OECD DEVELOPMENT CENTRE
Working Paper No. 113
(Formerly Technical Paper No. 113)
CHINESE OUTWARD INVESTMENT
IN HONG KONG: TRENDS, PROSPECTS
AND POLICY IMPLICATIONS
by
Yun-Wing Sung
Research programme on:
Reform and Growth of Large Developing Countries
July 1996
OCDE/GD(96)53

5
TABLE OF CONTENTS
RÉSUMÉ ................................................................................................................ 7
SUMMARY ............................................................................................................ 7
PREFACE ............................................................................................................... 9
I. INTRODUCTION.................................................................................................. 11
II. CHINESE INVESTMENT IN HONG KONG: AN APPRAISAL................................. 13
III. THE DETERMINANTS OF CHINESE INVESTMENT IN HONG KONG .................. 25
IV. PROBLEMS AND PROSPECTS.......................................................................... 33
NOTES ................................................................................................................... 35
APPENDIX TABLES ................................................................................................ 37
BIBLIOGRAPHY ..................................................................................................... 45

6

7
RÉSUMÉ
Depuis une dizaine d’années, la Chine est le premier investisseur parmi les pays
en développement, et Hong Kong la première destination des investissements chinois.
Toutefois, en raison de la sous-déclaration liée à la fraude du contrôle des changes,
les statistiques officielles sous-estiment largement les flux d’investissement extérieur
de la Chine. Ce document technique tente d’évaluer le montant de ces flux
d’investissement et d’en décrire la nature.
Il recense les nombreuses estimations des investissements chinois vers Hong
Kong, en identifiant leurs sources, ainsi que les informations sur lesquelles elles sont
fondées. Il apparaît que la plupart de ces estimations sont des approximations
grossières, établies sur la base de données très incomplètes. Néanmoins, il est possible
d’évaluer le niveau de ces investissements d’après la valeur des actifs des entreprises
chinoises à Hong Kong et leur capitalisation boursière, ainsi que sur la base d’entretiens
avec des interlocuteurs informés. De plus, ce document évalue le poids des entreprises
chinoises dans l’économie de Hong Kong. Il analyse la répartition de leurs
investissements par secteur et selon la nature des investisseurs (ministères centraux,
gouvernements locaux ou provinciaux, organismes militaires). Enfin, il analyse les
déterminants économiques et politiques des flux d’investissement de la Chine vers
Hong Kong, et présente des conclusions de politique économique pour les deux
économies.
SUMMARY
Over the last decade, China has been the leading investor among developing
countries and Hong Kong is the foremost destination of Chinese investment. However,
China’s outward investment has been grossly understated in official statistics due to
avoidance of China’s foreign exchange controls. This paper tries to appraise those
investment flows both quantitatively and qualitatively.
It examines the many estimates of Chinese investment in Hong Kong, tracing
their sources and bases of estimation. Most of these estimates are found to be crude
guesses with very little empirical support. However, from the data on asset value and
market capitalisation of listed Chinese companies in Hong Kong, and also from
interviews with knowledgeable sources, it is possible to gauge the rough size of Chinese
investment in Hong Kong. The paper also examines China’s economic presence in
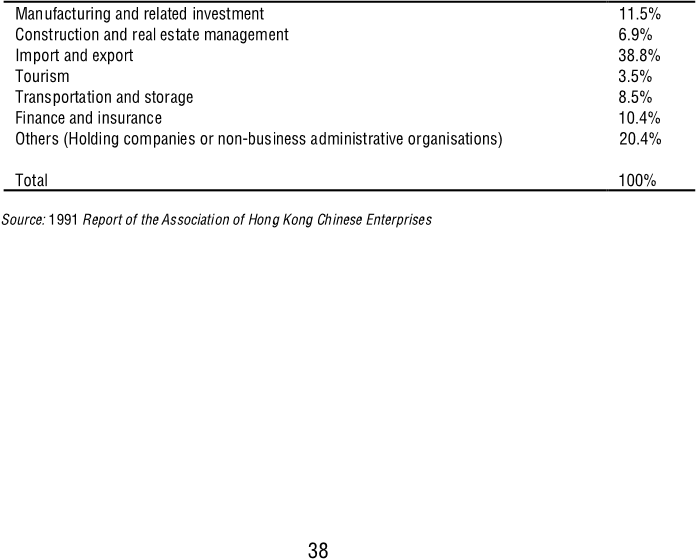
major sectors of the Hong Kong economy. It discusses the composition of Chinese
investment by industry and by ownership (central ministries, provincial and local
governments, and military-backed). The economic and political determinants of China’s
investment in Hong Kong are analysed, and the policy implications for Hong Kong
and China are examined.

8