A dynamic programming approach to price installment options
Summary (2 min read)
1 Introduction
- Installment Options (IO) are akin to Bermudan options except that the holder must regularly pay a premium (the “installment”) to keep the option alive.
- Instead of paying a lump sum for a derivative instrument, the holder of the IO will pay the installments as long as the need for being long in the option is present.
- In particular, this considerably reduces the cost of entering into a hedging strategy.
- Second, the authors investigate the properties of IOs through theoretical and numerical analysis in the Black and Scholes (1973) setting.
- Dynamic programming stands as an alternative for low dimensional option pricing.
2 The model
- Let the price of the underlying asset {S} be a Markov process that verifies the fundamental no-arbitrage property.
- Equation (3) models the choices that are available to the option holder: he will pay the installment and hold the option as long as the net holding value is larger than the exercise value.
- Otherwise, according to the exercise value, he will either exercise the option (when positive) or abandon the contract (when null).
- One way of pricing this IO is via backward induction using (1)-(3) from the known function vn = ve.
3 Solving the DP equation
- The idea is to partition the positive real axis into a collection of intervals and then to approximate the option value by a piecewise linear interpolation.
- (11) Key in the applicability of the DP procedure is how efficiently the integrals (9)-(10) can be computed.
- This is the well known problem of estimating the probability of rare events.
- The authors also derive some theoretical properties of the IO contract within this framework.
4 The Geometric Brownian Motion framework
- The authors now derive some theoretical properties related to the design of installment call options in the GBM framework.
- Symmetric results hold for installment put options.
- Obviously, this function is always strictly positive.
- The net holding value reaches 0 at a unique threshold xn−1, and the exercise value at a unique threshold yn−1, where xn−1 and yn−1 depend on the IO parameters.
- Figure 1 plots the curve representing the net holding value of the installment call option vhm (s)− πm for any decision date m.
5.1 Convergence speed and accuracy
- The model for the diffusion is the Geometric Brownian Motion with no dividend (Black-Scholes model).
- Matrices [Aki] and [Bki] are precomputed before doing the first iteration.
- Table 1 displays the main pricing properties of their approach.
- A four-digit accuracy can be obtained with a 1000-point grid, which implies a computational time that does not exceed two seconds.
- Third and most importantly, convergence to the “true” price is monotonic.
5.2 Non-redundant IO contracts
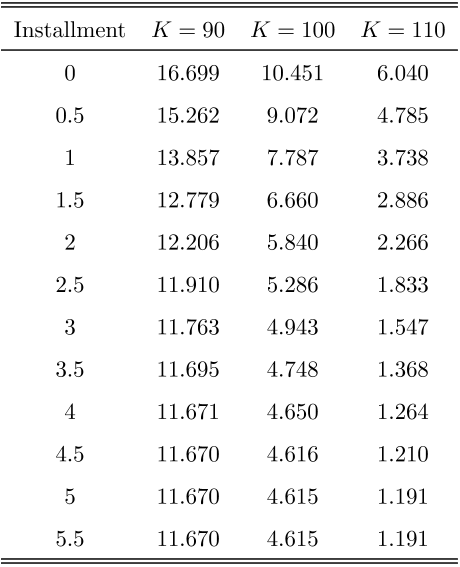
- Table 2 reports prices of installment calls for various levels of constant installments.
- Thus, for any installment greater than 5.076, the holding region vanishes, and the installment call is worth the European call expiring at the next decision date.
- Table 2 reports installment call upfront payments for various levels of installment and strikes.
- It is worth mentioning that the IO “greeks” may be readily obtained from the approximate value function, a piecewise linear function which is known at all dates for all possible values of the underlying asset.
6 Application to ASX installment warrants
- One of the most actively traded installment options throughout the world are currently the installment warrants on Australian stocks.
- Some of the ASX installment warrants (called rolling installment warrants) have several installments and their expiry date may be up to 10 years.
- Table 3 reports installment warrant upfront payments for various degrees of dilution.
7 Conclusion
- The authors have developed a pricing methodology for installment options using dynamic programming.
- Numerical experiments indicate that prices converge monotonically and quickly reach good levels of accuracy.
- The authors approach is flexible enough to be extended to other pricing issues involving installment options.
- Levered equity may be seen as a compound call on asset value when debt bears discrete coupons (see Geske (1977)).
- At each coupon date, shareholders decide whether or not to call the debt.
Did you find this useful? Give us your feedback
Citations
9 citations
7 citations
7 citations
7 citations
Cites background or methods from "A dynamic programming approach to p..."
...Notre programme dynamique ne dépend pas directement de portefeuilles d’options d’achat mais, à la place, d’ingrédients clefs : des paramètres de transition du processus d’état....
[...]
...These tables are available in closed form under geometric Brownian motions (Ben-Ameur, Breton, and François 2006) and mean-reverting Gaussian and chi-squared processes (Ben-Ameur et al. 2007)....
[...]
...…1977 and 1978, Courtadon 1982, and Hull and White 1990); 4. finite-elements (Barone-Adesi, Bermudez, and Hatgioannides 2003, and de Frutos 2005 and 2006); 5. finite volumes(Zvan, Forsyth, and Vetzal 2001); 6. stochastic dynamic programming (Chen 1970 and Ben-Ameur, Breton, and François 2006); 7....
[...]
7 citations
References
28,434 citations
"A dynamic programming approach to p..." refers background or methods in this paper
...Second, we investigate the properties of IOs through theoretical and numerical analysis in the Black and Scholes (1973) setting....
[...]
...Second, we investigate the properties of IOs through theoretical and numerical analysis in the Black and Scholes (1973) setting. Literature on IOs is scarce. Davis et al. (2001, 2002) derive no-arbitrage bounds for the price of the IO and study static versus dynamic hedging strategies within a Black–Scholes framework with stochastic volatility. Their analysis however is restricted to European-style IOs, which allows for an analogy with compound options. Davis et al. (2003) value venture capital using an analogy with IO....
[...]
...Black and Scholes (1973) suggest to price warrants as an option on the issuer s equity (i.e. stocks plus warrants). For so doing, the valuation formula must be adjusted for dilution. Specifically, let M, N, and c respectively denote the number of outstanding warrants, the number of outstanding shares, and the conversion ratio. Extending the approach by Lauterbach and Schultz (1990), the installment warrant in this context is interpreted as––a fraction of––an IO issued by the firm....
[...]
...Black and Scholes (1973) suggest to price warrants as an option on the issuer s equity (i....
[...]
...Black and Scholes (1973) suggest to price warrants as an option on the issuer s equity (i.e. stocks plus warrants)....
[...]
6,334 citations
901 citations
"A dynamic programming approach to p..." refers background in this paper
...For instance, levered equity may be seen as a compound call on asset value when debt bears discrete coupons (see Geske, 1977)....
[...]
854 citations
"A dynamic programming approach to p..." refers background in this paper
...…attractive for corporations which massively hedge interest rate and currency risks with forwards, futures or swaps because standard option contracts imply a cost at entry that may be incompatible with a temporary cash shortage. closed-form solution (see e.g. Wilmott et al. (1993) for a survey)....
[...]