Q1. What have the authors contributed in "Geochemistry of trace metals in a fresh water sediment: field results and diagenetic modeling" ?
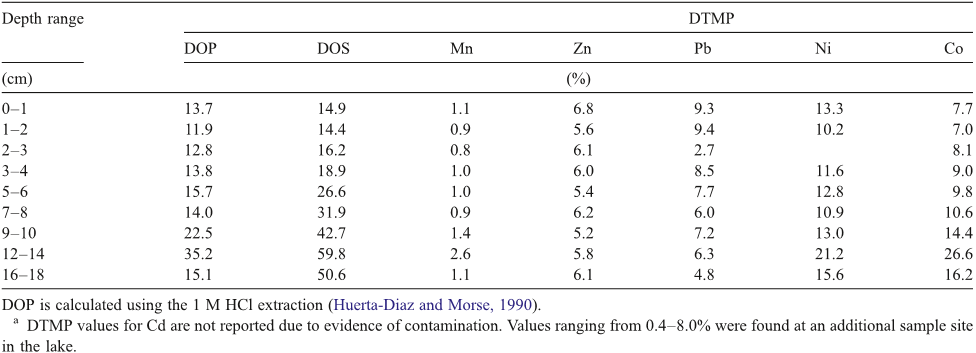
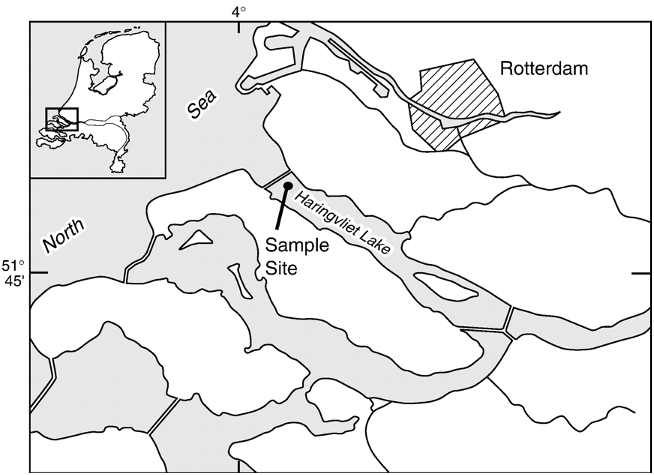
Canavan et al. this paper measured trace metal concentrations in pore water and sediment of a coastal fresh water lake ( Haringvliet Lake, The Netherlands ).