A Detection of Water in the Transmission Spectrum of the Hot Jupiter WASP-12b and Implications for its Atmospheric Composition
TL;DR: In this article, a near-infrared transmission spectrum for WASP-12b based on six transit observations with the Hubble Space Telescope/Wide Field Camera 3 (HST-WFC) was reported.
Abstract: Detailed characterization of exoplanets has begun to yield measurements of their atmospheric properties that constrain the planets’ origins and evolution. For example, past observations of the dayside emission spectrum of the hot Jupiter WASP-12b indicated that its atmosphere has a high carbon-tooxygen ratio (C/O > 1), suggesting it had a dierent formation pathway than is commonly assumed for giant planets. Here we report a precise near-infrared transmission spectrum for WASP-12b based on six transit observations with the Hubble Space Telescope/Wide Field Camera 3. We bin the data in 13 spectrophotometric light curves from 0.84 - 1.67 m and measure the transit depths to a median precision of 51 ppm. We retrieve the atmospheric properties using the transmission spectrum and nd strong evidence for water absorption (7 condence). This detection marks the rst high-condence, spectroscopic identication of a molecule in the atmosphere of WASP-12b. The retrieved 1 water volume mixing ratio is between 10 5 10 2 , which is consistent with C/O > 1 to within 2 . However, we also introduce a new retrieval parameterization that ts for C/O and metallicity under the assumption of chemical equilibrium. With this approach, we constrain C/O to 0:5 +0:2 0:3 at 1 and rule out a carbon-rich atmosphere composition (C/O> 1) at > 3 condence. Further observations and modeling of the planet’s global thermal structure and dynamics would aid in resolving the tension between our inferred C/O and previous constraints. Our ndings highlight the importance of obtaining high-precision data with multiple observing techniques in order to obtain robust constraints on the chemistry and physics of exoplanet atmospheres. Subject headings: planets and satellites: atmospheres | planets and satellites: composition | planets and satellites: individual: WASP-12b
Figures (19)
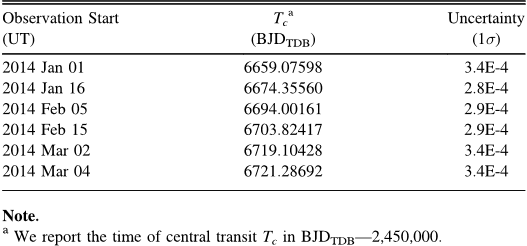
Table 2 Transit Times 
Figure 6. Systematics decorrelation parameters from the light curve fits plotted as a function of normalization c. We show (from top to bottom) the visit-long slope v, ramp rate constant a, ramp amplitude b, and ramp delay d. The normalization constant c is linearly proportional to the per-pixel flux in a spectroscopic channel. Measurements from the G102 and G141 data are shown in light and dark gray, respectively. The error bars indicate 1σ uncertainties from an MCMC fit to the light curves using the analytic model for instrument systematics. 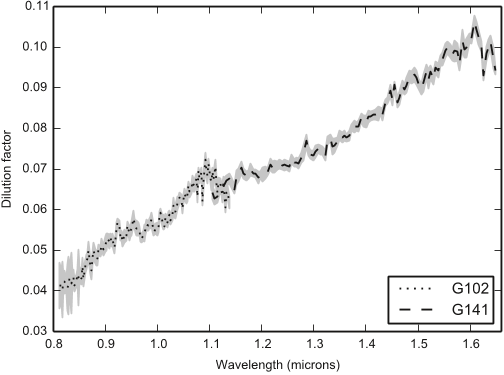
Figure 7. Dilution factor αComp, determined from the ratio of flux from WASP12 BC to WASP-12 A. The median dilution (over the 10 staring mode observations) is shown with black lines (dotted for G102 and dashed for G141). The gray shaded region indicates 1σ uncertainty, determined from the median absolute deviation. To calculate the dilution and uncertainty, we interpolate the spectra from each grism onto a common wavelength scale. 
Figure 12. Retrieval results from the C-C parameterization. The left and middle panels show the marginalized distribution for C/O and metallicity. The right panel shows the median (black lines) and 1σ range (shaded regions) of 1000 randomly sampled temperature–pressure profiles for each scenario. Yellow, blue, and red shading correspond to constraints from the fiducial scenario (an uninformative prior on C/O), the oxygen-rich scenario (C/O < 1), and a carbon-rich scenario (C/O > 1). The distribution of C/O values for the carbon-rich model is normalized to have a probability mass of unity over the plotted range; however, the distribution has an extended tail toward higher C/O values that is not shown. 
Table 1 Summary of Photometric Observations for WASP-12 
Figure 1. Raw HST/WFC3 images taken with the G102 grism. Spatial scan and staring mode data are shown in the top and bottom panels, respectively. The images are cutouts from a 256 × 256 pixel subarray. The spectrum of WASP-12A’s binary companion is visible in the bottom panel near row 10. 
Figure 8. Transmission spectrum of WASP-12b measured with HST/WFC3 (points). The error bars on the transit depths are 1σ uncertainties from an MCMC fit to the light curves. We show the best fit model binned to the resolution of the data (blue squares). The shaded regions indicate 1 and 2σ credible intervals in the retrieved spectrum (medium and light blue, respectively), relative to the median fit (dark blue line). The secondary y-axis labels indicate the atmospheric scale height. One scale height corresponds to 470 km (for a temperature of 1400 K). The increase in transit depth near 1.4 μm corresponds to an H2O bandhead. 
Table 3 Transit Fit Parameters 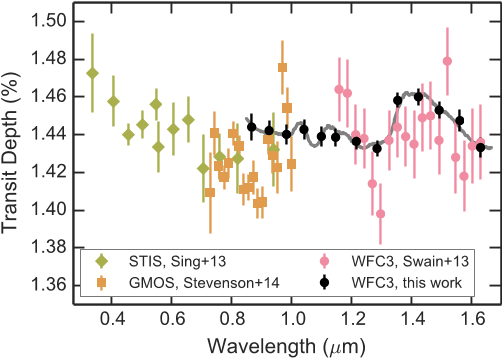
Figure 9. High-precision optical/near-IR transit depth measurements for WASP-12b. We show measurements from HST/STIS (green diamonds), Gemini/GMOS (orange squares), and HST/WFC3 (from this work, black circles; from staring mode data, pink circles). The best fit model from the CHIMERA FULL retrieval is indicated by the gray line. Note that this model was fit to the WFC3 data only. There may be small offsets between data sets due to different corrections for the companion star dilution and the challenge of measuring absolute transit depths in the presence of systematic errors (Stevenson et al. 2014a, 2014c). 
Figure 11. Pairs plot of the distribution of parameters retrieved with CHIMERA for the FULL model. The parameters are the scale height temperature Ts (in Kelvin), the planet radius scale factor Rscale, the cloud-top pressure Pc (in log bars), the logarithm (base 10) of the molecular abundances, and the haze scattering amplitude σ0 and slope γ. The off-diagonal plots show marginalized posterior probability density for pairs of parameters (darker shading corresponds to higher probability). The diagonal plots show marginalized posterior probability distributions for individual parameters, with the median and 68% credible interval marked with dashed lines. 
Figure 3. Example extracted spectra (solid lines). The wavelength ranges covered by the transmission spectra are indicated with dashed and dotted lines (for the G102 and G141 data, respectively). The uncertainties on the spectra are smaller than the plot linewidth. 
Figure 2. Nightly Cousins R-band photometric observations of WASP-12 over three observing seasons (points). The data are differential magnitudes relative to the average brightness of 17 comparison stars. The differential magnitudes have a mean of −0.281 and a standard deviation of 0.003. The horizontal dashed line indicates the mean brightness from the first observing season. The vertical dotted lines span the time range of the HST observations. 
Figure 14. Histogram of equivalent pressures corresponding to an optical depth of 0.56 at 1.4 μm for each step in the MCMC chain for the FULL retrieval. The dotted lines indicate the median and surrounding 68% confidence interval. 
Figure 10. Best fits for different assumed models (lines) compared to the WFC3 transmission spectrum (points). Models are binned to a wavelength resolution of 0.01 μm. Results from the FREE and C-C parameterizations are shown in the top and bottom panels, respectively. 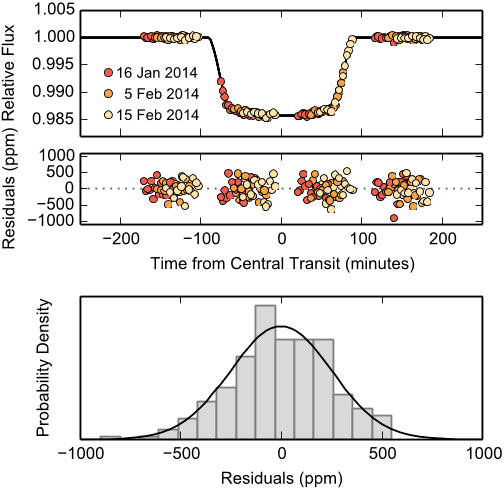
Figure 4. An example light curve fit to the 1.320–1.389 μm spectroscopic channel from the G141 grism. The top panel shows the best fitting model light curve (black line), overlaid with the systematics-corrected data (points). Residuals from the light curve fit are shown in the middle panel. The bottom panel shows a normalized histogram of the residuals compared to a Gaussian probability density with mean zero and standard deviation equal to the predicted photon+read noise (252 ppm). 
Table 5 C-C Retrieval Results 
Figure 13. Left: measurement of the water abundance and scale height temperature for WASP-12b (points) compared to equilibrium chemistry predictions of the water content for different atmospheric compositions (lines and shading). The black point indicates the water abundance and temperature measurements from the FULL model from the CHIMERA fit to the WFC3 spectrum. Results from other nested models are shown in gray. The black dashed line and blue shading correspond to water abundance predictions for a solar C/O composition, and the black dotted line and red shading correspond to C/O=1. Both models have solar metallicity. For each model composition, the shading shows the span of predicted water abundances over pressures ranging from 0.1 to 10 mbar. The black lines correspond to 1 mbar, which is the typical pressure level probed by our observations. Right: Histogram of observed minus calculated water abundances for the FULL retrieval results relative to different model compositions. The red histogram (dotted line) shows the comparison with a carbon-rich model, and the blue histogram (dashed line) shows results for the oxygen-rich model. The gray vertical line marks zero, where the observations are an exact match to the model predictions. 
Table 4 FREE Retrieval Results 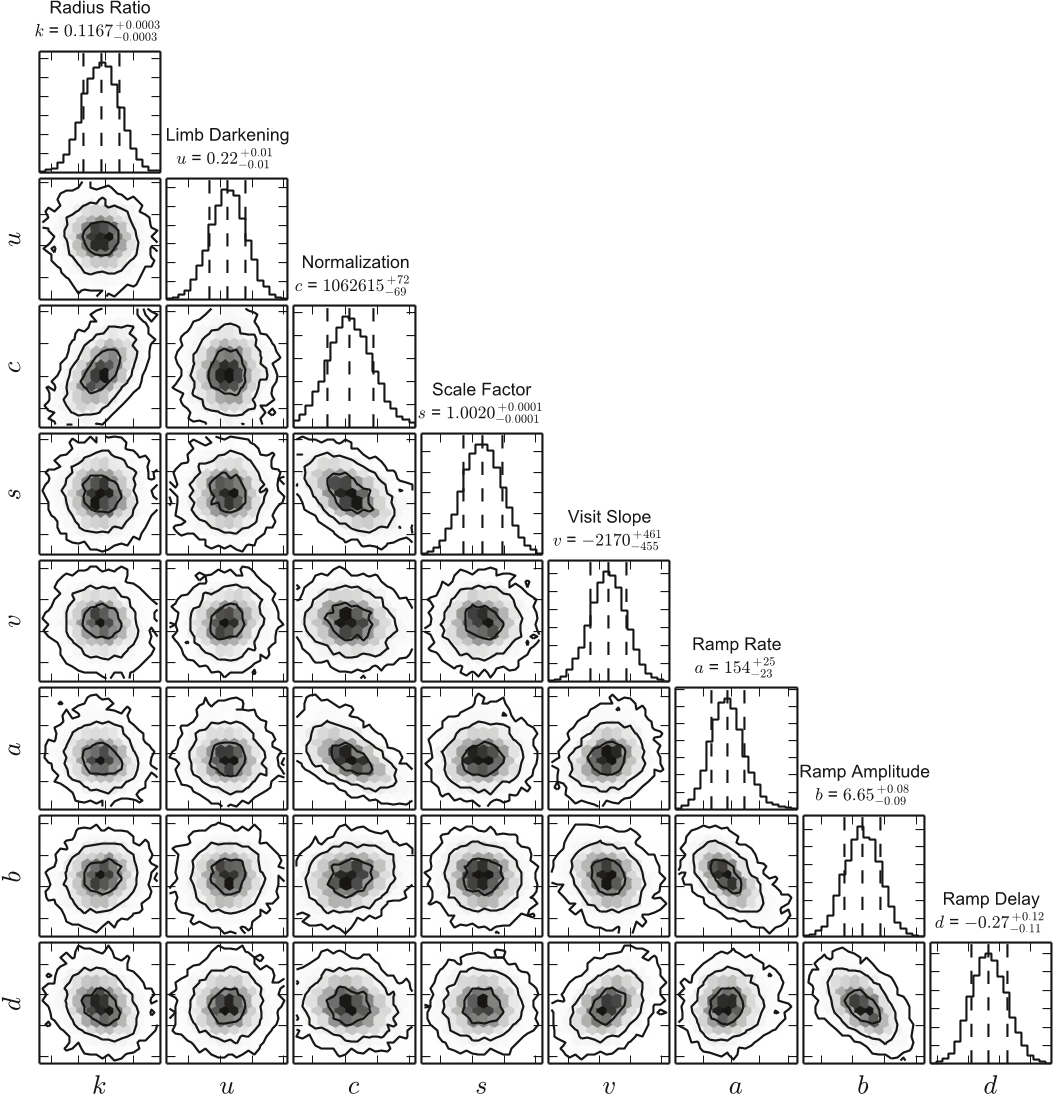
Figure 5. Pairs plot showing distributions of MCMC fit parameters for the 1.320–1.389 μm light curve. The off-diagonal panels show marginalized posterior probability for pairs of parameters, with 1, 2, and 3σ credible intervals indicated with black contours. The gray shading corresponds to probability density (darker for higher probability). The panels on the diagonal show distributions of each parameter marginalized over the other model parameters, with the median and 68% credible interval marked with dashed lines. The planet-to-star radius ratio, k, is not strongly correlated with any of the other fit parameters. For parameters that are allowed to vary between transit observations (k, c, s, and v), we show distributions for the 2014 January 16 transit.
Citations
More filters
TL;DR: In this article, the authors explore how well spectra from the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) will likely constrain bulk atmospheric properties of transiting exoplanets.
Abstract: We explore how well spectra from the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) will likely constrain bulk atmospheric properties of transiting exoplanets. We start by modeling the atmospheres of archetypal hot Jupiter, warm Neptune, warm sub-Neptune, and cool super-Earth planets with atmospheres that are clear, cloudy, or of high mean molecular weight (HMMW). Next we simulate the λ = 1–11 μm transmission and emission spectra of these systems for several JWST instrument modes for single-transit or single-eclipse events. We then perform retrievals to determine how well temperatures and molecular mixing ratios (CH4, CO, CO2, H2O, NH3) can be constrained. We find that λ = 1–2.5 μm transmission spectra will often constrain the major molecular constituents of clear solar-composition atmospheres well. Cloudy or HMMW atmospheres will often require full 1–11 μm spectra for good constraints, and emission data may be more useful in cases of sufficiently high Fp and high Fp/F*. Strong temperature inversions in the solar-composition hot-Jupiter atmosphere should be detectable with 1–2.5+ μm emission spectra, and 1–5+ μm emission spectra will constrain the temperature–pressure profiles of warm planets. Transmission spectra over 1–5+ μm will constrain [Fe/H] values to better than 0.5 dex for the clear atmospheres of the hot and warm planets studied. Carbon-to-oxygen ratios can be constrained to better than a factor of 2 in some systems. We expect that these results will provide useful predictions of the scientific value of single-event JWST spectra until its on-orbit performance is known.
473 citations
TL;DR: In this article, the authors explore how well James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) spectra will likely constrain bulk atmospheric properties of transiting exoplanets, and they find that the JWST spectra can often constrain the major molecular constituents of clear solar composition atmospheres well.
Abstract: We explore how well James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) spectra will likely constrain bulk atmospheric properties of transiting exoplanets. We start by modeling the atmospheres of archetypal hot Jupiter, warm Neptune, warm sub-Neptune, and cool super-Earth planets with clear, cloudy, or high mean molecular weight atmospheres. Next we simulate the $\lambda = 1 - 11$ $\mu$m transmission and emission spectra of these systems for several JWST instrument modes for single transit and eclipse events. We then perform retrievals to determine how well temperatures and molecular mixing ratios (CH$_4$, CO, CO$_2$, H$_2$O, NH$_3$) can be constrained. We find that $\lambda = 1 - 2.5$ $\mu$m transmission spectra will often constrain the major molecular constituents of clear solar composition atmospheres well. Cloudy or high mean molecular weight atmospheres will often require full $1 - 11$ $\mu$m spectra for good constraints, and emission data may be more useful in cases of sufficiently high $F_p$ and high $F_p/F_*$. Strong temperature inversions in the solar composition hot Jupiter atmosphere should be detectable with $1 - 2.5+$ $\mu$m emission spectra, and $1 - 5+$ $\mu$m emission spectra will constrain the temperature-pressure profiles of warm planets. Transmission spectra over $1 - 5+$ $\mu$m will constrain [Fe/H] values to better than 0.5 dex for the clear atmospheres of the hot and warm planets studied. Carbon-to-oxygen ratios can be constrained to better than a factor of 2 in some systems. We expect that these results will provide useful predictions of the scientific value of single event JWST spectra until its on-orbit performance is known.
351 citations
01 Oct 2015
TL;DR: Batman as discussed by the authors is a Python package for modeling exoplanet transit light curves that uses C extension modules to speed up model calculation and is parallelized with OpenMP, which can calculate one million quadratic limb-darkened models in 30 seconds with a single 1.7 GHz Intel Core i5 processor.
Abstract: I introduce batman, a Python package for modeling exoplanet transit light curves. The batman package supports calculation of light curves for any radially symmetric stellar limb darkening law, using a new integration algorithm for models that cannot be quickly calculated analytically. The code uses C extension modules to speed up model calculation and is parallelized with OpenMP. For a typical light curve with 100 data points in transit, batman can calculate one million quadratic limb-darkened models in 30 seconds with a single 1.7 GHz Intel Core i5 processor. The same calculation takes seven minutes using the four-parameter nonlinear limb darkening model (computed to 1 ppm accuracy). Maximum truncation error for integrated models is an input parameter that can be set as low as 0.001 ppm, ensuring that the community is prepared for the precise transit light curves we anticipate measuring with upcoming facilities. The batman package is open source and publicly available at https://github.com/lkreidberg/batman. Subject headings: methods: data analysis – methods: numerical
299 citations
TL;DR: The spectral properties of ultra hot Jupiters were investigated in this article, where the authors used the SPARC/MITgcm spectral model to model the atmospheres of the four ultra hot supergiants and discussed more thoroughly the case of WASP-121b.
Abstract: Context A new class of exoplanets has emerged: the ultra hot Jupiters, the hottest close-in gas giants. The majority of them have weaker-than-expected spectral features in the 1.1−1.7 μm bandpass probed by HST/WFC3 but stronger spectral features at longer wavelengths probed by Spitzer. This led previous authors to puzzling conclusions about the thermal structures and chemical abundances of these planets. Aims We investigate how thermal dissociation, ionization, H− opacity, and clouds shape the thermal structures and spectral properties of ultra hot Jupiters. Methods We use the SPARC/MITgcm to model the atmospheres of four ultra hot Jupiters and discuss more thoroughly the case of WASP-121b. We expand our findings to the whole population of ultra hot Jupiters through analytical quantification of the thermal dissociation and its influence on the strength of spectral features. Results We predict that most molecules are thermally dissociated and alkalies are ionized in the dayside photospheres of ultra hot Jupiters. This includes H2O, TiO, VO, and H2 but not CO, which has a stronger molecular bond. The vertical molecular gradient created by the dissociation significantly weakens the spectral features from H2O while the 4.5 μm CO feature remains unchanged. The water band in the HST/WFC3 bandpass is further weakened by the continuous opacity of the H− ions. Molecules are expected to recombine before reaching the limb, leading to order of magnitude variations of the chemical composition and cloud coverage between the limb and the dayside. Conclusions Molecular dissociation provides a qualitative understanding of the lack of strong spectral features of water in the 1−2 μm bandpass observed in most ultra hot Jupiters. Quantitatively, our model does not provide a satisfactory match to the WASP-121b emission spectrum. Together with WASP-33b and Kepler-33Ab, they seem the outliers among the population of ultra hot Jupiters, in need of a more thorough understanding.
294 citations
TL;DR: In this article, a chain of models, linking the formation of a planet to its observable present-day spectrum, is presented, including the planet's formation and migration, its long-term thermodynamic evolution, a variety of disk chemistry models, a non-gray atmospheric model, and a radiometric model to obtain simulated spectroscopic observations with James Webb Space Telescope and ARIEL.
Abstract: The composition of a planet's atmosphere is determined by its formation, evolution, and present-day insolation. A planet's spectrum therefore may hold clues on its origins. We present a "chain" of models, linking the formation of a planet to its observable present-day spectrum. The chain links include (1) the planet's formation and migration, (2) its long-term thermodynamic evolution, (3) a variety of disk chemistry models, (4) a non-gray atmospheric model, and (5) a radiometric model to obtain simulated spectroscopic observations with James Webb Space Telescope and ARIEL. In our standard chemistry model the inner disk is depleted in refractory carbon as in the Solar System and in white dwarfs polluted by extrasolar planetesimals. Our main findings are: (1) envelope enrichment by planetesimal impacts during formation dominates the final planetary atmospheric composition of hot Jupiters. We investigate two, under this finding, prototypical formation pathways: a formation inside or outside the water iceline, called "dry" and "wet" planets, respectively. (2) Both the "dry" and "wet" planets are oxygen-rich (C/O 1 for the "dry" planet. (3) While we consistently find C/O ratios <1, they still vary significantly. To link a formation history to a specific C/O, a better understanding of the disk chemistry is thus needed.
281 citations
References
More filters
TL;DR: The emcee algorithm as mentioned in this paper is a Python implementation of the affine-invariant ensemble sampler for Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) proposed by Goodman & Weare (2010).
Abstract: We introduce a stable, well tested Python implementation of the affine-invariant ensemble sampler for Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) proposed by Goodman & Weare (2010). The code is open source and has already been used in several published projects in the astrophysics literature. The algorithm behind emcee has several advantages over traditional MCMC sampling methods and it has excellent performance as measured by the autocorrelation time (or function calls per independent sample). One major advantage of the algorithm is that it requires hand-tuning of only 1 or 2 parameters compared to ~N2 for a traditional algorithm in an N-dimensional parameter space. In this document, we describe the algorithm and the details of our implementation. Exploiting the parallelism of the ensemble method, emcee permits any user to take advantage of multiple CPU cores without extra effort. The code is available online at http://dan.iel.fm/emcee under the GNU General Public License v2.
8,805 citations
TL;DR: The solar chemical composition is an important ingredient in our understanding of the formation, structure, and evolution of both the Sun and our Solar System as discussed by the authors, and it is an essential refer...
Abstract: The solar chemical composition is an important ingredient in our understanding of the formation, structure, and evolution of both the Sun and our Solar System. Furthermore, it is an essential refer ...
8,605 citations
TL;DR: This document introduces a stable, well tested Python implementation of the affine-invariant ensemble sampler for Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) proposed by Goodman & Weare (2010).
Abstract: We introduce a stable, well tested Python implementation of the affine-invariant ensemble sampler for Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) proposed by Goodman & Weare (2010). The code is open source and has already been used in several published projects in the astrophysics literature. The algorithm behind emcee has several advantages over traditional MCMC sampling methods and it has excellent performance as measured by the autocorrelation time (or function calls per independent sample). One major advantage of the algorithm is that it requires hand-tuning of only 1 or 2 parameters compared to $\sim N^2$ for a traditional algorithm in an N-dimensional parameter space. In this document, we describe the algorithm and the details of our implementation and API. Exploiting the parallelism of the ensemble method, emcee permits any user to take advantage of multiple CPU cores without extra effort. The code is available online at this http URL under the MIT License.
5,293 citations
TL;DR: In this paper, exact analytic formulae for the eclipse of a star described by quadratic or nonlinear limb darkening are presented for the HST observations of HD 209458, showing that the ratio of the planetary to stellar radii is 0.1207+-0.0003.
Abstract: We present exact analytic formulae for the eclipse of a star described by quadratic or nonlinear limb darkening. In the limit that the planet radius is less than a tenth of the stellar radius, we show that the exact lightcurve can be well approximated by assuming the region of the star blocked by the planet has constant surface brightness. We apply these results to the HST observations of HD 209458, showing that the ratio of the planetary to stellar radii is 0.1207+-0.0003. These formulae give a fast and accurate means of computing lightcurves using limb-darkening coefficients from model atmospheres which should aid in the detection, simulation, and parameter fitting of planetary transits.
2,370 citations
TL;DR: In this paper, the exact analytic formulae for the eclipse of a star described by quadratic or nonlinear limb darkening were presented, and the authors applied these results to the Hubble Space Telescope observations of HD 209458, showing that the ratio of the planetary to stellar radii is 0.1207 ± 0.0003.
Abstract: We present exact analytic formulae for the eclipse of a star described by quadratic or nonlinear limb darkening. In the limit that the planet radius is less than a tenth of the stellar radius, we show that the exact light curve can be well approximated by assuming the region of the star blocked by the planet has constant surface brightness. We apply these results to the Hubble Space Telescope observations of HD 209458, showing that the ratio of the planetary to stellar radii is 0.1207 ± 0.0003. These formulae give a fast and accurate means of computing light curves using limb-darkening coefficients from model atmospheres that should aid in the detection, simulation, and parameter fitting of planetary transits.
2,253 citations