UNIVERSIDADE DA BEIRA INTERIOR
Faculdade de Engenharia
Departamento de Informática
Ubiquitous Model for Wireless
Sensor Networks Monitoring
André Gaudêncio Ferreira Elias
Submitted to the University of Beira Interior in candidature for the
Degree of Master of Science in Informatics Engineering
Supervised by Prof. Doutor Joel José Puga Coelho Rodrigues
Co-supervised by Prof. Doutor Bruno Bogaz Zarpelão
Department of Informatics
University of Beira Interior
Covilhã, Portugal
http://www.di.ubi.pt

ii

iii
Acknowledgments
First of all, I would like to express my gratitude to my supervisor
Professor Joel José Puga Coelho Rodrigues for his expertise, guidance,
continuous support and words of encouragement.
I also want to thank to my co-supervisor Professor Bruno Bogaz
Zarpelão for all the support throughout this work and for the fantastic
reception and guidance during my Master’s studies at University of
Campinas (UNICAMP), in Brazil.
I am most grateful to the University of Beira Interior, Instituto de
Telecomunicações (Covilhã Delegation), Next Generation Networks and
Applications Group (NetGNA), and University of Campinas (UNICAMP) for
many kinds of all the support that was given to me.
I owe particular thanks to Professor Luís Oliveira and my colleague
Gilberto Almeida, who worked closest to me and gave me all the necessary
support during this work.
Many thanks to all members of NetGNA for the constant support and
for creating an excellent work environment.
Special thanks to my friends David Albuquerque and Patrícia Nunes
for keeping me focused and motivated during this months of hard work and
dedication.
Last but not least, I am most grateful to my family, especially my
mother Maria Fernanda Gaudêncio Elias, my brother Bruno Elias and my
cousins Pedro Gaudêncio, Susana Baptista, Carolina and Mafalda, for their
support, love, patient and constant encouragement.
I dedicate this work to my father António Gabriel Elias for making
me the person I am today.

iv

v
Resumo
As redes de sensores sem fios fazem parte de uma nova tendência
tecnológica na qual pequenos dispositivos com recursos limitados
comunicam entre si, sem fios, e interagem com o ambiente envolvente
recolhendo uma grande diversidade de dados, tais como a temperatura e a
humidade.
Recentemente, devido ao enorme crescimento no uso de dispositivos
móveis com ligação à Internet, os smartphones estão a tornar-se o centro
das futuras redes sem fios ubíquas permitindo aos utilizadores aceder a
dados, a qualquer hora e em qualquer lugar. De acordo com a visão da
Internet of Things, interligar redes de sensores sem fios e smartphones
usando a Internet é um grande desafio e novas arquitecturas são
necessárias devido à heterogeneidade destes dispositivos.
Esta dissertação centra-se na proposta e construção de uma arquitectura
ubíqua para a monitorização de redes de sensores sem fios, baseada em
serviços Web, apoiada numa base de dados relacional e uma aplicação
móvel para o sistema operative Android. Esta arquitectura permite que os
utilizadores móveis acedam a dados em tempo real e também a dados
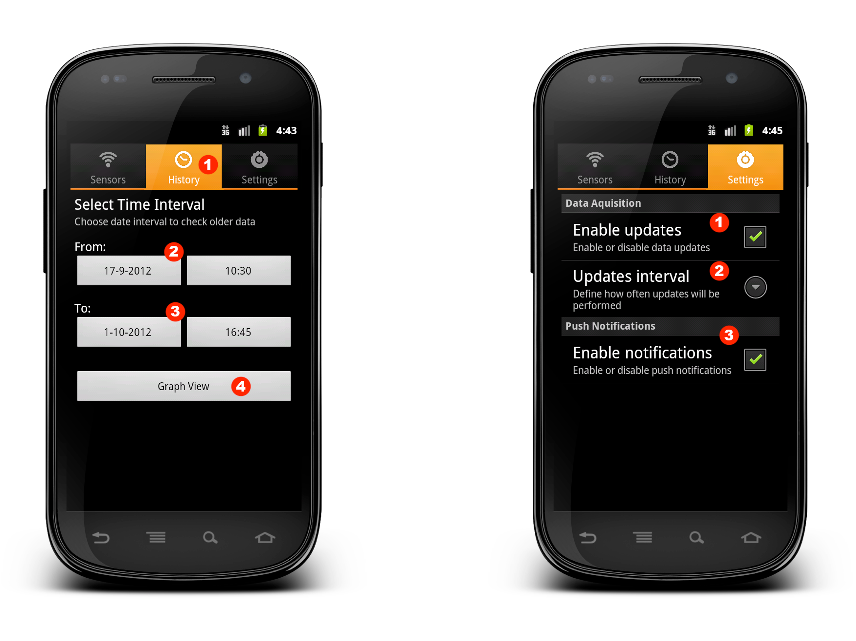
históricos, num ambiente móvel, usando smartphones. Além disso, foi
desenvolvido um sistema de notificações push que alerta o utilizador
quando um dado parâmetro de um sensor ultrapassa um limiar
pré-definido.
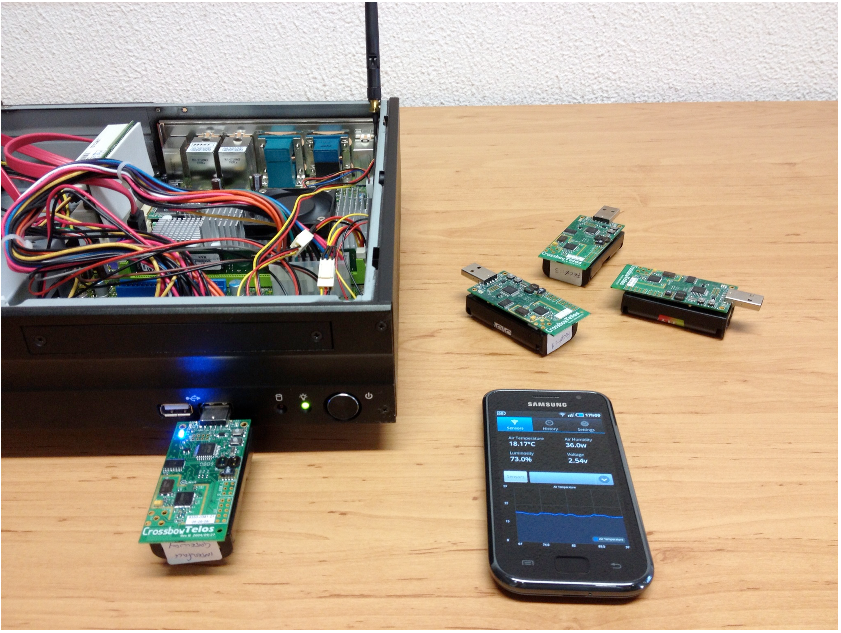
A solução construída foi testada e demonstrada utilizando uma testbed
laboratorial e está pronta para utilização.