Acceptability of oral solid medicines in older adults with and without dysphagia: A nested pilot validation questionnaire based observational study
Reads0
Chats0
TLDR
Assessment of acceptability of oral solid medicines in older ambulatory patients with and without dysphagia found that higher acceptability scores were seen in the dysphagic population than in the non-dysphagic population for all of the dosage forms that were easier to swallow than tablets and capsules.About:
This article is published in International Journal of Pharmaceutics.The article was published on 2016-10-30 and is currently open access. It has received 71 citations till now. The article focuses on the topics: Dysphagia & Population.read more
Figures
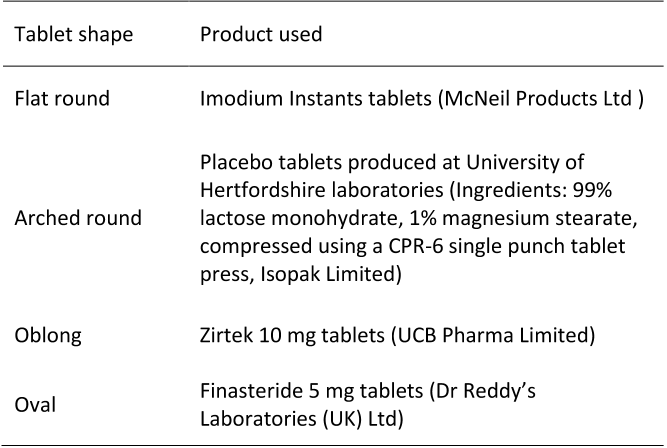
Table 1. Products used to represent 9 mm tablets in different shapes 
Table 2. Products used to represent various oral formulations 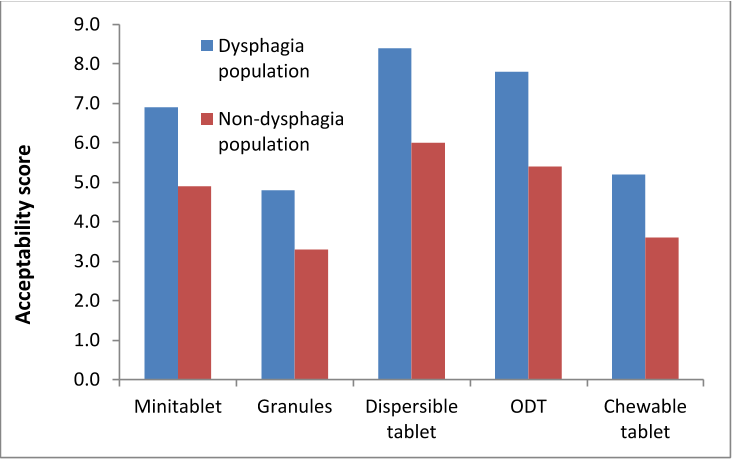
Fig 3. Acceptability scores of different oral solid dosage forms (ODT: orally disintegrating tablet). 
Table 4. Participants’ impression on the flexible solid oral dosage forms. 2 
Figure 1. Percentage of participants selecting the tablet size and shape that started to cause difficulty in swallowing. 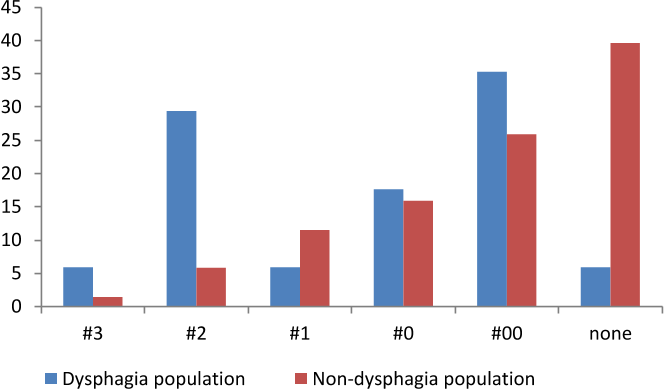
Fig 2. Percentage of participants selecting the capsule size that might start to cause difficulty in swallowing
Citations
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
3D printed drug delivery and testing systems - a passing fad or the future?
TL;DR: An overview of the advantages and limitations of 3D printing for drug delivery and testing, as compared to traditional manufacturing techniques is provided.
Journal ArticleDOI
Patient acceptability of 3D printed medicines.
TL;DR: This study is the first to guide the pharmaceutical industry towards developing patient-centric medicine in different geometries via 3DP, with the highest acceptability scores for torus printlets indicating that FDM 3DP is a promising fabrication technology towards increasing patient acceptability of solid oral medicines.
Journal ArticleDOI
Patient acceptability, safety and access: A balancing act for selecting age-appropriate oral dosage forms for paediatric and geriatric populations.
TL;DR: This review provides a comprehensive and up-to-date analysis of oral dosage forms considering key aspects of formulation design including dosage considerations, ease of use, tolerability and safety, manufacturing complexity, stability, supply and cost.
Journal ArticleDOI
Patient Centric Pharmaceutical Drug Product Design-The Impact on Medication Adherence.
Enrica Menditto,Valentina Orlando,Giuseppe De Rosa,Paola Minghetti,Umberto M. Musazzi,Caitriona Cahir,Marta Kurczewska-Michalak,Przemyslaw Kardas,Elísio Costa,José Manuel Sousa Lobo,Isabel Almeida +10 more
TL;DR: Packaging, orodispersible formulations, fixed dose combinations products, multiparticulate formulations, topical formulations and 3D printing are of particular relevance in a PCDPD process and will be addressed in this review.
Journal ArticleDOI
3D printing technology as innovative solutions for biomedical applications.
TL;DR: This review condense the findings, summarize the improvements that are needed for the use of 3D printing in medicine, as well as plausible methods for creating medicines and medical devices in the future.
References
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Prevalence and symptom profiling of oropharyngeal dysphagia in a community dwelling of an elderly population: a self-reporting questionnaire survey.
TL;DR: A questionnaire-based survey of swallowing dysfunction in a large, otherwise 'healthy' community dwelling older population in the UK in which additional cognitive and depression related scores were evaluated.
Journal ArticleDOI
Prevalence of perceived dysphagia and quality-of-life impairment in a geriatric population
TL;DR: There is a relatively high prevalence of dysphagia in the community-based geriatric population; significant quality-of-life impairment is a frequent finding.
Journal ArticleDOI
Difficulties swallowing solid oral dosage forms in a general practice population: prevalence, causes, and relationship to dosage forms
TL;DR: One in 11 primary care patients had frequent difficulties in swallowing tablets and capsules while GPs grossly underestimated these problems, therefore, physicians should rule out swallowing difficulties regularly to avoid non-adherence and inappropriate drug modifications.
Journal ArticleDOI
Prevalence of subjective dysphagia in community residents aged over 87.
TL;DR: A chronology of key events leading to and after death of patients diagnosed with asthma, bronchial asthma, and status of asthmaticus and related disorders.
Journal ArticleDOI
Oesophageal transit of six commonly used tablets and capsules.
TL;DR: The oesophageal transit of six commonly used tablets and capsules containing barium sulphate was evaluated radiologically using fluoroscopy in 121 healthy volunteers and it was recommended that subjects should remain standing for at least 90 seconds after taking capsules or tablets and that all preparations should be taken with at least 100 ml of water.