Q1. What are the contributions mentioned in the paper "A multi-actor multi-criteria analysis of the performance of global cities" ?
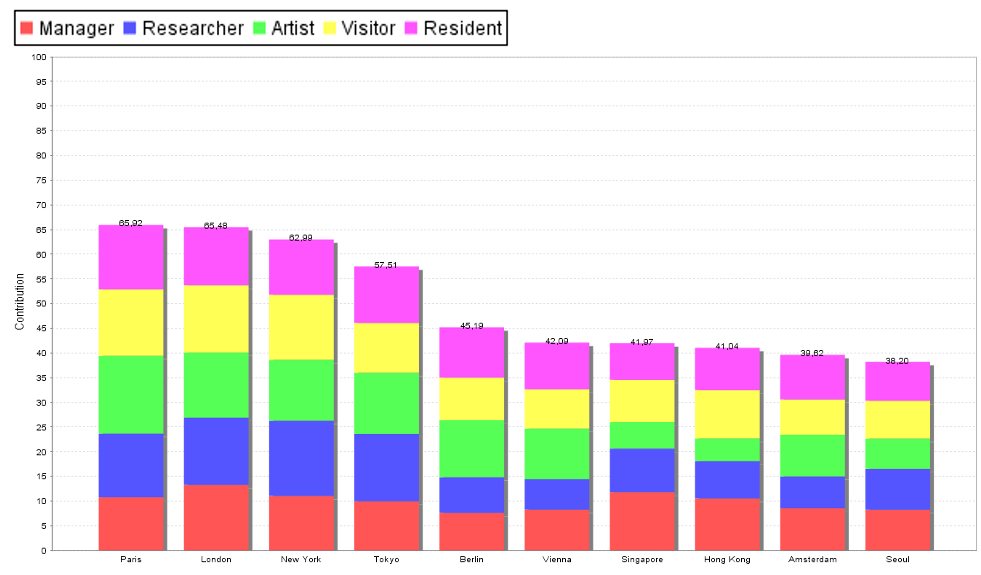
The present paper aims to trace to what extent and why some cities outperform others. Starting from an extensive database on many important characteristics of global cities, this paper offers a multi-criteria methodology for identifying the relative position of various important cities on the basis of distinct assessment criteria. From a technical assessment perspective, the applied part of the paper employs the MAMCA and PROMETHEE multi-criteria methodology, which have proven their analytical power in various multi-criteria evaluation problems over the past years. The paper concludes with some policy perspectives and lessons.