Acceptability of oral solid medicines in older adults with and without dysphagia: A nested pilot validation questionnaire based observational study
Reads0
Chats0
TLDR
Assessment of acceptability of oral solid medicines in older ambulatory patients with and without dysphagia found that higher acceptability scores were seen in the dysphagic population than in the non-dysphagic population for all of the dosage forms that were easier to swallow than tablets and capsules.About:
This article is published in International Journal of Pharmaceutics.The article was published on 2016-10-30 and is currently open access. It has received 71 citations till now. The article focuses on the topics: Dysphagia & Population.read more
Figures
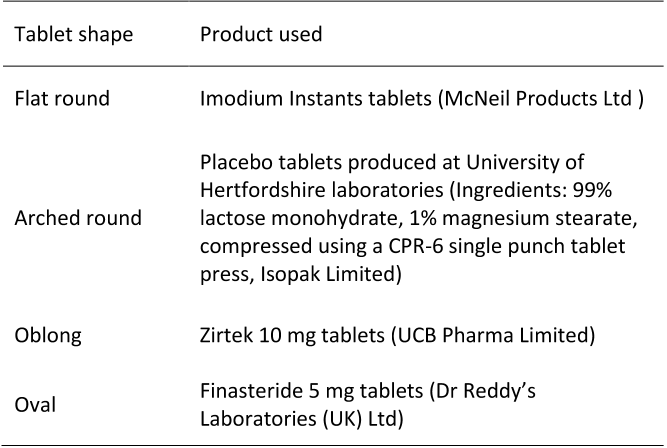
Table 1. Products used to represent 9 mm tablets in different shapes 
Table 2. Products used to represent various oral formulations 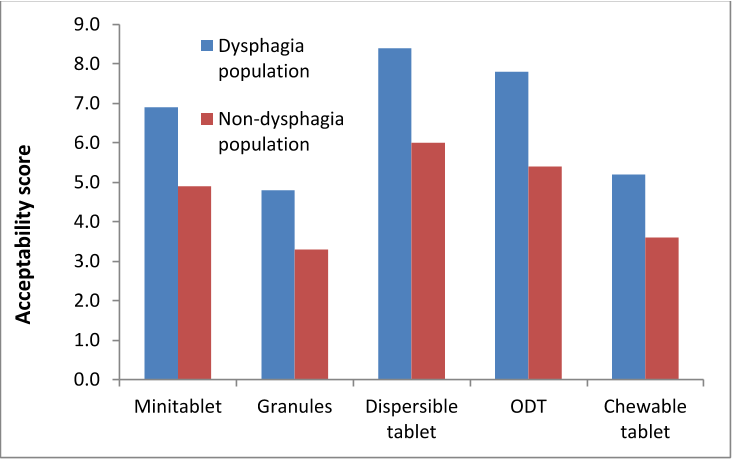
Fig 3. Acceptability scores of different oral solid dosage forms (ODT: orally disintegrating tablet). 
Table 4. Participants’ impression on the flexible solid oral dosage forms. 2 
Figure 1. Percentage of participants selecting the tablet size and shape that started to cause difficulty in swallowing. 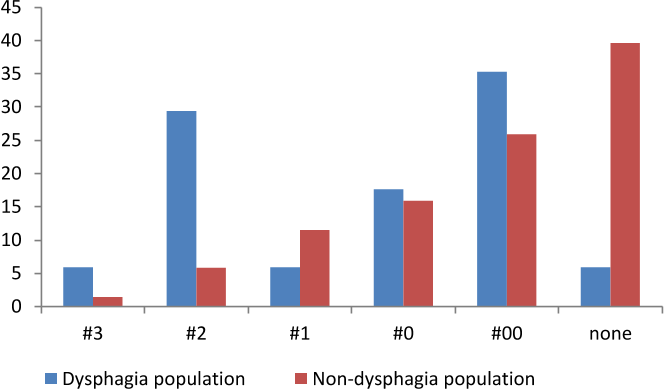
Fig 2. Percentage of participants selecting the capsule size that might start to cause difficulty in swallowing
Citations
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Assessment of Mini-Tablets Coating Uniformity as a Function of Fluid Bed Coater Inlet Conditions
TL;DR: In this paper, the quality of mini-tablets' coating uniformity obtained by either the bottom spray chamber with a classical Wurster distributor (CW) or a swirl distributor (SW) was investigated.
Journal ArticleDOI
Dysphagia for medication in Parkinson’s disease
Bendix Labeit,Elijahu Berkovich,Inga Claus,Malte Roderigo,Anna-Lena Schwake,Dvora Izgelov,Dorit Mimrod,Sigrid Ahring,Stephan Oelenberg,Paul Muhle,Verena Zentsch,Fiona Wenninger,Sonja Suntrup-Krueger,Rainer Dziewas,Tobias Warnecke +14 more
TL;DR: In this paper , a two-dimensional and graduated classification of dysphagia for medication was introduced differentiating swallowing efficiency and swallowing safety in Parkinson's patients, and sixty-six PD patients underwent flexible endoscopic evaluation of swallowing, which included the swallowing of 2 tablets and capsules of different sizes.
Journal ArticleDOI
Stability and compatibility of Basmisanil granules co-administered with soft food.
TL;DR: Basmisanil shows good chemical stability when the granules are mixed with soft food and consumed within two hours, and no polymorphic conversion could be detected in the granule/food mixtures after preparation and after storage up to 24 h.
Journal ArticleDOI
Assessment of oral solid dosage forms administration manner and acceptability
TL;DR: Conventional white, round tablets were found to be the most preferred type of OSDF drug and can be valuable to pharmaceutical manufacturers, regulatory agencies, and pharmacists to enhancing patient awareness and compliance with OSDF administration for safe and effective drug administration.
Journal ArticleDOI
Preference, Perception, and Acceptability of Fluid Gels as a Potential Age-Appropriate Dosage Form for Elderly Patients with Dysphagia
Zulkarnain Aziz,Haliza Katas,Marhanis Salihah Omar,Noraida Mohamed Shah,Salma Mohamad Yusop,Mohamad Nasir Shafiee,Siti Fatimah Mohd Tarmizi +6 more
TL;DR: Fl fluid gels have shown great potential as an innovative oral formulation that is suitable for consumption by elderly patients with dysphagia and were perceived positively by consumers.
References
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Polypharmacy cutoff and outcomes: five or more medicines were used to identify community-dwelling older men at risk of different adverse outcomes.
Danijela Gnjidic,Sarah N. Hilmer,Sarah N. Hilmer,Fiona M. Blyth,Fiona M. Blyth,Vasi Naganathan,Vasi Naganathan,Louise M. Waite,Louise M. Waite,Markus J. Seibel,Markus J. Seibel,Andrew J. McLachlan,Andrew J. McLachlan,Robert G. Cumming,Robert G. Cumming,David J. Handelsman,David J. Handelsman,David G. Le Couteur,David G. Le Couteur +18 more
TL;DR: The study supports the use of five or more medications in the current definition of polypharmacy to estimate the medication-related adverse effects for frailty, disability, mortality, and falls.
Journal ArticleDOI
Prevalence of dysphagia among community-dwelling elderly individuals as estimated using a questionnaire for dysphagia screening
TL;DR: After matching for age and sex, there were significant differences in the competence scores, history of stroke, and perceived ill health status observed between the group with dysphagia and the group without dysphagIA.
Journal ArticleDOI
Mealtime Difficulties in a Home for the Aged: Not Just Dysphagia
TL;DR: The results clearly demonstrate that the prevalence of a wide range of eating-related problems far exceeds accepted estimates of dysphagia alone and support a multidisciplinary approach to mealtime interventions for the institutionalized elderly.
Journal ArticleDOI
Development and validation of a self-report symptom inventory to assess the severity of oral-pharyngeal dysphagia.
TL;DR: Applied to patients with neuromyogenic dysphagia, the 17-question inventory shows strong test-retest reliability over 2 weeks as well as face, content, and construct validity.
Journal ArticleDOI
Prevalence and predictors of polypharmacy among older primary care patients in Germany
TL;DR: This older general practice population in Germany is among the top pharmaceutical user group of European study samples and GPs should be aware that low subjective health and medication disagreement are independent predictors of polypharmacy.