HAL Id: hal-01420238
https://hal.inria.fr/hal-01420238
Submitted on 20 Dec 2016
HAL is a multi-disciplinary open access
archive for the deposit and dissemination of sci-
entic research documents, whether they are pub-
lished or not. The documents may come from
teaching and research institutions in France or
abroad, or from public or private research centers.
L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est
destinée au dépôt et à la diusion de documents
scientiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non,
émanant des établissements d’enseignement et de
recherche français ou étrangers, des laboratoires
publics ou privés.
Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution| 4.0 International License
A Method to Determine the Maximum Side Perspective
of Satellite with the Constraints of Mapping Accuracy
Jihong Yang, Haiwei Li, Yin Zhan, Liangshu Shi, Jinqiang Wang, Zhengchao
Chen
To cite this version:
Jihong Yang, Haiwei Li, Yin Zhan, Liangshu Shi, Jinqiang Wang, et al.. A Method to Determine the
Maximum Side Perspective of Satellite with the Constraints of Mapping Accuracy. 8th International
Conference on Computer and Computing Technologies in Agriculture (CCTA), Sep 2014, Beijing,
China. pp.13-22, �10.1007/978-3-319-19620-6_2�. �hal-01420238�

A Method to Determine the Maximum Side
Perspective of Satellite with the Constraints of
Mapping accuracy
Jihong Yang
1
, Haiwei Li
2,4
, Yin Zhan&Liangshu Shi
1
, Jinqiang Wang
3
,
Zhengchao Chen
4*
1 Chinese Land Surveying and Planning Institute, Beijing 100035, China;
2 School of Geosciences and Info-Physics, Central South University, Changsha
410083, China; 3 Surveying and Mapping Bureau of Yunnan Province, Kunming
650034, Yunnan, China; 4 Institute of Remote Sensing and Digital Earth, Chinese
Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100094, China
Corresponding author: Z.C.CHEN e-mail: zcchen@ceode.ac.cn
ABSTRACT: In order to shorten the revisit period, and improve the efficiency
of imaging, currently, all the in orbit high resolution remote sensing satellites
adopt side-view imaging technology. When satellites imaging with a side
perspective, it would inevitably cause the degradation of image quality, like
spatial resolution reduction, image deformation incensement, and the reduction
of positioning accuracy. In addition, with the increase of the side perspective,
the error of DEM data will be amplified in the process of ortho-rectification,
which, thus, will bring bigger error for image mapping accuracy. To address
this problem, embarked from the impact of side view and DEM precision on
image point error, this paper used Quick bird image data of the same area but
different side perspectives, and simulate the impacts of different DEM elevation
error on different side view image. At last we put forward a method to
determine the maximum side perspective with map precision constraints, and
set up a conversion relationship among satellite side view, DEM error and
image point error. Finally, the paper combines the errors of 1:50000 DEM,
ASTERGDEM and the requirement of ortho-image drawing, discusses and
gives the values of maximum side perspective in the mountains and plains.
Keywords: DEM accuracy, satellite side perspective, ortho-rectification,
geolocation accuracy
1 Introduction
Along with the continuous improvement of remote sensing satellites’ spatial
resolution, it also brought adverse effects of the image width and image acquisition
efficiency reduction. In order to shorten the return cycle and to improve the efficiency
of imaging, currently, on-orbit high resolution remote sensing satellites use the side-
view imaging technology to improve the flexibility towards observation objects and
image acquisition efficiency. As is well-known, when the satellites side-view imaging,

the observation path is increased, the relative geometric relationship between satellite
and ground objects is changed, which caused the degeneration of image quality
[1]
(such as the spatial resolution reduced, image deformation increase, etc.) According
to the principle of projection, from a point in space (viewpoint) observing the surface,
each point on the surface along with topographic relief will generate geometric
distortion on the image. The specific performance on the optical remote sensing
imageries is as follows: the ground point, which is away from the viewpoint and with
higher elevation, will fall to the opposite side of the viewpoint
[2]
. Ortho-rectification
is to make use of terrain elevation model (DEM) to perform terrain distortion
correction for each pixel in image, and make the image meet the orthographic
projection, thus eliminating this distortion.
According to the error analysis of satellite imagery ortho-rectification model, the
main factors affect the accuracy of ortho-rectification are as follows: ortho-
rectification model error, satellite orbital attitude error, control point accuracy, DEM
error, etc
[3]
. In which the ortho-rectification model commonly used strict physical
model and rational polynomial model (RPC). Strict physical model are considered to
be theoretically rigorous, thus, It can be considered without error;The RPC model is a
simulation of strict physical model, the model conversion error is generally less than
1m (Liu Shijie, 2008); The error of satellite orbit and attitude is decided by the control
accuracy of the satellite itself and the in-orbit state, which cannot be changed by the
average user. The precision of control points can be controlled through field
measurement, currently using GPS can get higher precision. DEM data are input
parameters of ortho-rectification, which generally directly adopt national fundamental
geographic information data, the precision of is slightly different in the mountains and
plains. In addition, when the satellites side-view imaging, their orbit and attitude
control precision and measurement accuracy will decrease because of satellites or
remote sensors’ side swing
[4]
; Furthermore, according to the theory of projection, the
increase of side perspective will definitely magnify the effects caused by DEM error.
Therefore, the satellite side perspective is also one of the main error sources of
satellite images ortho-rectification.
It can be seen from the above error analysis of ortho-rectification, in general case, the
factors to be considered most by users are side perspective and DEM errors. Many
scholars have carried out some research work about the effects on image quality
degradation and ortho-rectification precision caused by side perspective, and the
effects on ortho-rectification precision caused by DEM errors. Such as Han Wenli,
Yuan Xiuxiao, and Wang Xuejun, etc. Han Wenli(2010) quantitatively analyzed
the impact on ortho-rectification precision caused by side perspective in theory, and
proved the validity of its conclusions through experiments. The conclusions indicate
that with increment of the side perspective, the image ortho-rectification accuracy will
gradually decline, and the decrease amplitude is quite obvious
[3]
. Taking into account
changes of the side perspective, Yuan Xiuxiao et al., 2009, established the geometry
model of high-resolution satellite remote sensing image processing, which improved
the image positioning accuracy on the ground targets. It concluded that the change of

the side perspective is a factor that cannot be neglected in the high-resolution satellite
remote sensing image geometry processing model
[5]
. Wang Xuejun et al., 2008,
selecting different DEM scales, conducted ortho-rectification to the data with
different side perspectives acquired by SPOT5. It certified that when SPOT5 imaging,
the side perspective is the key factor leading layer-over phenomenon of SPOT5
orthophoto products, with the premise of ensuring the accuracy of ground control
points. It also certified that in the calibration process the improvement of DEM
accuracy cannot effectively eliminate layer-over phenomenon of the mountains with
complex terrain and large elevation drop. About the impact on image correcting
accuracy caused by DEM data, Shi Yuhua (2007) , using two different DEM data,
calibrated the same scene image. The results show that the ortho-rectification
accuracy is higher with small basic grid and high-precision DEM data
[6]
.
However, these studies only consider the impact of unilateral side perspective or
DEM error on ortho-rectification precision, and failed to combine both. Actually it is
a coupling effect between side perspective and DEM error: DEM error will be
amplified with the increase of side perspective; Errors caused by side perspective will
change along with the change DEM data. As the input conditions of ortho-
rectification the accuracy of DEM data are often unable to change. Therefore, in
practice, it is more significant to study how to determine the maximum satellite
observation side perspective in the premise that there is some error in DEM data, as
well as guarantee certain accuracy of ortho-rectification and mapping. Aiming at this
problem, this paper adopted Quickbird image data with different side perspectives in
Beijing, proposed a method to determine the maximum satellite imaging side
perspective with certain constraints of mapping accuracy by simulating different
influence law on the accuracy of image ortho-rectification caused by DEM elevation
error, and established a quantitative conversion relationship among satellite side
perspective, DEM error, and the error of ortho-rectification image points.
2 Experiments and Methods
2.1 Experimental DATA
The experimental area is the northern part of Beijing, including plain and mountain.
Experimental data are multispectral image collected by using high-resolution
Quickbird satellite in 2002 to 2012. With 2.44 m resolution, side perspective spanning
from 5.6°to 43.7°ten different angles in total. Image side perspective spanned
broadly, evenly distributed, specifically details can be seen in the table below.
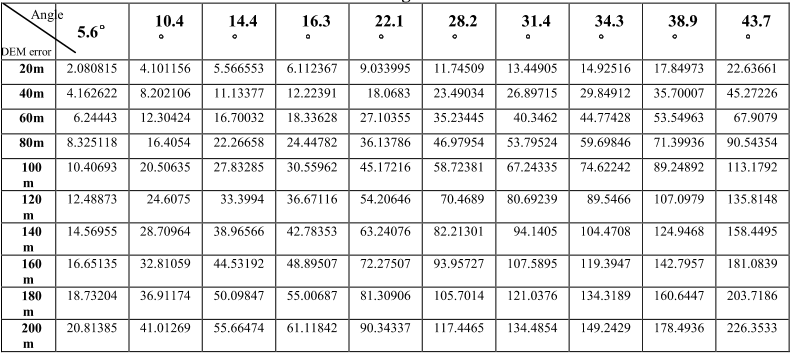
Table 1 Test data tables side perspective Statistics
Satellite Name
Side perspective( °)

QuickBird
5.6
10.4
14.4
16.3
22.1
28.2
31.8
34.3
38.9
43.7
2.2 Experimental Methods
According to the principle of photogrammetry, the comparation between image point
error caused by the side perspective and imaginary horizontal photograph as Figure
1(a) shows.
P is the tilted photograph and P0 is the imaginary horizontal photograph with the
same observation conditions. They intersect at isocon line hc. Imagine that ground
point M is
(
m
)
on tilted photograph P and
(
m
0
)
on horizontal photograph P
0
,
respectively. After two photograph overlapping along isocon line,the position of (m)
in the horizontal photograph is m, obviously mm
0
is the tilt error. With the increase of
side perspective, the tilt error will become bigger. Image point error caused by the
relief is shown as follows(right). To facilitate discussion, assume that photograph is
horizontal, and the height difference between ground point A and the datum is h. The
image point of ground piont A is point a on the photograph; the projection of A on
the datum is A
0
, whose image point is a
0
. aa
0
is the displacement of image points
caused by the relief. As can be seen, the displacement of image points will increase
with the increasement of height difference h
[7-9]
.
(a) (b)
Figure 1 the error of displacement of image points caused by side perspective and
relief((a): side perspective; (b): relief)
During the process of ortho-rectification, image points error will be affected by
side perspective and relief at the same time. In the existing research results, different
influence factors are often analyzed independently, which ignores the mutual
influence and internal relations of different factors and is not real and comprehensive
enough to reflect the objective situation of data. Because the strict physical model to
calibrate the satellite image contains quantities of trigonometric functions and
complex variables. If directly use strict physical model to deduce the error model of
ortho-rectification, it will be very complicated. It is also why many scholars assume
that the variables are independent in the derivation of the law of ortho-rectification
error
[10][11]
. In addition, RPC model is an approximate mathematical simulation of the
physical model. RPC model without satellite orbit and attitude parameters, there is no
way to establish the error model of ortho-rectification, DEM and orbit attitude
parameters. Based on these considerations, this paper used the real images with