A Sentiment Information Collector-Extractor Architecture Based Neural Network for Sentiment Analysis
Reads0
Chats0
TLDR
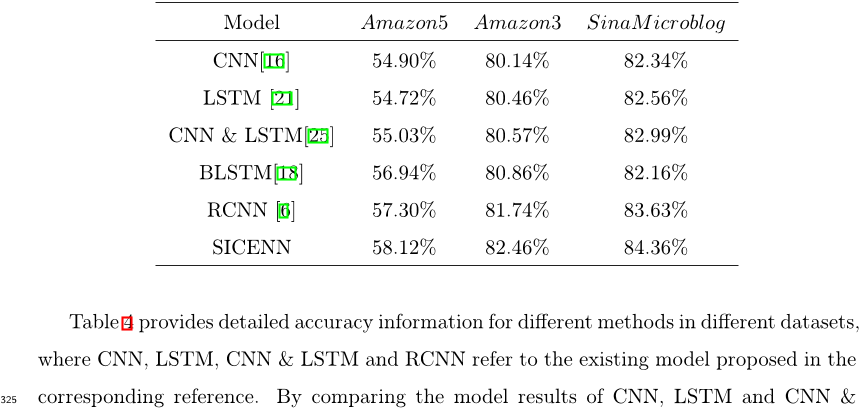
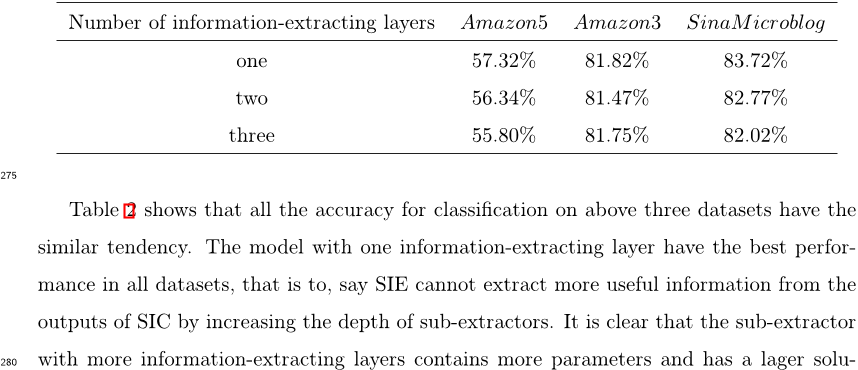
A new ensemble strategy is applied to combine the results of different sub-extractors, making the SIE more universal and outperform any single sub- Extractor and outperforms the state-of-the-art methods on three datasets of different language.About:
This article is published in Information Sciences.The article was published on 2018-10-01 and is currently open access. It has received 21 citations till now. The article focuses on the topics: Sentiment analysis & Deep learning.read more
Figures
Citations
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Carrying out consensual Group Decision Making processes under social networks using sentiment analysis over comparative expressions
Juan Antonio Morente-Molinera,Gang Kou,K. Samuylov,Raquel Ureña,Enrique Herrera-Viedma,Enrique Herrera-Viedma +5 more
TL;DR: This paper presents a novel model for experts to carry out Group Decision Making processes using free text and alternatives pairwise comparisons and introduces two ways of applying consensus measures over the Group decision Making process.
Journal ArticleDOI
A comparative study of machine translation for multilingual sentence-level sentiment analysis
TL;DR: This work evaluates existing efforts proposed to do language specific sentiment analysis with a simple yet effective baseline approach and suggests that simply translating the input text in a specific language to English and then using one of the existing best methods developed for English can be better than the existing language-specific approach evaluated.
Journal ArticleDOI
Convolution-deconvolution word embedding: an end-to-end multi-prototype fusion embedding method for natural language processing
TL;DR: In this paper, an end-to-end multi-prototype fusion embedding that fuses context-specific and task-specific information was proposed to solve the problem of polysemous-unaware word embedding.
References
More filters
Proceedings Article
Explicit and Implicit Syntactic Features for Text Classification
Matt Post,Shane Bergsma +1 more
TL;DR: This work compares tree kernels to dierent explicit sets of tree features on five diverse tasks, and finds that explicit features often perform as well as tree kernels on accuracy and always in orders of magnitude less time, and with smaller models.
Proceedings ArticleDOI
Deep Sentiment Representation Based on CNN and LSTM
TL;DR: The model uses the pre-trained word vectors as input and employs CNN to gain significant local features of the text, then features are fed to two-layer LSTMs, which can extract context-dependent features and generate sentence representation for sentiment classification.
Proceedings ArticleDOI
Intrusion detection of multiple attack classes using a deep neural net ensemble
TL;DR: The IDS is designed with a neural network ensemble method to classify the different attacks and the NSL-KDD data set is used to measure the detection rate and false alarm rate of the implemented neuralnetwork ensemble method.
Proceedings ArticleDOI
YNU-HPCC at SemEval 2017 Task 4: Using A Multi-Channel CNN-LSTM Model for Sentiment Classification.
TL;DR: By combining both CNN and LSTM, this model can consider both local information within tweets and long-distance dependency across tweets in the classification process, and results show that the system outperforms the baseline algo-rithm.
Proceedings Article
Learning paraphrase identification with structural alignment
TL;DR: A new alignment-based approach to learn semantic similarity using a hybrid representation, attributed relational graphs, to encode lexical, syntactic and semantic information and introduced structural constraints inspired by a cognitive theory of similarity and analogy.