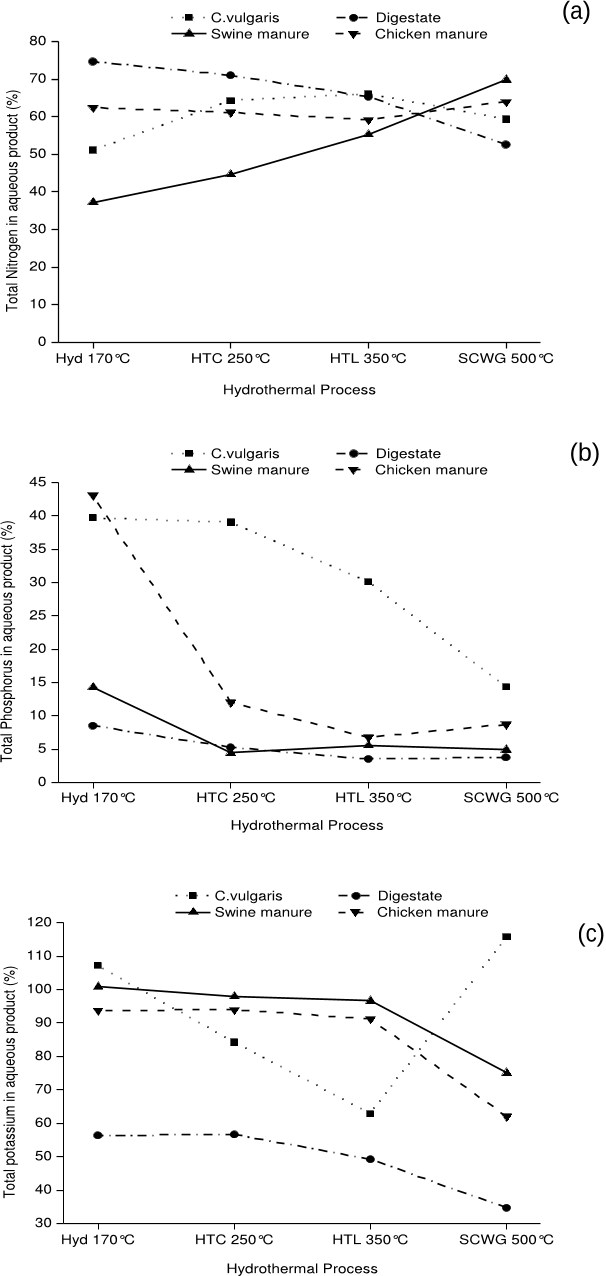
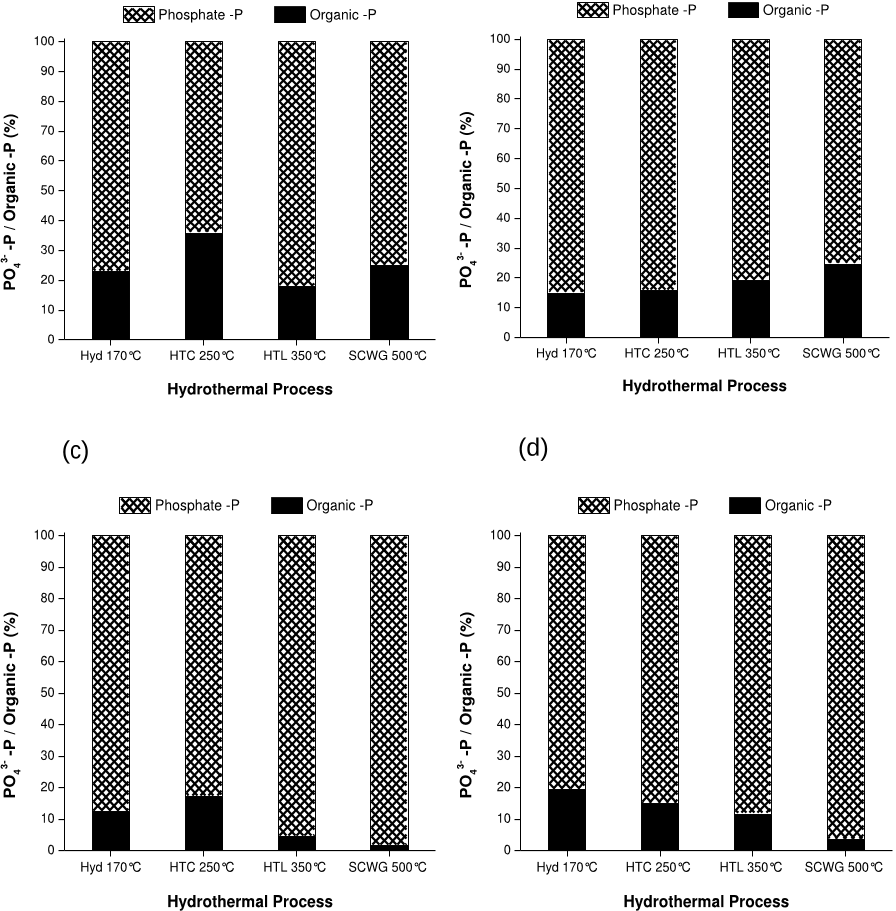
Q1. What are the contributions mentioned in the paper "A comparison of product yields and inorganic content in process streams" ?
The copyright exception in section 29 of the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988 allows the making of a single copy solely for the purpose of non-commercial research or private study within the limits of fair dealing. The publisher or other rights-holder may allow further reproduction and re-use of this version refer to the White Rose Research Online record for this item.