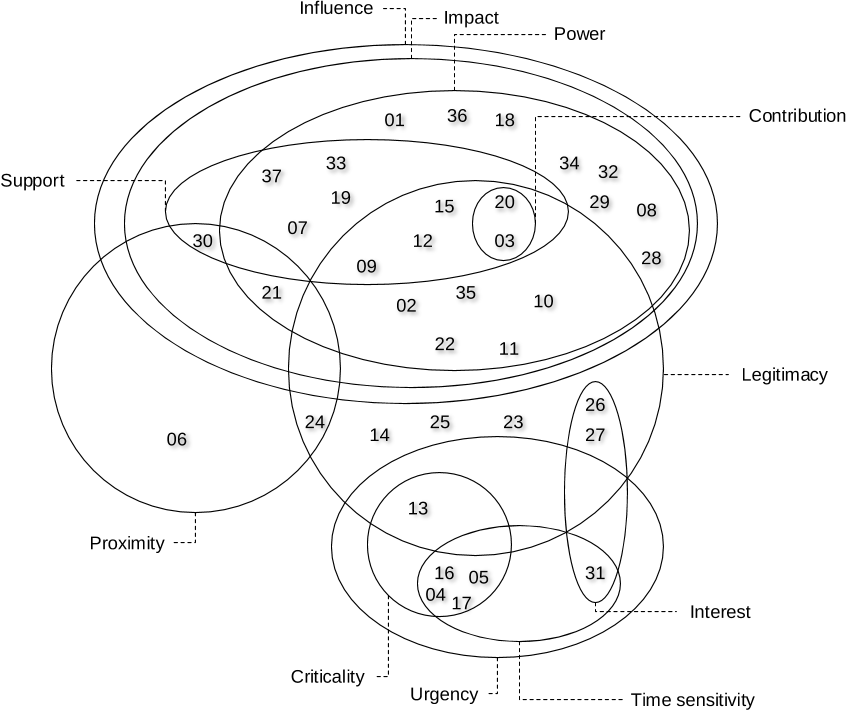
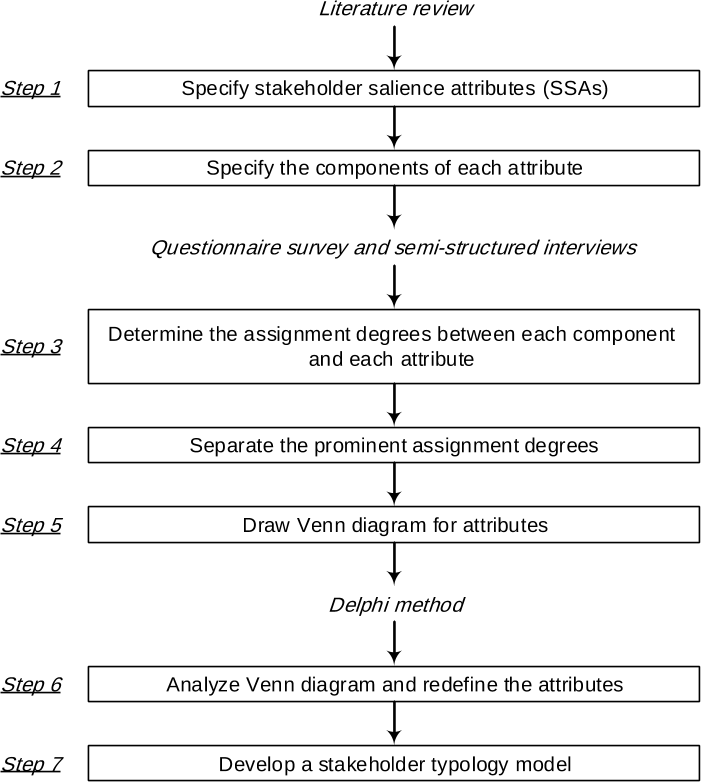
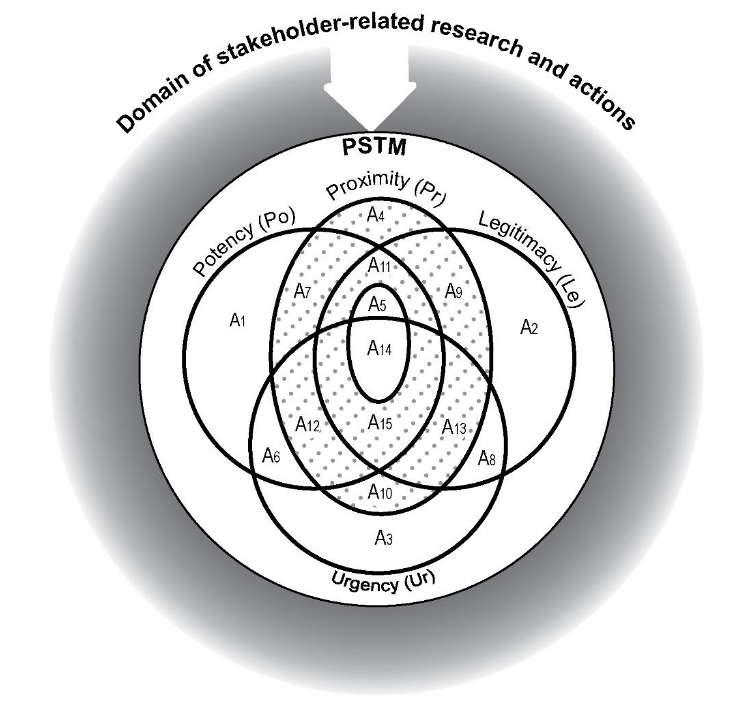
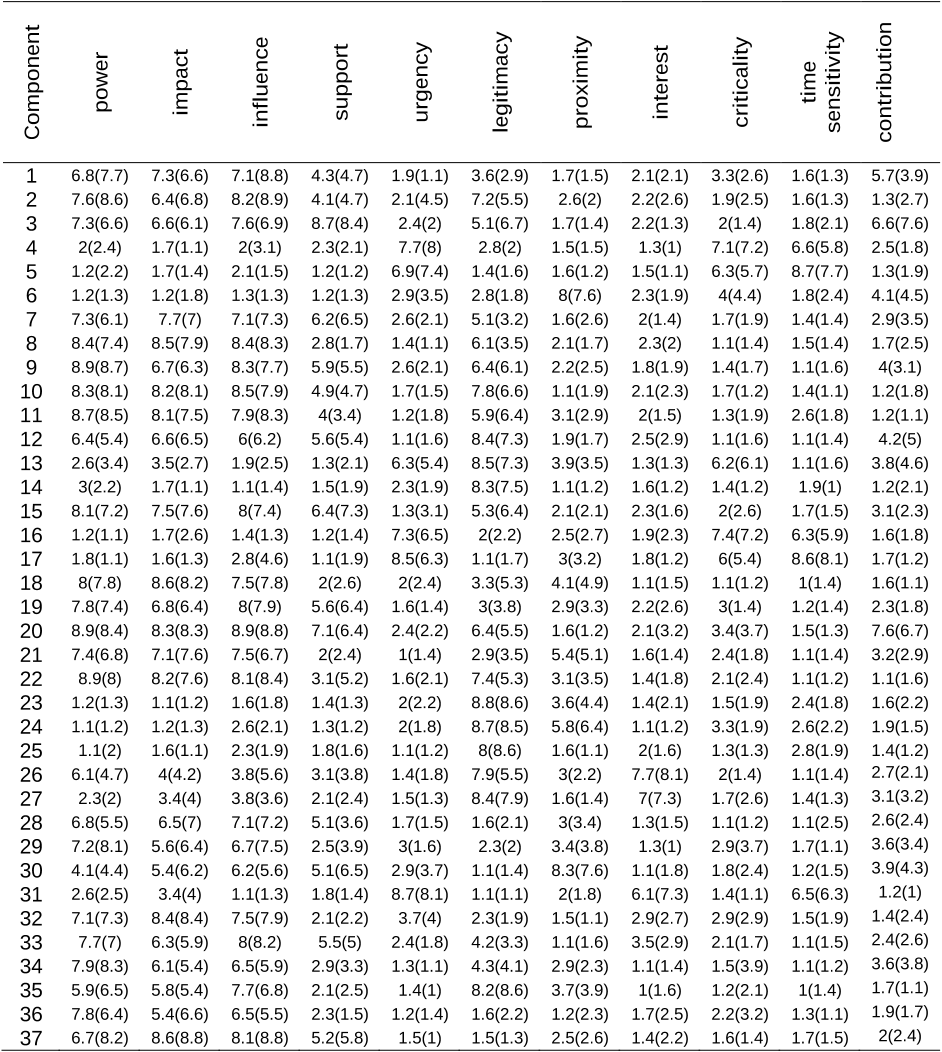
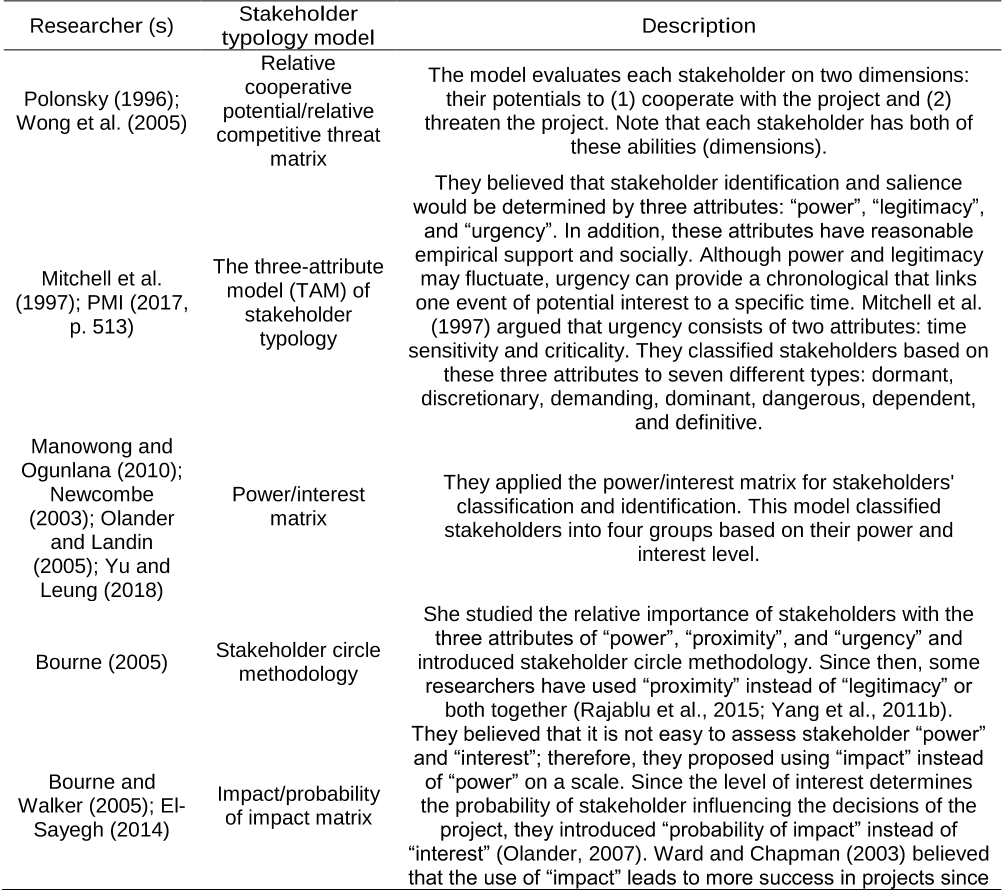
Abstract: Past research recommends integration of social sustainability (SS) considerations in construction project feasibility study for benefitting a larger group of project stakeholders. However, there is a lack of empirical evidence to this effect, especially from the developing economies. The purpose of this study is to address this knowledge gap through a SS-centric analysis of feasibility study reports using a stakeholder salience perspective.,Feasibility study reports for 61 projects were obtained from various government organizations in India. The SS considerations were identified in the reports using a combination of quantitative and qualitative assessments. The former was based on content analysis and the latter was conducted using “VOSviewer” text analysis software.,SS considerations related to occupational health and safety, workers' employment practices and proactive involvement of communities and end-users were found to be inadequately addressed in the reports. Based on occurrences of the SS considerations, project-affected community was found to be the most salient stakeholder, followed by the end-users and the construction workers. Statistical analysis revealed significant relationship between the SS considerations and the type of project as well as the type of project delivery system.,This study contributes to better understanding of integrating SS considerations in feasibility study of construction projects. Its results provide useful inputs to decision-makers for orienting construction projects, right from the early phases, towards benefitting the disadvantaged and weaker stakeholders irrespective of their salience attributes. In developing economies, such interventions may improve quality of lives of a large number of project stakeholders and also cultivate a positive societal image of the construction industry as a respectful, ethical and employee friendly industry.