212
기초간호자연과학 교육과 연구에 대한 임상 간호사와
간호학 교수의 상호지향성 인식
최명애
1
·안경주
2
·정재심
3
1
서울대학교 간호대학 교수,
2
청주대학교 간호학과 교수,
3
울산대학교 임상전문간호학 부교수
A Coorientation Analysis of Perception on Bionursing between Clinical Nurses and Nursing
Professors
Myoung-Ae Choe¹, Gyeong-Ju An², Jae-Sim Jeong³
¹Professor, Seoul National University College of Nursing, Seoul; ²Professor, Department of Nursing, Cheongju University, Cheongju; ³Associate Professor, Department
of Clinical Nursing, University of Ulsan, Seoul, Korea
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to compare perception on bionursing and satisfaction and importance about bionursing
subjects of clinical nurses with that of professors using a coorientation model. Methods: Subjects for this study consisted of 135
clinical nurses at a tertiary hospital and 114 nursing professors. Questionnaire for perception on bionursing consisted of competency
of professor, linkage with clinical practice and research of bionursing. Perceptions on bionursing education and research, satisfaction
and importance about subjects of bionursing were measured. The data were analyzed by t-test. Results: Perception of clinical nurses
on research of bionursing was more positive than professors. Perception of professors on research of bionursing was significantly
less than that of professors estimated by clinical nurses. Perception of clinical nurses on linkage with clinical practice and research of
bionursing estimated by nursing professor was significantly less than that of clinical nurses. Satisfaction of clinical nurses with the
subjects of bionursing was significantly less than that of professors. Clinical nurses perceived anatomy the most important while pro-
fessors perceived physiology the most important. Conclusion: Perceptions of clinical nurses on bionursing as well as satisfaction and
importance about subjects of bionursing were identified to be different from those of professors.
Key Words: Coorientation; Bionursing; Perception; Nurses; Professor
국문주요어: 상호지향성, 기초간호자연과학, 인식, 간호사, 교수
서 론
1. 연구의 필요성
간호학의 대상자인 인간의 신체적 측면에 대한 교육은 간호학의
기초가 되며 필수적인 부분으로서 이러한 내용의 교과목인 생리
학, 해부학, 병태생리학, 미생물학, 약리학을 기초간호자연과학이라
한다(Choe et al., 2000). 기초간호자연과학은 간호 임상실무를 뒷받
침하는 등뼈와 같은 학문으로 임상현장에서 기초간호자연과학 지
식은 근거기반간호에 필수적이며 환자의 회복에도 영향을 미친다
(Friedel & Treagust, 2005). 이론적으로 간호학은 대상자를 신체적,
정신적, 사회적, 영적 측면에서 다각도로 접근해야 한다고 강조하지
만 막상 임상현장에서 환자의 증상을 관리해야 하는 상황에서는
신체적 측면의 지식이 필수적임을 부인할 수 없다(Rudy & Grady,
2005).
간호사는 임상에서 비판적 사고 및 과학적 근거에 기반을 둔 임
상적 결정을 내릴 수 있어야 하고 최상의 정보를 환자에게 효율적
방법으로 제공할 수 있어야 한다. 이를 수행함에 있어 기본이 되는
기초간호자연과학회지 2012;14(3):212-220
ISSN: 1229-6155
http://dx.doi.org/10.7586/jkbns.2012.14.3.212 www.bionursing.or.kr
Corresponding author:
Jae Sim
Jeong,
Department of Clinical Nursing, University of Ulsan, 88 Olympic-ro
43-gil, Songpa-gu, Seoul 138-736, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3010-5311 Fax: +82-2-3010-5332 E-mail: jsjeong@amc.seoul.kr
투고일:
2012년 10월 30일
심사의뢰일:
2012년 10월 30일
게재확정일:
2012년 11월 19일
is is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0) which permits unre-
stricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the origi-
nal work is properly cited.

기초간호자연과학 교육과 연구에 대한 임상 간호사와 간호학 교수의 상호지향성 인식
213
http://dx.doi.org/10.7586/jkbns.2012.14.3.212
www.bionursing.or.kr
기초간호자연과학 지식은 간호사에게 있어 환자간호의 질과 효율
성 및 안정성을 결정하는데 중요한 필수요인이 된다(Yoo, Ahn, Yeo,
& Chu, 2008). 그동안 임상에 근무하는 일반간호사들이 실무수행
시 가장 큰 어려운 점을 기초간호자연과학에 대한 기본지식이 매
우 약한 것이라고 지속적으로 호소해왔으며 기초간호자연과학내
용의 보수교육에 대한 요구도가 매우 컸음은 이미 잘 알려진 사실
이다(Choe & Shin, 1999).
그 동안 우리나라 간호대학과 간호학과의 기초간호자연과학 교
육은 해부학, 생리학, 미생물학, 생화학, 병리학, 약리학 등의 교과목
을 의학과 교수들에 의해 의학교육의 모델을 모방하여 이루어져왔
으며 의과대학에서 학습하는 기초과학지식을 그대로 도입하면서
간호학적 특성에 기초한 교과과정이 개발되지 못하였다(Choe &
Shin, 1999). 기초의학 교수들이 강의를 담당 하는 경우 간호학에서
필요로 하는 개념을 정확히 모르는 상태에서 가르치게 되어 강의
의 초점과 방식이 전혀 체계가 없으며 효율적이지 못했다(Choe &
Shin, 1999). 또한 내용면에서도 간호학의 틀 속에서 임상에 적용할
수 있도록 그 근거가 되는 자연과학적 지식들을 고유한 지식체로서
제공한 것이 아니라 대부분 의과대학 강의를 축약한 내용으로 강
의가 이루어져서 간호학 전공과목과의 연계성이 부족했다(Choe &
Shin, 1997).
이러한 문제를 해결하기위해 대한기초간호자연과학회에서는 의
과학 모델에서 탈피하여 간호학적 모형에서 기초간호자연과학이
라는 간호학 고유의 교과목명으로 전환시켰으며(Choe et al., 1999)
기초간호자연과학 교과목과 교과내용 표준화를 위한 연구를 수행
해왔다.
일반적으로 간호학은 실용적인 응용학문의 범주에 속하기 때문
에 실무에서의 필요도가 간호학 발전에 큰 영향을 주게 된다. 이 같
은 점에서 대학에서의 기초간호자연과학 교육 목표는 실무에서의
기초가 되는 이론의 바탕이 되며 연계성을 가져야 된다고 보지만,
우리나라의 간호대학과 간호학과의 기초간호자연과학 교육은 교
육의 수혜자인 간호학을 전공하는 학부생들의 관점에서도 충분한
만족을 주지 못하는 것으로 알려져 있다(Choe et al., 1999). 간호학
전공과목 교육의 기초가 되는 기초간호자연과학을 전공한 교수진
의 부족으로 인해 기초간호자연과학 교육이 체계적으로 이루어지
지지 않아 특히 해부학과 생리학은 많은 간호학생들이 다른 과목보
다 어렵다고 인식하고 있으며 학생들에게 불안의 원인이 되기도 한
다(Meehan-Andrews, 2009).
기초간호자연과학 연구는 인간보다는 동물이나 세포를 대상으
로 하는 순수실험연구를 많이 시도하고 있으며 연구의 초점은 다
양한 인간 생체반응을 단순한 현상으로 설명하기보다 생리기전 또
는 병태생리기전, 약리기전을 통해 또는 유전적인 분석을 통해 설명
하고 있다(Lee, Park, Cho, & Park, 2011). 기초간호자연과학에 근거한
생행동연구(biobehavioral research)는 정신, 심리, 환경, 감성적 요소
및 의생물학적 요인들을 건강행위와 엮어 상호 간의 유기적인 관계
를 이해함으로써 건강을 증진시키려는 연구방법이며 전인적 건강
을 지향하는 간호의 철학적 토대와 일치한다(Yoo et al., 2008). 이는
잠재적인 미래간호연구의 발전 방향이며, 생행동 연구결과에서 나
타난 새로운 과학적 지식은 간호학 발전에 기여하고 있다. 따라서
간호연구자들은 생물학적 반응 및 이의 정확한 과학적 측정에 익
숙해져야 하며 생리학적 복잡성과 기초과학 분야에서 최신 지식의
지속적 습득이 요구되고 있다(Kang, 2003).
국내에서 기초간호자연과학 교육과 관련된 연구는 임상간호사
들을 대상으로 기초간호자연과학 교과목별로 필요로 하는 내용을
파악한 연구(Choe et al., 1999, 2000; Seo & Lee, 1999)가 있었으나 임
상간호사만을 대상으로 이루어졌기 때문에 간호학 교수들의 기초
간호자연과학 교육과 연구에 대한 인식은 확인된 바가 없다.
이 같은 점에서, 본 연구는 국내 간호학교수들과 임상간호사들의
기초간호자연과학 교육과 연구에 대한 인식에 대해 심리학과 커뮤
니케이션 분야에서 이용되어 왔던 상호지향성(coorientation) 모델
을 이용하여 집단 간의 인식차이를 체계적으로 분석하여 학교와
실무에서의 시각차가 얼마나 있는지 상대방에 대해 정확히 인식하
고 있는지에 대해 살펴보고자 한다. 상호지향성이란
‘
어떠한 개념이
나 사물 그리고 사람에 대해서 동시에 지향하는 것
’
이라 정의하며,
두 집단 간 상호이해의 정도를 커뮤니케이션 효과 차원으로 설명하
는데 유용하게 사용될 수 있다(Avery, Lariscy, & Sweetser, 2010). 상호
지향성 모델은 특정대상에 대한 집단 간의 차이점을 파악함으로써
두 집단 간의 인식을 보다 심층적으로 비교할 수 있는 방법론적인
도구이다. 그리고 이 같은 상호지향성 모델은 최근까지 다양한 집
단 간의 상호이해를 파악하는데 중요한 분석 틀로 활용되고 있다.
또한 기존의 간호학 교육에 대한 연구는 간호학교수, 학생 및 임
상간호사 중심으로 한 집단만을 조사한 연구가 있지만 동시에 임상
간호사와 간호학교수 두 집단의 인식을 비교하고 상호이해의 정도
등을 측정하는 연구가 수행된 적이 없었다. 따라서 본 연구에서 기
초간호자연과학 교육과 연구에 대한 임상간호사와 간호학 교수의
인식 차이를 파악함으로써, 또한 기초간호자연과학 교과목의 중요
도와 만족도에 대한 임상간호사와 간호학교수의 인식차이를 확인
함으로써 국내 간호학 교육에서 기초간호자연과학의 문제점을 도
출하여 개선방안을 제시하는데 중요한 기초자료가 될 것이다.
최명애· 안경주· 정재심
214
http://dx.doi.org/10.7586/jkbns.2012.14.3.212
www.bionursing.or.kr
2. 연구 목적
본 연구의 목적은 간호대학과 간호학과에서 기초간호자연과학
교육과 연구에 대한 전반적인 문제의식과 이에 대한 해결책을 모색
하기 위해 간호학 교수와 임상간호사 집단 간의 상호이해와 인식의
차이를 규명하기 위한 것으로 구체적인 목적은 다음과 같다.
1) 간호대학과 간호학과에서의 기초간호자연과학 교육과 연구
현황에 대한 임상간호사와 간호학 교수의 인식 차이를 객관적 일치
도와 정확도를 이용해 규명한다.
2) 간호대학과 간호학과에서의 기초간호자연과학 교과목의 중
요도와 만족도에 대한 임상간호사와 간호학 교수의 인식 차이를 규
명한다.
연구 방법
1. 연구 설계
본 연구는 기초간호자연과학 교육 및 연구에 대한 임상간호사와
간호학교수의 상호이해와 인식에 대한 차이를 규명하기 위해 상호
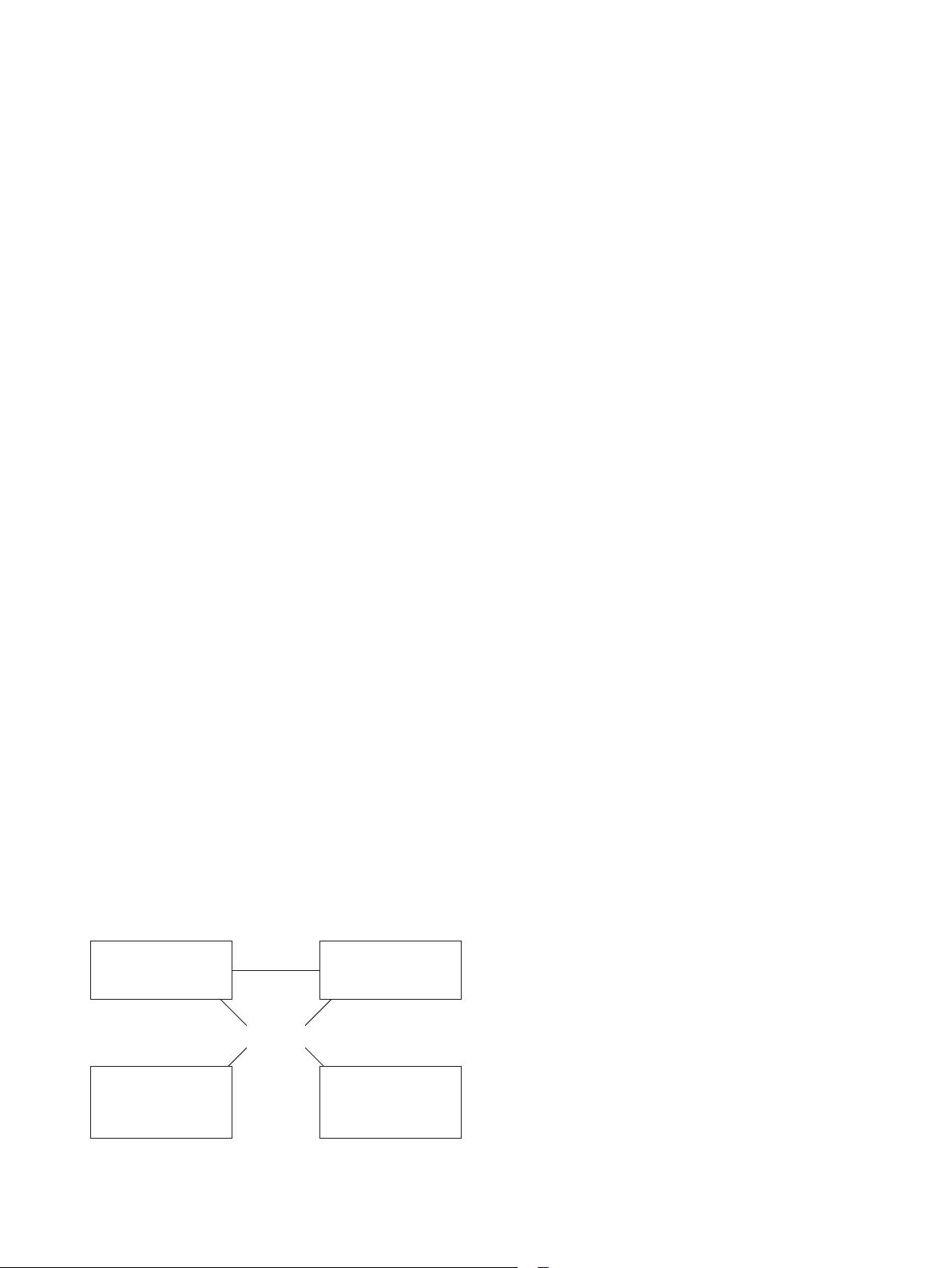
지향성 모델을 이용한 서술적 조사연구이다. Figure 1에서 나타난
바와 같이 상호지향성 모델의 주요 개념 중 객관적 일치도(agree-
ment)는 한 대상에 대한 두 집단의 인식이 일치하는 정도를 말하는
것으로 대상에 대한 두 집단의 인식이 일치하는 정도를 알 수 있다.
그리고 정확도(accuracy)는 얼마나 정확하게 상대방을 이해했는가
를 나타내 주는 것으로 상대방의 의견에 대한 자신의 추측 인식이
상대방이 실제로 인식하는 바와 어느 정도 일치하는가의 정도를
말한다(Avery, Lariscy, & Sweetser, 2010).
2. 연구 대상
본 연구의 대상자는 임의표출법(convenient sampling)을 이용하
여 서울시내 3차 의료기관에 근무하는 임상간호사와 전국의 간호
대학과 간호학과의 간호학교수로 본 연구에 참여하기를 동의하는
자로 하였다. 대상자 선정 기준은 교수인 경우 교육경력 2년 이상의
전임강사 이상, 임상간호사는 임상경력 2년 이상의 임상간호사로
선정하였다. 본 연구에서는 임상간호사 140명과 전국 4년제 간호대
학과 간호학과의 간호학 교수 121명의 설문지를 수거하였으나 응답
이 일부 누락된 설문지를 제외한 결과, 임상간호사 135명, 간호학 교
수 114명의 자료를 분석에 이용하여 본 연구 대상자는 총 249명이
되었다. 상호지향성 분석을 위한 연구 대상자 수는 G*power pro-
gram을 이용하여 t-test에서 유의수준 0.05, 효과크기 0.4, 검정력 0.8
을 유지하는데 필요한 표본 수를 구한 결과 200명이었으므로, 본 연
구의 대상자 수는 적합한 것으로 볼 수 있다.
3. 연구 도구
1) 기초간호자연과학에 대한 인식
본 연구에 이용한 기초간호자연과학에 대한 인식을 조사한 설문
지는 문항을 개발하기 위해 서술형 설문조사를 국내 간호학 교수
10명에게 실시하여 응답 내용을 토대로 30항목을 구성하였다. 이
설문 문항을 토대로 사전조사를 간호학 교수와 임상간호사에게 24
부 배부하여 문항간 신뢰도를 검증하여 Cronbach
’
s
α
=.60 미만으로
나온 3문항을 제거하여 최종 27문항으로 확정하였다. 설문 문항을
소영역별로 세분화하면 기초간호자연과학 교수의 역량 7문항, 기초
간호자연과학 교과목의 임상과의 연계성 13문항, 기초간호자연과
학 분야의 연구방향 7문항으로 구성되었다. 상호지향성 모델은 동
일한 대상에 대한 평서문의 형태로 구성하고 이에 대한 긍정, 부정
정도를 5점 척도로 응답하도록 하였으며 상대방에 대한 추측 인식
도 같이 기입하도록 구성되어있다. 5점 척도의 점수는 전혀 그렇지
않다 1점, 약간 그렇지않다 2점, 보통이다 3점, 약간 그렇다 4점, 매우
그렇다 5점이다. 본 연구에서 기초간호자연과학에 대한 인식 도구
의 신뢰도는 Cronbach
’
s
α
=.852로 나타났다.
2) 기초간호자연과학 교과목의 만족도와 중요도
국내 간호학과 기초간호자연과학 교과목인 해부학, 생리학, 병태
생리학, 미생물학, 약리학에 대한 만족도와 중요도를 각 교과목별
로 5점 척도로 측정하였다. 만족도의 5점 척도의 점수는 전혀 만족
하지 않음 1점, 약간 만족하지 많음 2점, 약간 만족함 3점, 보통 만족
함 4점, 매우 만족함 5점이다. 중요도의 5점 척도의 점수는 전혀 중
요하지 않음 1점, 약간 중요하지 않음 2점, 약간 중요함 3점, 보통 중
요함 4점, 매우 중요함 5점이다.
4. 자료 수집 방법
본 연구는 S대학교 연구윤리위원회의 승인을 받은 후 규정에 따
Figure 1. Coorientation model for bionursing in this study.
Agreement
Nurse’s perception of
bionursing
Nurses’ estimate of
nursing professors’
perception of bionursing
Nursing professors’
perception of bionursing
Nursing professors’
estimate of nurses’
perception of bionursing
Accuracy

기초간호자연과학 교육과 연구에 대한 임상 간호사와 간호학 교수의 상호지향성 인식
215
http://dx.doi.org/10.7586/jkbns.2012.14.3.212
www.bionursing.or.kr
라 진행되었다(IRB 승인번호: 2011-49). 본 연구를 위해 임상 간호사
집단은 서울 지역 3개 병원의 간호사 140명에게 연구 목적과 방법을
설명하고 연구 참여에 동의하는 경우 서면동의서를 받았고, 설문지
를 배부한 후 응답지를 수거하였다. 간호학교수 집단은 전국에 소재
한 간호대학과 간호학과 교수들에게 이메일로 연구 목적과 방법이
설명되어있는 연구 참여 동의서와 설문지를 발송한 후 연구에 동의
하는 동의서에 서명을 하고 설문응답을 보내온 114명의 자료를 이
용하였다. 자료 수집 기간은 2011년 11월부터 2012년 3월까지였다.
5. 자료 분석 방법
SPSS 14.0 프로그램을 이용하여 대상자들의 일반적 특성을 살펴
보기 위해 빈도분석을 수행했으며, 임상간호사와 간호학교수의 인
식을 비교하는 객관적 일치도, 얼마나 정확하게 상대방을 이해했는
가를 나타내 주는 정확도를 비교하기 위해 t-test를 이용하였다. 그
리고 현재 기초간호자연과학 교과목의 만족도와 중요도에 대한 두
군의 차이를 알아보기 위해 t-test를 이용하여 분석하였다. 모든 통
계적 유의 수준은 p <.05에서 채택하였다.
연구 결과
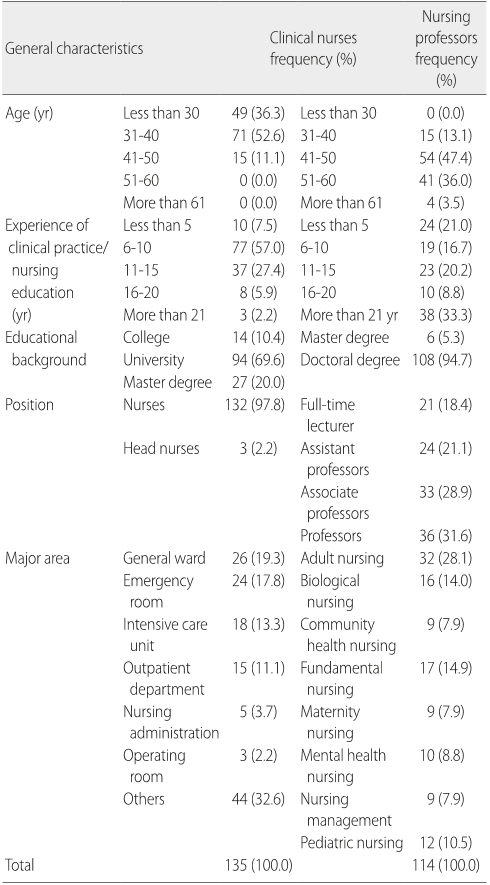
1. 대상자의 일반적 특성
임상간호사 135명, 간호학교수 114명 모두 여성이었고, 대상자의
평균 연령은 임상간호사 32.50
±
5.50세, 간호학교수 47.60
±
7.53세로
나타났으며, 임상간호사의 임상경력은 평균 8.50
±
4.13년, 간호학교
수의 교육경력은 평균 14.30
±
10.71년이었다. 직급별 분포는 임상간
호사 중 일반간호사가 132명(97.8%)으로 대부분을 차지하였고 간호
학교수 중 정교수가 36명(31.6%)으로 가장 많은 것으로 나타났다. 임
상간호사의 근무지는 기타 44명(32.6%)으로 가장 많은 것으로 나타
났고 기타 근무지로는 주로 간호행정, 간호교육, 공급실, 투석실, 감
염관리 등이 포함되었다. 간호학교수의 전공영역은 성인간호학 전
공이 32명(28.1%)으로 가장 많았다(Table 1).
2. 기초간호자연과학에 대한 상호인식
1) 객관적 일치도(agreement)
기초간호자연과학 전반에 대한 임상간호사와 간호학교수 간의
인식의 차이를 보여주는 객관적 일치도(agreement)는 Table 2와 같
다. 교수 역량 영역에서 임상간호사 24.77
±
2.97 (70.7점/100점), 간호
학 교수 25.16
±
2.89 (71.8점/100점)로 두 군 간에 유의한 차이는 없었
다. 임상과의 연관성 영역에서 임상간호사는 54.29
±
5.79 (83.5점/100
점), 간호학 교수는 53.83
±
5.74 (82.8점/100점)로 나타났고 두 군 간에
유의한 차이가 없었다. 기초간호자연과학 연구영역에 관해서는 임
Table 1. General Characteristics of Clinical Nurses and Nursing Profes-
sors
(N= 249)
General characteristics
Clinical nurses
frequency (%)
Nursing
professors
frequency
(%)
Age (yr) Less than 30 49 (36.3) Less than 30 0 (0.0)
31-40 71 (52.6) 31-40 15 (13.1)
41-50 15 (11.1) 41-50 54 (47.4)
51-60 0 (0.0) 51-60 41 (36.0)
More than 61 0 (0.0) More than 61 4 (3.5)
Experience of Less than 5 10 (7.5) Less than 5 24 (21.0)
clinical practice/ 6-10 77 (57.0) 6-10 19 (16.7)
nursing 11-15 37 (27.4) 11-15 23 (20.2)
education 16-20 8 (5.9) 16-20 10 (8.8)
(yr) More than 21 3 (2.2) More than 21 yr 38 (33.3)
Educational College 14 (10.4) Master degree 6 (5.3)
background University 94 (69.6) Doctoral degree 108 (94.7)
Master degree 27 (20.0)
Position Nurses 132 (97.8) Full-time
lecturer
21 (18.4)
Head nurses 3 (2.2) Assistant
professors
24 (21.1)
Associate
professors
33 (28.9)
Professors 36 (31.6)
Major area General ward 26 (19.3) Adult nursing 32 (28.1)
Emergency
room
24 (17.8) Biological
nursing
16 (14.0)
Intensive care
unit
18 (13.3) Community
health nursing
9 (7.9)
Outpatient
department
15 (11.1) Fundamental
nursing
17 (14.9)
Nursing
administration
5 (3.7) Maternity
nursing
9 (7.9)
Operating
room
3 (2.2) Mental health
nursing
10 (8.8)
Others 44 (32.6) Nursing
management
9 (7.9)
Pediatric nursing 12 (10.5)
Total 135 (100.0) 114 (100.0)
Table 2. Agreement between Clinical Nurses and Nursing Professors
(N= 249)
Perception of
bionursing
Group n Mean ±SD t p
Competency of Clinical Nurses 135 24.77± 2.97 1.05 .291
professor Nursing professors 114 25.16± 2.89
Linkage with Clinical Nurses 135 54.29± 5.79 0.63 .529
clinical practice Nursing professors 114 53.83± 5.74
Research of Clinical Nurses 135 28.54± 4.33 2.07 .039
bionursing Nursing professors 114 27.36± 4.63
Total Clinical Nurses 135 107.61± 10.72 0.89 .372
Nursing professors 114 106.36± 11.21

최명애· 안경주· 정재심
216
http://dx.doi.org/10.7586/jkbns.2012.14.3.212
www.bionursing.or.kr
상간호사 28.54
±
4.33점, 간호학 교수는 27.36
±
4.63점으로 두 군 간
에 유의한 차이를 보여 임상간호사들이 간호학 교수보다 더 긍정적
으로 인식하고 있는 것으로 나타났다(t=.89, p = .372).
2) 정확도(accuracy)
정확도란 상대방이 이렇게 인식할 것이라는 추측과 상대방이 실
제로 생각한 바와 일치하는 정도를 말하는 것으로 상대방을 정확
히 인식했는지를 알 수 있다. 교수역량과 임상과의 연관성 영역에서
임상간호사들이 추측한 간호학교수의 인식과 간호학교수의 실제
인식 사이에서 유의한 차이가 없는 것으로 나타나 임상간호사는
기초간호자연과학에서 교수역량과 임상과의 연관성 영역에서 간
호학교수의 인식을 정확히 인식했다고 본다. Table 3에 나타난 바와
같이 기초간호자연과학 연구영역에서 임상간호사들이 추측한 간
호학교수의 인식은 29.34
±
4.04점이고 실제 간호학교수의 인식은
27.36
±
4.63점으로 유의하게 낮은 것으로 나타났다(t=3.60, p< .001).
즉 기초간호자연과학 연구에 대해 간호학교수들은 임상간호사들
의 추측보다 실제 낮게 인식하고 있어 임상간호사의 정확도가 낮음
을 볼 수 있다.
간호학교수가 추측한 임상간호사의 인식과 실제 임상간호사의
인식 사이의 차이를 알아본 결과는 다음과 같다. 교수역량 영역에
Table 3. Accuracy of Estimation in Clinical Nurses and Nursing Professors
(N= 249)
Perception of bionursing Group n Mean ±SD t p
Accuracy of clinical nurses Competency of professor Clinical nurses‘s speculative score 135 24.51± 3.61 1.54 .123
Nursing professors's actual score 114 25.16 ±2.89
Linkage with clinical practice Clinical nurses‘s speculative score
135
53.51± 6.11 0.41
.678
Nursing professors's actual score 114 53.83 ±5.74
Research of Bionursing Clinical nurses‘s speculative score 135 29.34 ±4.04 3.60 < .001
Nursing professors's actual score 114 27.36 ±4.63
Total Clinical nurses‘s speculative score 135 107.31± 11.20 0.66 .509
Nursing professors's actual score 114 106.36± 11.21
Accuracy of nursing professors Competency of professor Clinical nurses's actual score 135 24.77 ±2.97 0.94 .348
Nursing professors‘s speculative score 114 24.41 ±2.93
Linkage with clinical practice Clinical nurses's actual score 135 54.29± 5.79 3.10 .002
Nursing professors‘s speculative score 114 51.84 ±6.67
Research of Bionursing Clinical nurses's actual score 135 28.54± 4.33 5.06 <.001
Nursing professors‘s speculative score 114 25.64 ±4.71
Total Clinical nurses's actual score 135 107.61 ± 10.72 3.93 < .001
Nursing professors‘s speculative score 114 101.92± 12.07
Table 4. Satisfaction and Importance about Subjects of Bionursing
(N= 249)
Subject of bionursing Group n Mean ±SD t p
Satisfaction Anatomy Clinical nurses 135 2.96 ±1.190 3.53 < .001
Nursing professors 114 3.47 ±1.107
Physiology Clinical nurses 135 3.10 ±1.148 3.31 .001
Nursing professors 114 3.57 ±1.056
Pathophysiology Clinical nurses 135 2.47 ±1.221 5.30 < .001
Nursing professors 114 3.29 ±1.195
Microbiology Clinical nurses 135 2.24 ±1.192 3.58 < .001
Nursing professors 114 2.79 ±1.237
Pharmacology Clinical nurses 135 2.57 ±1.194 3.79 < .001
Nursing professors 114 3.14 ±1.166
Importance Anatomy Clinical nurses 135 4.57 ±0.778 0.26 .790
Nursing professors 114 4.54 ±0.789
Physiology Clinical nurses 135 4.48 ±0.863 1.90 .058
Nursing professors 114 4.68 ±0.723
Pathophysiology Clinical nurses 135 4.04 ±1.202 3.47 .001
Nursing professors 114 4.51 ±0.833
Microbiology Clinical nurses 135 3.41 ±1.224 2.31 .022
Nursing professors 114 3.75 ±1.054
Pharmacology Clinical nurses 135 4.19 ±1.087 1.84 .067
Nursing professors 114 4.42 ±0.901