LETTERS
A c-ray burst at a redshift of z < 8.2
N. R. Tanvir
1
, D. B. Fox
2
, A. J. Levan
3
, E. Berger
4
, K. Wiersema
1
, J. P. U. Fynbo
5
, A. Cucchiara
2
, T. Kru
¨
hler
6,7
,
N. Gehrels
8
, J. S. Bloom
9
, J. Greiner
6
, P. A. Evans
1
, E. Rol
10
, F. Olivares
6
, J. Hjorth
5
, P. Jakobsson
11
, J. Farihi
1
,
R. Willingale
1
, R. L. C. Starling
1
, S. B. Cenko
9
, D. Perley
9
, J. R. Maund
5
, J. Duke
1
, R. A. M. J. Wijers
10
, A. J. Adamson
12
,
A. Allan
13
, M. N. Bremer
14
, D. N. Burrows
2
, A. J. Castro-Tirado
15
, B. Cavanagh
12
, A. de Ugarte Postigo
16
,
M. A. Dopita
17
, T. A. Fatkhullin
18
, A. S. Fruchter
19
, R. J. Foley
4
, J. Gorosabel
15
, J. Kennea
2
, T. Kerr
12
, S. Klose
20
,
H. A. Krimm
21,22
, V. N. Komarova
18
, S. R. Kulkarni
23
, A. S. Moskvitin
18
, C. G. Mundell
24
, T. Naylor
13
, K. Page
1
,
B. E. Penprase
25
, M. Perri
26
, P. Podsiadlowski
27
, K. Roth
28
, R. E. Rutledge
29
, T. Sakamoto
21
, P. Schady
30
, B. P. Schmidt
17
,
A. M. Soderberg
4
, J. Sollerman
5,31
, A. W. Stephens
28
, G. Stratta
26
, T. N. Ukwatta
8,32
, D. Watson
5
, E. Westra
4
,
T. Wold
12
& C. Wolf
27
Long-duration c-ray bursts (GRBs) are thought to result from the
explosions of certain massive stars
1
, and some are bright enough
that they should be observable out to redshifts of z . 20 using
current technology
2–4
. Hitherto, the highest redshift measured
for any object was z 5 6.96, for a Lyman-a emitting galaxy
5
.
Here we report that GRB 090423 lies at a redshift of z < 8.2, imply-
ing that massive stars were being produced and dying as GRBs
630 Myr after the Big Bang. The burst also pinpoints the location
of its host galaxy.
GRB 090423 was detected by the Burst Alert Telescope (BAT) on
NASA’s Swift satellite
6
at 07:55:19 UT on 23 April 2009. Observations
with Swift’s X-ray Telescope (XRT), which began 73 s after the trig-
ger, revealed a variable X-ray counterpart and localized its position to
a precision of 2.3 arcsec (at the 90% confidence level). Ground-based
optical observations in the r, i and z filters starting within a few min-
utes of the burst revealed no counterpart at these wavelengths
(Supplementary Information).
The United Kingdom Infrared Telescope (UKIRT), Hawaii, began
imaging about 20 min after the burst, in response to an automated
request, and provided the first infrared (2.15-m m) detection of the
GRB afterglow. In parallel, observations in other near-infrared (NIR)
filters using the Gemini North 8-m telescope, Hawaii, showed that
the counterpart was only visible at wavelengths greater than about
1.2 mm (Fig. 1). In this range, the afterglow was relatively bright and
exhibited a shallow spectral slope, F
n
/ n
20.26
, in contrast to the deep
limit on any flux at 1.02 mm. Later observations from Chile using the
MPI/ESO 2.2-m telescope, Gemini South and the Very Large
Telescope (VLT) confirmed this finding. Such a sharp spectral break
cannot be produced by dust absorption at any redshift, and is a
textbook case of a short-wavelength ‘drop-out’ source. The full
grizYJHK spectral energy distribution (SED) obtained ,17 h after
burst gives a photometric redshift of z 5 8:06
z0:21
{0:28
, assuming a simple
intergalactic medium (IGM) absorption model. Complete details of
our imaging campaign are given in Supplementary Table 1.
Our first NIR spectroscopy was performed with the European
Southern Observatory (ESO) 8.2-m VLT, starting about 17.5 h after
the burst. These observations revealed a flat continuum that abruptly
disappeared at wavelengths less than about 1.13 mm, confirming the
origin of the break as being due to Lyman-a absorption by neutral
1
Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Leicester, University Road, Leicester LE1 7RH, UK.
2
Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics, Pennsylvania State University,
University Park, Pennsylvania 16802, USA.
3
Department of Physics, University of Warwick, Coventry CV4 7AL, UK.
4
Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, 60 Garden Street,
Cambridge, Massachusetts 02138, USA.
5
Dark Cosmology Centre, Niels Bohr Institute, University of Copenhagen, Juliane Maries Vej 30, 2100 Copenhagen, Denmark.
6
Max-Planck-
Institut fu¨r Extraterrestrische Physik, Giessenbachstraße 1, 85740 Garching, Germany.
7
Universe Cluster, Technische Universita
¨
tMu¨nchen, Boltzmannstrasse 2, 85748 Garching,
Germany.
8
NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland 20771, USA.
9
Department of Astronomy, University of California, Berkeley, California 94720-3411, USA.
10
Astronomical Institute ‘‘Anton Pannekoek’’, University of Amsterdam, PO Box 94249, 1090 GE Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
11
Centre for Astrophysics and Cosmology, Science
Institute, University of Iceland, Dunhagi 5, 107 Reykjavı
´
k, Iceland.
12
Joint Astronomy Centre, 660 North A’ohoku Place, University Park, Hilo, Hawaii 96720, USA.
13
School of Physics,
University of Exeter, Stocker Road, Exeter EX4 4QL, UK.
14
H. H. Wills Physics Laboratory, University of Bristol, Tyndall Avenue, Bristol BS8 1TL, UK.
15
Instituto de Astrofı
´
sica de
Andalucı
´
a del Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Cientı
´
ficas, PO Box 03004, 18080 Granada, Spain.
16
European Southern Observatory, Casilla 19001, Santiago 19, Chile.
17
Research
School of Astronomy & Astrophysics, The Australian National University, Cotter Road, Weston Creek, Australian Capital Territory 2611, Australia.
18
Special Astrophysical
Observatory, Nizhnij Arkhyz, Karachai-Cirkassian Republic, 369167, Russia.
19
Space Telescope Science Institute, 3700 San Martin Drive, Baltimore, Maryland 21218, USA.
20
Thu¨ringer
Landessternwarte Tautenburg, Sternwarte 5, 07778 Tautenburg, Germany.
21
CRESST and NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland 20771, USA.
22
Universities Space
Research Association, 10211 Wincopin Circle, Suite 500, Columbia, Maryland 21044, USA.
23
Department of Astronomy, California Institute of Technology, MC 249-17, Pasadena,
California 91125, USA.
24
Astrophysics Research Institute, Liverpool John Moores University, Birkenhead CH41 1LD, UK.
25
Department of Physics and Astronomy, Pomona College,
Claremont, California 91711, USA.
26
ASI Science Data Center, Via Galileo Galilei, 00044 Frascati, Italy.
27
Department of Physics, Oxford University, Keble Road, Oxford OX1 3RH, UK.
28
Gemini Observatory, Hilo, Hawaii 96720, USA.
29
Physics Department, McGill University, 3600 Rue University, Montreal, Quebec H3A 2T8, Canada.
30
The UCL Mullard Space
Science Laboratory, Holmbury St Mary, Dorking, Surrey RH5 6NT, UK.
31
The Oskar Klein Centre, Department of Astronomy, Stockholm University, 106 91 Stockholm, Sweden.
32
The
George Washington University, Washington DC 20052, USA.
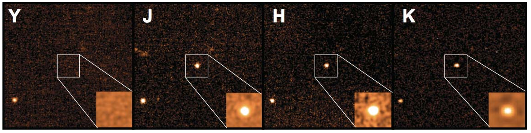
Figure 1
|
Multiband images of the afterglow of GRB 090423. The right-
most panel shows the discovery image made using the UKIRT Wide Field
Infrared Camera with the K filter (centred at 2.15 mm) at a mid-time of about
30 min after the burst. The other three images (Y, 1.02 mm; J, 1.26 mm;
H, 1.65 mm) were obtained approximately 1.5 h after the burst using Gemini
North’s Near Infrared Imager and Spectrometer (NIRI). The main panels are
40 arcsec to a side, oriented with north to the top and east to the left. Insets,
regions around the GRB, smoothed and at higher contrast. The absence of
any flux in Y implies a power-law spectral slope between Y and J steeper than
F
n
/ n
218
and, coupled with the blue colour at longer wavelengths
(J2H(AB) < 0.15 mag), immediately implies a redshift greater than about
7.8 for GRB 090423.
Vol 461
|
29 October 2009
|
doi:10.1038/nature08459
1254
Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved
©2009

hydrogen, with a redshift of z < 8.2. The spectrum and broadband
photometric observations, plotted over model data, are shown in
Fig. 2. To obtain a more quantitative estimate of the redshift, we fit
the spectra in redshift versus log[N
H
I
(cm
22
)] space, assuming a flat
prior likelihood value for log[N
H
I
(cm
22
)] of between 19 and 23,
which is broadly consistent with the distribution observed for
lower-redshift GRB hosts
7–9
. We take the neutral fraction of the
IGM to be 10%, although our conclusions depend only weakly on
this assumption. We find the redshift from ISAAC spectroscopy to be
z 5 8:19
z0:03
{0:06
. An additional spectrum, recorded ,40 h after the
burst using the VLT’s Spectrograph for INtegral Field Observations
in the Near Infrared confirms this analysis, yielding z 5 8:33
z0:06
{0:11
(Supplementary Information). Fitting simultaneously to both spec-
tra and the photometric data points gives our best estimate of the
redshift, z 5 8:23
z0:06
{0:07
. The low signal-to-noise ratio means we that
are unable to detect metal absorption features in either spectrum—
which would provide a more precise value of the redshift—and pre-
vents a meaningful attempt to measure the IGM H
I column density
in this instance. Our three independent redshift measures are con-
sistent with that reported from a low-resolution spectrum obtained
with the Telescopio Nazionale Galileo, La Palma
10
.
The X-ray and NIR light curves of GRB 090423 (Fig. 3) show a
broken power-law decay, with evidence of flares in both the X-ray
and the infrared bands. The spectral energy distribution is consistent
with the presence of the cooling break between the X-ray and optical
bands. Apart from the unusually shallow spectral slope of the con-
tinuum at wavelengths greater than 1.2 mm, its afterglow properties in
general appear to be consistent with the bulk GRB population (see
Supplementary Information for further discussion).
With the standard cosmological parameters (Hubble parameter,
H
0
5 71 km s
21
Mpc
21
; total matter density, V
M
5 0.27; dark-
energy density, V
L
5 0.73) a redshift of z 5 8.2 corresponds to a time
of only 630 Myr after the Big Bang, when the Universe was just 4.6%
of its current age. GRB 090423’s inferred isotropic equivalent energy,
E
iso
5 1 3 10
53
erg (8–1,000 keV)
11
, indicates that it was a bright, but
not extreme, GRB. Thus, we find no evidence of exceptional beha-
viour that might indicate an origin in a population III progenitor.
First-generation stars are thought more likely to collapse into par-
ticularly massive black holes, which in turn may produce unusually
long-lived GRBs
12
; this seems not to be the case for GRB 090423.
Indeed, we note that the c-ray duration of GRB 090423,
t
90
5 10.3 s, corresponds in the rest frame to only 1.1 s, and the peak
energy measured by BAT, 49 keV, is moderately hard in the rest
frame. Two other GRBs with z . 5 (GRB 060927 and GRB 080913)
had similarly short rest-frame durations, leading to some debate
13
as
to whether their progenitors were similar to those of the ‘short-hard’
class of GRBs, which are not thought to be directly related to core
collapse. However, in the case of GRB 090423, a more careful extra-
polation of the observed c-ray and X-ray light curves to lower red-
shifts shows that its duration would have appeared significantly
longer than suggested by naive time-dilation considerations
14
.In
any event, short GRBs probably have their origins in compact objects
that are themselves the end products of massive stars, so the above
conclusions will hold irrespective of the population from which
GRB 090423 derives.
It has long been recognized that GRBs have the potential to be power-
ful probes of the early Universe
15
. Their association with individual stars
means that they serve as a signpost of star formation, even if their host
0.1
12
Flux density at 16 h (μJy)
20
10
0
–10
–20
0.2
Rest-frame wavelength (μm)
Observed wavelength (μm)
SZ J
23
22
21
20
19
8 8.5
Redshift
H
K
J
z
Y
log[N
H I
(cm
–2
)]
Figure 2
|
The composite infrared spectrum of the GRB 090423 afterglow.
SZ-band (0.98–1.1 mm) and J-band (1.1–1.4 mm) one- and two-dimensional
spectra obtained with the VLT using the Infrared Spectrometer And Array
Camera (ISAAC). Also plotted are the sky-subtracted photometric data
points obtained using Gemini North’s NIRI (red) and the VLT’s High Acuity
Wide field K-band Imager and Gemini South’s Gemini Multi-Object
Spectrograph (blue) (scaled to 16 h after the burst and expressed in
microjanskys; 1 Jy 5 10
226
Wm
22
Hz
21
). The vertical error bars show the
2s (95%) confidence level, and the horizontal lines indicate the widths of the
filters. The shorter-wavelength measurements are non-detections, and
emphasize the tight constraints on any transmitted flux below the break. The
break itself, at an observed wavelength of about 1.13 mm, is seen to occur
close to the short-wavelength limit of the J-band spectrum, below which,
although noisy, the spectrum shows no evidence of any detected continuum.
Details of the data-reduction steps and adaptive binning used to construct
these spectra are given in Supplementary Information. A model spectrum
showing the H
I damping wing for a host galaxy with a hydrogen column
density of N
H
I
5 10
21
cm
22
at a redshift of z 5 8.23 is also plotted (solid
black line), and provides a good fit to the data. Inset, allowing for a wider
range in possible host N
H
I
values gives the 1s (68%) and 2s confidence
contours shown. The fact that no deviation is seen from a power-law
spectrum at wavelengths greater than 1.2 mm, together with its shallow
spectral slope, suggests that there is little or no dust along the line of sight
through the GRB host galaxy (unless it is ‘grey’), consistent with the galaxy
being relatively unevolved, and having a low abundance of metals.
NATURE
|
Vol 461
|
29 October 2009 LETTERS
1255
Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved
©2009
galaxies are too faint to detect directly. Equally important, precise deter-
mination of the hydrogen Lyman-a absorption profile can provide a
measure of the neutral fraction of the IGM at the location of the
burst
16–20
. With multiple GRBs at redshifts of z . 7, and the associated
information about the IGM, we could therefore trace the process of
reionization from its early stages
21
.
The high redshift of GRB 090423 has several crucial implications.
Predictions based on extrapolating the global star-formation-rate
density suggest that the observed rate of GRBs at z < 8 should be about
40% of that at z < 6 (ref. 12). Given the extra difficulty of identifying
afterglows at higher redshifts, our finding is broadly consistent with
these predictions. This is extremely encouraging for the prospects of
future initiatives aimed at finding high-redshift GRBs and using them
to locate and study primordial galaxies and measure the history of star
formation at early times
22–24
. Furthermore, it is close to the redshift
range in which the bulk of the cosmic reionization is thought to have
taken place
25–27
. Very high-redshift GRBs for which infrared spectro-
scopy was possible earlier, or which had brighter afterglows, would
provide a direct probe of the progress of reionization. Finding such
events is not an unreasonable hope: the most extreme GRBs have had
afterglows that were intrinsically significantly brighter than that of
GRB 090423 at the same rest-frame time
3,4
, and our first spectra were
recorded more than 15 h after the burst. Spectroscopy with a high
signal-to-noise ratio would also provide a measure of the metallicity
of the host galaxy, which potentially offers important clues to the
nature of any earlier generations of stars. Because the massive stars
that yield GRBs are also likely to belong to the same population that is
responsible for reionization, this suggests that GRBs will ultimately be
used to constrain both sides—supply and demand—of the cosmic
ionization budget in the early Universe.
Received 3 June; accepted 19 August 2009.
1. Woosley, S. E. & Bloom, J. S. The supernova gamma-ray burst connection. Annu.
Rev. Astron. Astrophys. 44, 507
–
556 (2006).
2. Lamb, D. Q. & Reichart, D. E. Gamma-ray bursts as a probe of the very high
redshift universe. Astrophys. J. 536, 1
–
18 (2000).
3. Racusin, J. L. et al. Broadband observations of the naked-eye c -ray burst
GRB 080319B. Nature 455, 183
–
188 (2008).
4. Bloom, J. S. et al. Observations of the naked-eye GRB080319B: implications of
nature’s brightest explosion. Astrophys. J. 691, 723
–
737 (2009).
5. Iye, M. et al. A galaxy at a redshift z 5 6.96. Nature 443, 186
–
188 (2006).
6. Gehrels, N. et al. The Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Mission. Astrophys. J. 611,
1005
–
1020 (2004).
7. Jakobsson, P. et al. H I column densities of z . 2 Swift gamma-ray bursts. Astron.
Astrophys. 460, L13
–
L17 (2006).
8. Chen, H.-W., Prochaska, J. X. & Gnedin, N. Y. A new constraint on the escape
fraction in distant galaxies using c-ray burst afterglow spectroscopy. Astrophys. J.
667, L125
–
L128 (2007).
9. Fynbo, J. P. U. et al. Low-resolution spectroscopy of gamma-ray burst optical
afterglows: biases in the Swift sample and characterization of the absorbers.
Preprint at Æhttp://arxiv.org/abs/0907.3449æ (2009).
10. Salvaterra, R. et al. GRB 090423 at a redshift of z < 8.1. Nature doi:10.1038/
nature08459 (this issue).
0.1
10
5
10
4
1,000
100
10
1
0.1
0.01
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
1 10 100 1,000
J band
H band
K band
10
4
10
5
10
6
10
7
1 10 100 1,000
Rest-frame time since GRB 090423 (s)
Observer time since GRB 090423 (s)
X-ray
Luminosity (erg s
–1
)
Flux (10
–12
erg s
–1
cm
–2
)
AB magnitude
M
AB
Infrared
10
4
10
5
10
6
10
52
10
51
10
50
10
49
10
48
10
47
10
46
–28
–27
–26
–25
–24
–23
–22
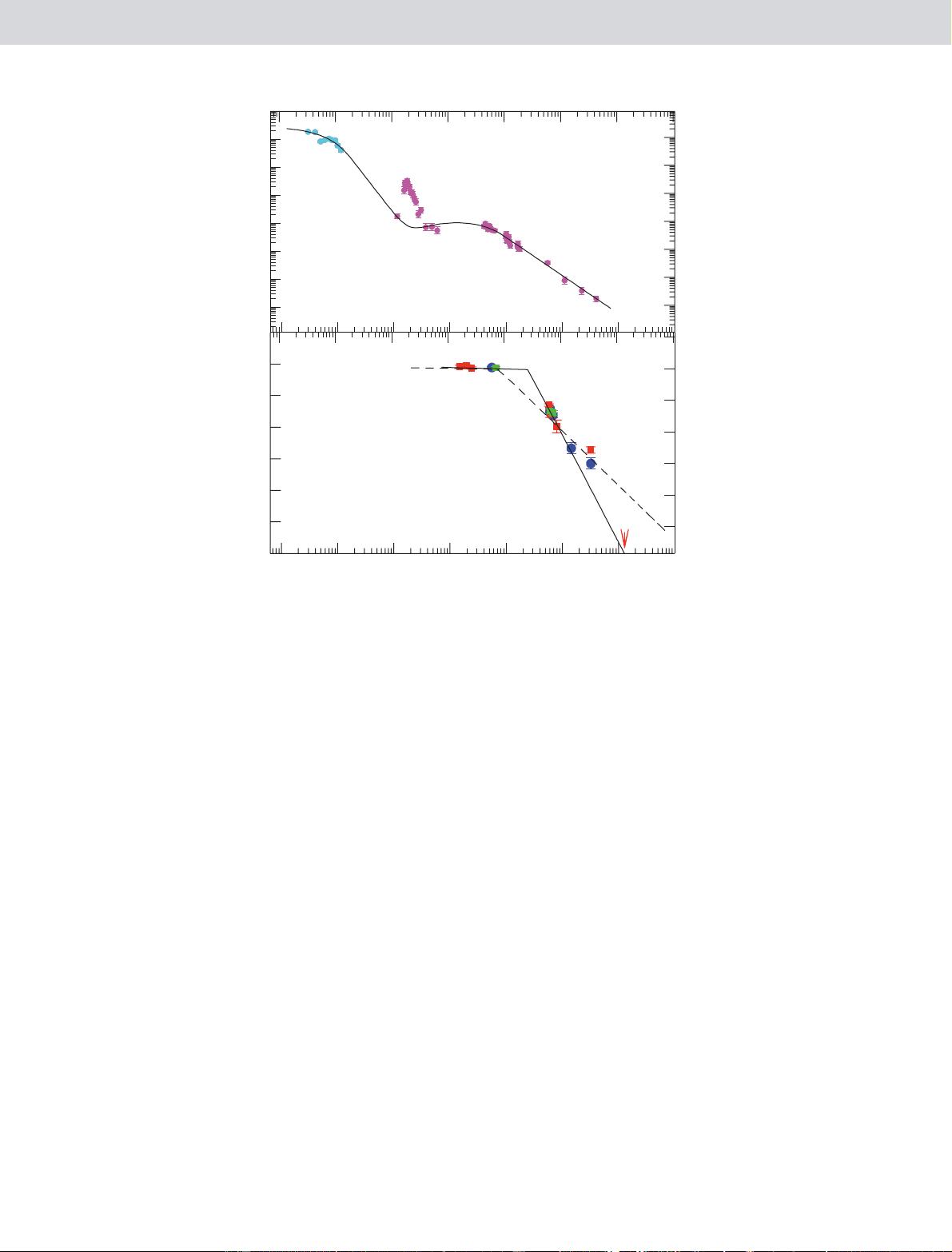
Figure 3
|
The X-ray and infrared light curves of GRB 090423. The axes
show both observed (left-hand and bottom axes) and rest-frame (right-hand
and top axes) quantities. The X-ray light curve was obtained using Swift’s
BAT (cyan) and XRT (magenta), where the BAT observations have been
extrapolated into the X-ray band. The fitted function represents a
phenomenological model
28
of the prompt and afterglow components. The
infrared light curve was obtained using UKIRT, Gemini North, the MPI/ESO
2.2-m telescope and the VLT. For consistency, although individual bands are
plotted, they have been transformed into absolute magnitudes in the J band
by means of the best-fitting SED (F
n
/ n
20.26
). We show two illustrative fits
to the infrared light curve. The solid line shows a plateau, breaking at
24,000 s to a steeper slope proportional to ,t
21.4
. This underestimates the
late time points, which must then be interpreted as a flare. The dashed line
shows an alternative model, in which mid-time points at ,60,000 s are
instead interpreted as a flare; this is more consistent with the later time
points and the X-ray break time at the end of the plateau. However, in this
case the post-break slope, proportional to ,t
20.7
, is much slower than the
X-ray decay at comparable times, and it further requires a additional break in
the light curve to accommodate the late-time upper limit. Error bars are 1s
(68% confidence level) and the absolute magnitude scale corresponds to
absolute AB magnitudes at 0.136 mm. See Supplementary Information for
further details.
LETTERS NATURE
|
Vol 461
|
29 October 2009
1256
Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved
©2009

11. von Kienlin, A. et al. GRB 090423: Fermi GBM observation (correction of isotropic
equivalent energy). GCN Circ. 9251 (2009).
12. Bromm, V. & Loeb, A. High-redshift gamma-ray bursts from population III
progenitors. Astrophys. J. 642, 382
–
388 (2006).
13. Zhang, B. et al. Physical classification scheme of cosmological gamma-ray bursts
and their observational characteristics: on the nature of z56.7 GRB 080913 and
some short/hard GRBs. Astrophys J. (in the press); preprint at Æhttp://arxiv.org/
abs/0902.2419v1æ (2009).
14. Zhang, B.-B. & Zhang, B. GRB 090423: pseudo burst at z51 and its relation to GRB
080913. GCN Circ. 9279 (2009).
15. Wijers, R. A. M. J. et al. Gamma-ray bursts from stellar remnants - probing the
universe at high redshift. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 294, L13
–
L17 (1998).
16. Miralda-Escude, J. Reionization of the intergalactic medium and the damping
wing of the Gunn-Peterson Trough. Astrophys. J. 501, 15
–
22 (1998).
17. Barkana, R. & Loeb, A. Gamma-ray bursts versus quasars: Lya signatures of
reionization versus cosmological infall. Astrophys. J. 601, 64
–
77 (2004).
18. Totani, T. et al. Implications for cosmic reionization from the optical afterglow
spectrum of the gamma-ray burst 050904 at z 5 6.3. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn 58,
485
–
498 (2009).
19. Greiner, J. et al. GRB 080913 at redshift 6.7. Astrophys. J. 693, 1610
–
1620 (2009).
20. Faucher-Giguere, C.-A., Lidz, A., Hernquist, L. & Zaldarriaga, M. Evolution of the
intergalactic opacity: implications for the ionizing background, cosmic star
formation, and quasar activity. Astrophys. J. 688, 85
–
107 (2008).
21. McQuinn, M. et al. Probing the neutral fraction of the IGM with GRBs during the
epoch of reionization. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 388, 1101
–
1110 (2008).
22. Grindlay, J. in Gamma-Ray Burst: Sixth Huntsville Symposium (eds Meegan, C.,
Kouveliotou, C. & Gehrels, N.) 18
–
24 (AIP Conf. Ser. 1113, American Institute of
Physics, 2009).
23. Tanvir, N. R. & Jakobsson, P. Observations of GRBs at high redshift. Phil. Trans. R.
Soc. A 365, 1377
–
1384 (2007).
24. Berger, E. et al. Hubble Space Telescope and Spitzer observations of the afterglow
and host galaxy of GRB 050904 at z 5 6.295. Astrophys. J. 665, 102
–
106 (2007).
25. Komatsu, E. et al. Five-year Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe observations:
cosmological interpretation. Astrophys. J. 180 (suppl.), 330
–
376 (2009).
26. Malhotra, S. & Rhoads, J. E. Luminosity functions of Lya emitters at redshifts
z56.5 and z55.7: evidence against reionization at z#6.5. Astrophys. J. 617, L5
–
L8
(2004).
27. Becker, G. D., Rauch, M. & Sargent, W. L. W. The evolution of optical depth in the
Lya forest: evidence against reionization at z,6. Astrophys. J. 662, 72
–
93 (2007).
28. Willingale, R. et al. Testing the standard fireball model of gamma-ray bursts using
late X-ray afterglows measured by Swift. Astrophys. J. 662, 1093
–
1110 (2007).
Supplementary Information is linked to the online version of the paper at
www.nature.com/nature.
Acknowledgements We thank Ph. Yock, B. Allen, P. Kubanek, M. Jelinek and
S. Guziy for their assistance with the BOOTES-3 YA telescope observations
(Supplementary Information). This work was partly based on observations
obtained at the Gemini Observatory, which is operated by the Association of
Universities for Research in Astronomy, Inc., under a cooperative agreement with
the US National Science Foundation on behalf of the Gemini partnership: the
National Science Foundation (United States), the Science and Technology Facilities
Council (United Kingdom), the National Research Council (Canada), CONICYT
(Chile), the Australian Research Council (Australia), the Ministe
´
rio da Cie
ˆ
ncia e
Tecnologia (Brazil) and SECYT (Argentina). This work was also partly based on
observations made using ESO telescopes at the La Silla or Paranal observatories by
G. Carraro, L. Schmidtobreick, G. Marconi, J. Smoker, V. Ivanov, E. Mason and
M. Huertas-Company. The UKIRT is operated by the Joint Astronomy Centre on
behalf of the UK Science and Technology Facilities Council. R.J.F. acknowledges a
Clay Fellowship.
Author Contributions Triggering observations: N.R.T., D.B.F., A.J.L., E.B., J.S.B.,
D.P., J. Greiner, A.J.C.-T., A.d.U.P.; analysis of ground-based data: N.R.T., D.B.F.,
A.J.L., E.B., K.W., J.P.U.F., A.C., J.S.B., J.F., J.D., J. Gorosabel, B.C., D.P., J.R.M.,
T. Kru¨hler, A.J.C.-T., A.d.U.P., C.G.M.; Swift analysis: P.A.E., R.L.C.S., K.P., R.W.,
A.J.L., N.R.T., N.G., D.W., P.S., T.S.; observations at various observatories and their
automation to accept GRB overrides: A.J.A., A.A., T. Kerr, T.N., A.W.S., K.R., T.W.
All authors made contributions through their involvement in the programmes from
which the data derive, and contributed to the interpretation, content and
discussion presented here. Writing was led by N.R.T., A.J.L., D.B.F. and E.B.
Author Information Reprints and permissions information is available at
www.nature.com/reprints. Correspondence and requests for materials should be
addressed to N.R.T. (nrt3@star.le.ac.uk).
NATURE
|
Vol 461
|
29 October 2009 LETTERS
1257
Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved
©2009