A shape-constraint adversarial framework with instance-normalized spatio-temporal features for inter-fetal membrane segmentation
TL;DR: In this paper, a new deep learning framework for inter-fetal membrane segmentation on in-vivo fetoscopic videos is presented, which enhances existing architectures by encoding a novel (instance-normalized) dense block, invariant to illumination changes, that extracts spatio-temporal features to enforce pixel connectivity in time, and relying on an adversarial training, which constrains macro appearance.
About: This article is published in Medical Image Analysis.The article was published on 2021-02-19 and is currently open access. It has received 9 citations till now.
Summary (3 min read)
Jump to: [1. Introduction] – [1.1. Contribution of the work] – [2. Methods] – [2.1. Segmentor] – [2.2. Critic] – [2.3. Adversarial training strategy] – [3.1. Dataset] – [3.2. Parameter setting] – [3.4. Ablation studies] and [5. Discussion and conclusions]
1. Introduction
- Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS) may occur, during identical twin pregnancies, when abnormal vascular anastomoses in the monochorionic placenta result in uneven blood flow between the fetuses.
- At the beginning of the surgical treatment, the surgeon identifies the interfetal membrane, which is used as a reference to explore the placenta vascular network and identify vessels to be treated.
- As for placental vessel segmentation, the work in Almoussa et al. (2011) proposes a30 neural network trained on manually handcrafted features from E4-vivo placenta images.
- The instance-normalized topology can tackle the il- lumination variability typical of fetoscopic videos acquired during TTTS surgery.
- The spatio-temporal features can boost segmentation performance enforcing the consistency of segmentation masks across sequential frames.
1.1. Contribution of the work
- The authors address the problem of automatic inter-fetal membrane segmentation to enhance surgeon context awareness during TTTS surgery.
- Specifically, the authors extend the adversarial framework presented in Casella et al. (2020) to process, via spatio-temporal convolution, surgical video clips.
- This allows us to70 exploit the temporal information naturally encoded in videos.
- The authors further design a dense block that encodes instance normalization, to account for illumination changes in the video clips.
- The authors will make the dataset collected for this work publicly available, to foster further research in the field.
2. Methods
- The proposed framework consists of the segmentor, described in Sec. 2.1, and a discriminator network , described in Sec. 2.2.
- The segmentor and critic are trained in an adversarial fashion, following the strategy proposed in Casella et al. (2020) and described in Sec. 2.3.90.
2.1. Segmentor
- The segmentor has a dense UNet-like architecture consisting of downsampling and upsampling path, linked via long-skip connections.
- This process is repeated until there are available frames, and results in a collection of temporal clips.
- Each dense block is followed by a transition down module for downscaling.
- By building upon the dense module proposed in (Huang et al., 2017), the authors propose a new dense module that uses two (leaky ReLu) pre-activated convolutions, instead of a single one.
2.2. Critic
- It is com-140 posed by two branches, as described in Table 1 and shown in Fig. 2, for extracting features from both the gold-standard segmentation and the segmentor output.
- The authors decided to keep the critic architecture similar to its original implementation because the role of the critic is to provide a shape constraining mechanism for the segmentor output.
- The use of dense blocks would have introduced unnecessary complexity with an increase in memory requirements.
- The segmentor branch takes as input x masked by the output of the segmentor (S(x)).
2.3. Adversarial training strategy
- The segmentor and critic layers are initialised using.
- While there160 is a possible risk of divergence of the loss during training, the introduction of hyper parameters may allow to balance the action of the two terms in the loss function avoiding possible divergences, However, this never occurred in their experiments.
3.1. Dataset
- To experimentally evaluate their two research hypotheses, the authors collected a dataset of 20 fetoscopic videos acquired during 20 different surgical procedures for treating TTTS in 20 women.
- The membrane was manually annotated in each frame under the supervision of the surgeon.
- This dataset, to the best of their knowledge, is the biggest dataset currently available for inter-fetal membrane segmentation.
- Each frame was cropped to contain only the FoV of the fetoscope and, resized185 to 128x128 pixels both for smoothing noise and limiting memory usage.
3.2. Parameter setting
- The authors used wlength = 4 due to the higher complexity of their framework, which required higher memory usage and computational power.
- Validation and testing temporal clips were built using the same parameters but with ∆w = 4 (i.e., without195 overlap).
- During training, at each iteration step, each batch was augmented200 with random rotation in range (−25◦,+25◦), horizontal and vertical flip, and scaling with a scaling factor in range (0.5, 1.5).
- The Mann–Whitney–Wilcoxon test on Acc and DSC, both imposing a significance level (p) equal to 0.05, were used to assess whether or not remarkable differences existed between the tested architectures.
3.4. Ablation studies
- The authors compared the results of the proposed framework against those of the adversarial network presented in Casella et al. (2020), which is the closest work with respect to ours.
- Considering that a comprehensive comparison with standard state of the art approaches (e.g., UNet (Ronneberger et al., 2015) and220 ResNet (He et al., 2016)) is already provided in Casella et al. (2020), the authors here focused on the ablation studies.
- For E6, the lowest performance was the one with ∆w = 4 (no overlap between temporal clips).
- Visual samples for the tested models are shown in Fig.
5. Discussion and conclusions
- This paper introduced a shape-constrained adversarial framework with instance-285 normalized spatio-temporal features to perform automatic inter-fetal membrane segmentation in fetoscopic video clips, while tackling the high illumination variability in fetoscopic videos.
- The authors noticed310 that 3D convolution alone was not able to boost segmentation consistency, as the results are comparable with the 2D vanilla adversarial framework (E3 ).
- In such cases, the temporal connectivity introduced to guarantee consistency across consecutive frames can affect the accuracy of segmentation negatively.
- To conclude, the achieved results suggest that the proposed approach may be effective in supporting surgeons in the identification of the inter-fetal membrane390 in fetoscopic videos.
- Data used for the analysis395 were acquired during actual surgery procedures and then were anonymized to allow researchers to conduct the study.
Did you find this useful? Give us your feedback
Figures (14)

Figure 10: Sample frames in which the membrane is not present.Each frame was extracted from a video not used to train the network, as described in Sec. 3.4. The predicted segmentation is highlighted in yellow. 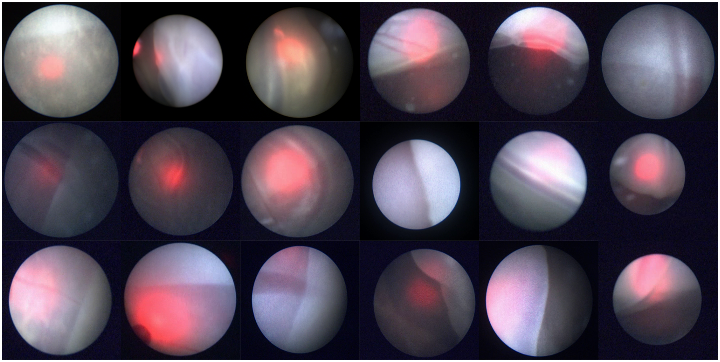
Figure 1: Sample frames from our dataset. The frames are extracted from intra-operative videos acquired in the actual surgical practice for Twin-to-Twin Transfusion Syndrome (TTTS). Each frame refers to a different video. Although video acquisition was performed with the same equipment, the frames present high variability, in terms of: (i) different membrane position, shape, tissue area in the field of view, contrast and texture, (ii) noise and blur, (iii) presence of amniotic fluid particles, (iv) vessels along the membrane equator, (v) different levels of illumination, (vi) presence of laser-guide light. 
Table 1: Architecture details for the (top) segmentor and (bottom) critic. The IN Conv3D and BN Conv3D refer to Instance Normalization - leaky ReLu - 3D Convolution and Batch Normalization - leaky ReLu - 3D Convolution, respectively. 
Figure 8: Sample results of inter-fetal membrane segmentation for three consecutive frames in a clip. Results are shown for the (second column) 2D adversarial framework and (third column) the proposed framework. The gold standard and segmentation prediction are highlighted in white and yellow, respectively. 
Table 4: Results of the sliding window configuration tested in E5, E6 in the ablation study. Segmentation Accuracy (Acc), Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC ) and Sensitivity (Sens) on the test set are reported in terms of mean ± standard deviation. The best results are highlighted in bold. 
Figure 5: Boxplot of performance comparison between E1, E2, E3, E4 in the ablation study and Casella et al. (2020). The comparison is shown in terms of Dice similarity coefficient (DSC ) for each fold. Black asterisks highlight significant differences between the different architectures (Mann–Whitney–Wilcoxon) (∗p < 0.05, ∗ ∗ p < 0.01, ∗ ∗ ∗p < 0.001). 
Figure 9: Sample frame from patients in the test set of Fold 2. V4 is a patient with posterior placenta and, V5 and V6 are patients with anterior placenta. Performance results for this fold are shown in Table 3, detailed metrics for each video are shown in the supplementary materials. 
Table 2: Summary of the ablation study described in Sec. 3.4: E1: 2D vanilla segmentor, E2: 3D vanilla segmentor, E3: 2D vanilla adversarial framework, E4: 2D adversarial framework. The work in Casella et al. (2020), which is the closest to ours, is shown, too. ![Table 3: Results of 3-fold cross-validation for E1, E2, E3, E4 and [Casella et al., 2020] in the ablation study. Segmentation Accuracy (Acc), Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC ) and Sensitivity (Sens) on the test set are reported in terms of mean ± standard deviation. The best results are highlighted in bold.](/figures/table-3-results-of-3-fold-cross-validation-for-e1-e2-e3-e4-3tzwcmof.png)
Table 3: Results of 3-fold cross-validation for E1, E2, E3, E4 and [Casella et al., 2020] in the ablation study. Segmentation Accuracy (Acc), Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC ) and Sensitivity (Sens) on the test set are reported in terms of mean ± standard deviation. The best results are highlighted in bold. 
Figure 2: Proposed framework to inter-fetal membrane segmentation in fetoscopic videos. The segmentor is a U-shaped network with long-skip connections, consisting of dense blocks, each of which is composed by multiple (number below each block) dense modules. Each module is composed of two pre-activated 3D convolutions, where the normalization is performed at instance (1st convolution) and batch (2nd convolution) level. The transition down and transition up modules perform downsampling and upsamplig, respectively. The critic, inspired by Casella et al. (2020), consists of a 3D version of the encoder branch of UNet. During training, as explained in Sec. 2.3, the critic extracts the feature vectors from the input masked by the segmentor output and the gold standard. The Mean Absolute Error (MAE) computed between the two vectors, contribute, along with the per-pixel binary cross entropy (BCE), to the loss that is minimized during training. 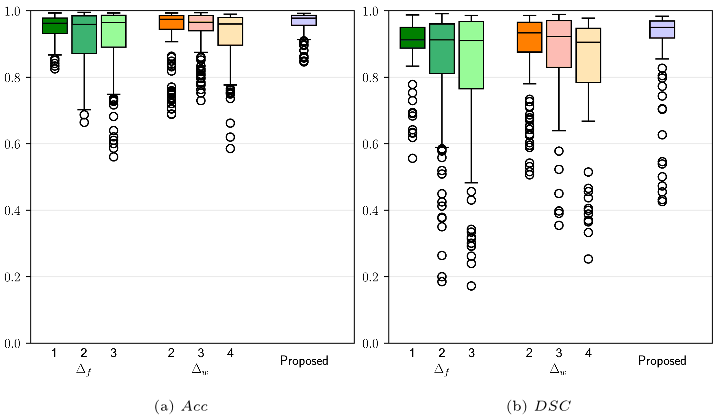
Figure 6: (a-b) Boxplot of performance for the sliding window ablation study for each value of the parameters (i.e. ∆f (E5 ) and ∆w (E6 )) shown in terms of (c) accuracy (Acc) and (d) Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC ). The proposed method refers to ∆f = 0 and ∆w = 1. 
Figure 4: Boxplot of performance comparison between E1, E2, E3, E4 in the ablation study and Casella et al. (2020). The comparison is shown in terms of accuracy (Acc) for each fold. Black asterisks highlight significant differences between the different architectures (Mann–Whitney–Wilcoxon) (∗p < 0.05, ∗ ∗ p < 0.01, ∗ ∗ ∗p < 0.001). 
Figure 3: Sliding window algorithm used for building temporal clips (w1, w2, w3). The window, consisting of wlength frames, slides of ∆w frames. For wlength = 4 and ∆w = 1, the generated clips overlap of 3 frames. While building a temporal clip, the sliding window can possibly skip ∆f frames. For ∆f = 0, clips consist of consecutive frames. 
Figure 7: Sample segmentation results obtained on the test set using the architectures described in the ablation study (Sec. 3) and in Casella et al. (2020). The gold standard and predicted segmentation are highlighted in white and yellow, respectively. Each row refers to a different video, while each column refers to a different experiment: input: original input frame, Casella et al. (2020): our previous work, E1: 2D vanilla segmentor, E2: 3D vanilla segmentor, E3: 2D vanilla adversarial framework, E4: 2D adversarial framework, and proposed: 3D adversarial framework.
Citations
More filters
TL;DR: A detailed survey of the most recent work in the field can be found in this paper , with a total of 145 research papers published after 2017 and each paper is analyzed and commented on from both the methodology and application perspective.
15 citations
TL;DR: A literature search on the use of AI in the diagnosis of NEC yielded 118 publications that were reduced to 8 after screening and checking for eligibility, and most publications showed promising results but no publications with evident clinical benefits were found.
3 citations
TL;DR: Wang et al. as discussed by the authors used Mask R-CNN with two additional transposed layers at segmentation head to accurately segment the median nerve directly on transverse US images, which achieved good performances both in median nerve detection and segmentation: Precision (Prec), Recall (Rec), Mean Average Precision (mAP) and Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC).
Abstract: Ultrasound (US) imaging is recognized as a useful support for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) assessment through the evaluation of median nerve morphology. However, US is still far to be systematically adopted to evaluate this common entrapment neuropathy, due to US intrinsic challenges, such as its operator dependency and the lack of standard protocols. To support sonographers, the present study proposes a fully-automatic deep learning approach to median nerve segmentation from US images. We collected and annotated a dataset of 246 images acquired in clinical practice involving 103 rheumatic patients, regardless of anatomical variants (bifid nerve, closed vessels). We developed a Mask R-CNN with two additional transposed layers at segmentation head to accurately segment the median nerve directly on transverse US images. We calculated the cross-sectional area (CSA) of the predicted median nerve. Proposed model achieved good performances both in median nerve detection and segmentation: Precision (Prec), Recall (Rec), Mean Average Precision (mAP) and Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) values are 0.916 ± 0.245, 0.938 ± 0.233, 0.936 ± 0.235 and 0.868 ± 0.201, respectively. The CSA values measured on true positive predictions were comparable with the sonographer manual measurements with a mean absolute error (MAE) of 0.918 mm2. Experimental results showed the potential of proposed model, which identified and segmented the median nerve section in normal anatomy images, while still struggling when dealing with infrequent anatomical variants. Future research will expand the dataset including a wider spectrum of normal anatomy and pathology to support sonographers in daily practice.
2 citations
TL;DR: In this paper , a fully-unsupervised approach for binary Surgical Instrument Segmentation is proposed, which uses shape-priors as realistic segmentation masks of the instruments, not necessarily coming from the same dataset/domain as the videos.
2 citations
TL;DR: This review uncovers the literature on computer‐assisted software solutions focused on TTTS and evaluates the current maturity of technologies by the technology readiness level and enumerates the necessary aspects to bring these new technologies to clinical practice.
Abstract: Fetal laser surgery has emerged as the preferred treatment of twin‐to‐twin transfusion syndrome (TTTS). However, the limited field of view of the fetoscope and the complexity of the procedure make the treatment challenging. Therefore, preoperative planning and intraoperative guidance solutions have been proposed to cope with these challenges. This review uncovers the literature on computer‐assisted software solutions focused on TTTS. These solutions are classified by the pre‐ or intraoperative phase of the procedure and further categorized by discussed hardware and software approaches. In addition, it evaluates the current maturity of technologies by the technology readiness level and enumerates the necessary aspects to bring these new technologies to clinical practice.
1 citations
References
More filters
TL;DR: An end-to-end pipeline is proposed by integrating 3-D CNN with LSTM, followed by a time series pooling layer and a softmax layer to predict the activities and outperforms the state-of-the-art end- to-end methods of action recognition by 3.8% and 3.2%, respectively.
Abstract: Human activity recognition in videos with convolutional neural network (CNN) features has received increasing attention in multimedia understanding. Taking videos as a sequence of frames, a new record was recently set on several benchmark datasets by feeding frame-level CNN sequence features to long short-term memory (LSTM) model for video activity recognition. This recurrent model-based visual recognition pipeline is a natural choice for perceptual problems with time-varying visual input or sequential outputs. However, the above-mentioned pipeline takes frame-level CNN sequence features as input for LSTM, which may fail to capture the rich motion information from adjacent frames or maybe multiple clips. Furthermore, an activity is conducted by a subject or multiple subjects. It is important to consider attention that allows for salient features, instead of mapping an entire frame into a static representation. To tackle these issues, we propose a novel pipeline, saliency-aware three-dimensional (3-D) CNN with LSTM, for video action recognition by integrating LSTM with salient-aware deep 3-D CNN features on videos shots. Specifically, we first apply saliency-aware methods to generate saliency-aware videos. Then, we design an end-to-end pipeline by integrating 3-D CNN with LSTM, followed by a time series pooling layer and a softmax layer to predict the activities. Noticeably, we set a new record on two benchmark datasets, i.e., UCF101 with 13 320 videos and HMDB-51 with 6766 videos. Our method outperforms the state-of-the-art end-to-end methods of action recognition by 3.8% and 3.2%, respectively on above two datasets.
243 citations
TL;DR: There is no current evidence from randomised trials to influence practice in twin-twin transfusion syndrome and three ongoing randomised studies have been identified.
Abstract: Background
Twin-twin transfusion syndrome, a condition affecting monochorionic twin pregnancies, is associated with a high risk of perinatal mortality and morbidity. A number of treatments have been introduced to treat the condition but it is unclear which intervention improves maternal and fetal outcome.
Objectives
The objective of this review was to evaluate the impact of treatment modalities in twin-twin transfusion syndrome.
Search methods
We searched the Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group's Trials Register (31 May 2013).
Selection criteria
Randomised and quasi-randomised studies of amnioreduction versus laser coagulation, septostomy versus laser coagulation or septostomy versus amnioreduction.
Data collection and analysis
Two review authors independently assessed eligibility and extracted data. We contacted study authors for additional information.
Main results
Three studies (253 women and 506 babies) were included. All three trials were judged to be of moderate quality. One study compared amnioreduction with septostomy (71 women), whilst the other two studies compared amnioreduction with endoscopic laser coagulation (182 women). Not all trials provided outcome data that could be included in all meta-analyses.
Amnioreduction compared with laser coagulation
Although there was no difference in overall death between amnioreduction and laser coagulation (average risk ratio (RR) 0.87; 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.55 to 1.38 adjusted for clustering, two trials) or death of at least one infant per pregnancy (RR 0.91; 95% CI 0.75 to 1.09, two trials), or death of both infants per pregnancy (average RR 0.76; 95% 0.27 to 2.10, two trials), more babies were alive without neurological abnormality at the age of six years in the laser group than in the amnioreduction groups (RR 1.57; 95% CI 1.05 to 2.34 adjusted for clustering, one trial). There were no significant differences in the babies alive at six years with major neurological abnormality treated by laser coagulation or amnioreduction (RR 0.97; 95% CI 0.34 to 2.77 adjusted for clustering, one trial). Outcomes for death in this 2013 update are different from the previous 2008 update, where improvements in perinatal death and death of both infants per pregnancy were shown in the laser intervention arm. The NIHCD trial included in this update exerts an opposite direction of effects to the Eurofetus study, which was previously the only included laser study, hence the difference in outcome.
Amnioreduction compared with septostomy
There are no differences in overall death (RR 0.83; 95% CI 0.47 to 1.47, adjusted for clustering, one trial), death of at least one infant per pregnancy (RR 0.80; 95% CI 0.48 to 1.35, one trial), or death of both infants per pregnancy (RR 0.90; 95% CI 0.37 to 2.22, one trial) or gestational age at birth (RR 1.20; 95% CI -0.81 to 3.21, one trial) between amnioreduction and septostomy.
Authors' conclusions
Endoscopic laser coagulation of anastomotic vessels should continue to be considered in the treatment of all stages of twin-twin transfusion syndrome to improve neurodevelopmental outcomes.
Further research targeted towards assessing the effect of treatment on milder (Quintero stage 1 and 2) and more severe (Quintero stage 4) forms of twin-twin transfusion syndrome is required. Studies should aim to assess long-term outcomes of survivors.
149 citations
German Cancer Research Center1, Johns Hopkins University2, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology3, Technische Universität München4, University of Bremen5, Harvard University6, University of Upper Alsace7, Imperial College London8, Heidelberg University9, Leipzig University10, University of Strasbourg11, University of Wisconsin-Madison12, University College London13, French Institute of Health and Medical Research14, University of Rennes15
TL;DR: In this article, the authors provide a consensus definition for Surgical Data Science, identify associated challenges and opportunities, and provide a roadmap for advancing the field, based on discussions during an intensive two-day international interactive workshop that brought together leading researchers working in the related field of computer assisted interventions.
Abstract: This paper introduces Surgical Data Science as an emerging scientific discipline. Key perspectives are based on discussions during an intensive two-day international interactive workshop that brought together leading researchers working in the related field of computer and robot assisted interventions. Our consensus opinion is that increasing access to large amounts of complex data, at scale, throughout the patient care process, complemented by advances in data science and machine learning techniques, has set the stage for a new generation of analytics that will support decision-making and quality improvement in interventional medicine. In this article, we provide a consensus definition for Surgical Data Science, identify associated challenges and opportunities and provide a roadmap for advancing the field.
129 citations
TL;DR: The maximum diameter of the instrument explains iPPROM rate, gestational age at birth and fetal survival as well as fetal survival after representative minimally invasive antenatal procedures.
Abstract: Objective: Iatrogenic preterm prelabor rupture of membranes (iPPROM; Methods: We systematically reviewed reported iPPROM rates, gestational age at delivery and fetal survival after representative minimally invasive antenatal procedures. Results: A total of 1,146, 36 and 194 cases with mean iPPROM rates of 27, 31 and 26% were included for placental laser in twin-twin transfusion syndrome, shunting in lower urinary tract obstruction and interventions for twin-reversed arterial perfusion, respectively. In the statistical analysis, the maximum diameter of the instrument predicted iPPROM rate and was significantly related to gestational age at birth as well as fetal survival. Information on duration of the respective procedures was scarce and did not allow for meaningful analysis. Conclusions: iPPROM occurs in about 30% of cases treated by minimally invasive fetal surgery. The maximum diameter of the instrument explains iPPROM rate, gestational age at birth and fetal survival. Great variations in the reporting of iPPROM make data analysis difficult.
120 citations
TL;DR: A novel high-resolution multi-scale encoder–decoder network (HMEDN), in whichMulti-scale dense connections are introduced for the encoder-decoder structure to finely exploit comprehensive semantic information to accurately locate indistinct boundaries.
Abstract: Automatic image segmentation is an essential step for many medical image analysis applications, include computer-aided radiation therapy, disease diagnosis, and treatment effect evaluation. One of the major challenges for this task is the blurry nature of medical images (e.g., CT, MR, and microscopic images), which can often result in low-contrast and vanishing boundaries. With the recent advances in convolutional neural networks, vast improvements have been made for image segmentation, mainly based on the skip-connection-linked encoder–decoder deep architectures. However, in many applications (with adjacent targets in blurry images), these models often fail to accurately locate complex boundaries and properly segment tiny isolated parts. In this paper, we aim to provide a method for blurry medical image segmentation and argue that skip connections are not enough to help accurately locate indistinct boundaries. Accordingly, we propose a novel high-resolution multi-scale encoder–decoder network (HMEDN), in which multi-scale dense connections are introduced for the encoder–decoder structure to finely exploit comprehensive semantic information. Besides skip connections, extra deeply supervised high-resolution pathways (comprised of densely connected dilated convolutions) are integrated to collect high-resolution semantic information for accurate boundary localization. These pathways are paired with a difficulty-guided cross-entropy loss function and a contour regression task to enhance the quality of boundary detection. The extensive experiments on a pelvic CT image dataset, a multi-modal brain tumor dataset, and a cell segmentation dataset show the effectiveness of our method for 2D/3D semantic segmentation and 2D instance segmentation, respectively. Our experimental results also show that besides increasing the network complexity, raising the resolution of semantic feature maps can largely affect the overall model performance. For different tasks, finding a balance between these two factors can further improve the performance of the corresponding network.
94 citations