GPS evidence for northward motion of the Sinai Block: Implications for E. Mediterranean tectonics
Reads0
Chats0
TLDR
In this article, an elastic block model constrained by the GPS results that is consistent with the regional tectonics and allows us to estimate slip rates for Sinai bounding faults, including the Gulf of Aqaba-southern Dead Sea fault system, is presented.About:
This article is published in Earth and Planetary Science Letters.The article was published on 2005-09-30 and is currently open access. It has received 119 citations till now. The article focuses on the topics: Strike-slip tectonics.read more
Figures
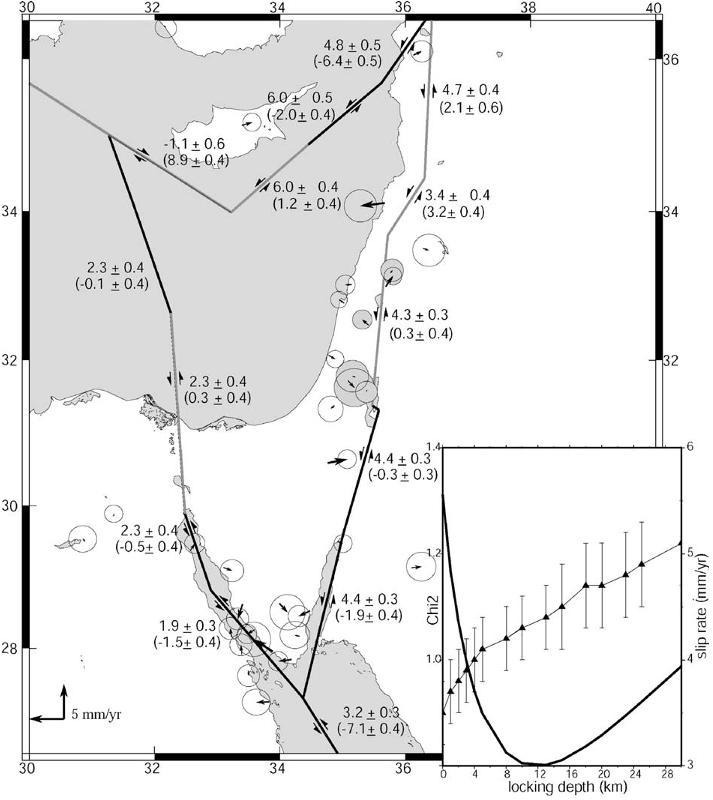
Fig. 3. Elastic block model for the Sinai area showing GPS residual velocities (given in Table 1) for the model described in the text. Faults are vertical and assigned locking depths of 15 km except for the Gulf of Aqaba/Dead Sea fault system that has a locking depth of 13 km, and the western Cyprus Arc that has a 308 dip down to the NE. Residuals are well within the uncertainties for the velocity determinations. Numbers show fault strike slip and fault-normal slip rates and 1-sigma formal uncertainties (fault normal component in brackets; negative for left lateral and extension). Slip rates are averages along each segment. Light modeled faults indicate segments with fault-normal shortening, and dark extension. Inset shows a plot of the local Chi*2 computed from sites close to the fault (shaded error ellipses indicate sites used to estimate fault locking depth) and estimated fault strike slip rate as a function of the locking depth for the Dead Sea fault. The best fit is for a 13 km locking depth and a strike slip rate of 4.3 mm/yr. 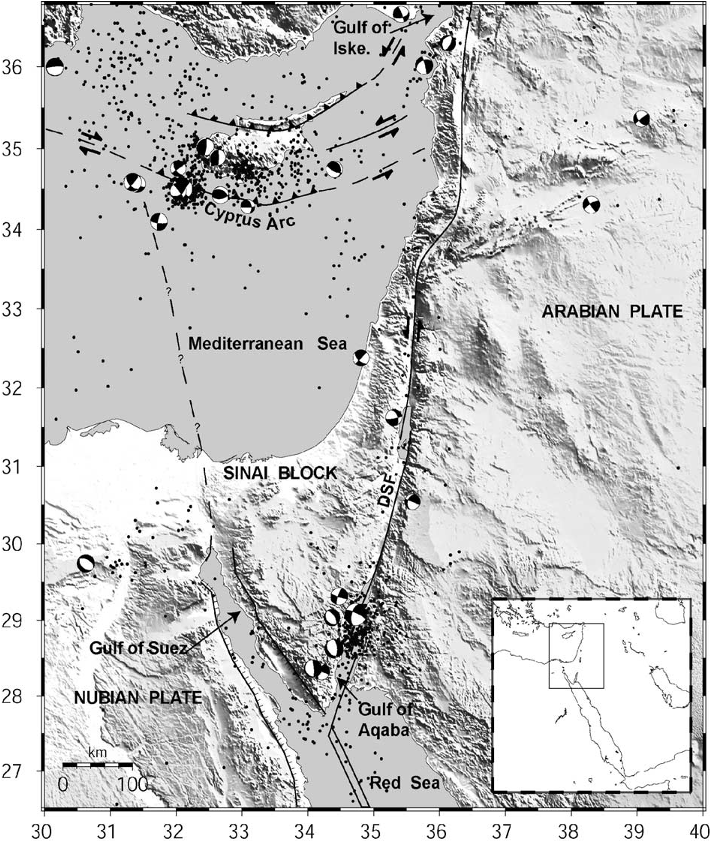
Fig. 1. Topographic (SRTM30) and tectonic map of the Sinai and surrounding region. Dots show seismicity (NEIC), focal mechanisms are from Harvard CMT. Inset shows location of study area within the context of the eastern Mediterranean. DSF=Dead Sea fault, Gulf of Iske.=Gulf of Iskenderum. 
Table 2 Euler vectors relative to Eurasia and 1-sigma uncertainties estimated from this study 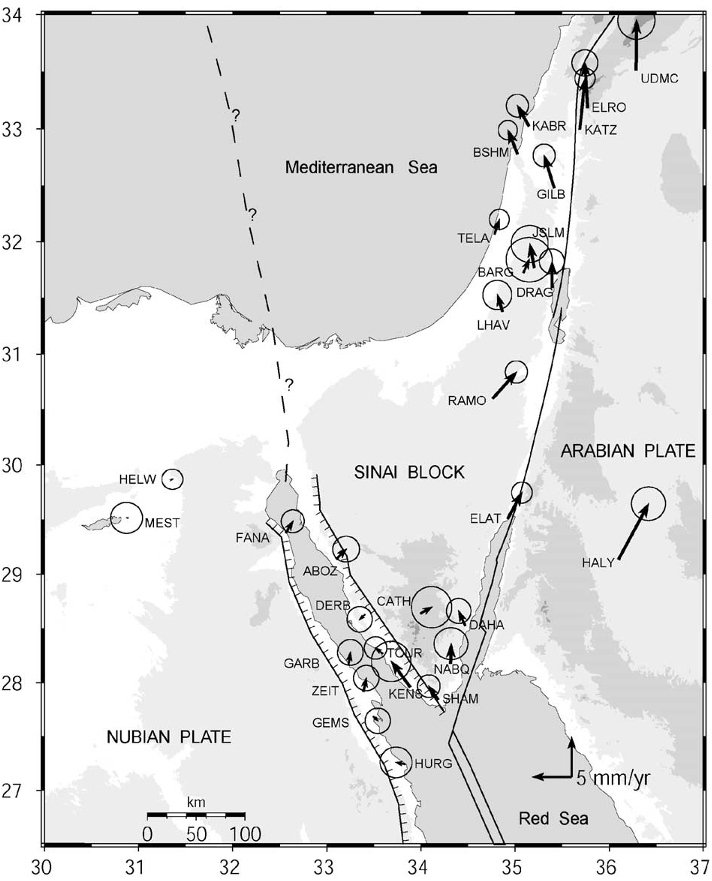
Fig. 2. Simplified tectonic map of the Sinai and surrounding regions show Lines with tick-marks are normal faults, ticks on downthrown block, doubl are given in Table 1. 
Table 1 GPS velocities in an Africa (Nubia)-fixed reference frame and 1-sigma uncertainties for sites shown in Fig. 2
Citations
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Crustal Strain and Stress Fields in Egypt from Geodetic and Seismological Data
TL;DR: In this article, a comparison between crustal stress and surface strain azimuthal patterns was performed for Egypt taking into account updated datasets of seismological and geodetic observations, which revealed that both patterns are near-parallel and driven by the same large-scale tectonic processes.
Geodetic constraints on continental rifting along the Red Sea
R. E. Reilinger,S. McClusky,A. Arrajehi,S. Mahmoud,A. Rayan,W. Ghebreab,G. Ogubazghi,A. Al-Aydrus +7 more
Journal ArticleDOI
Rate of seismic deformation in the Gulf of Aqaba inferred from moment-tensor summation
TL;DR: In this paper, a moment-tensor summation based on 44 focal mechanism solutions was used to calculate the shape of deformation in the Gulf of Aqaba, and the results suggest that the active deformation occurs due to the relative tectonic movements between the Arabian and African plates, as well as Sinai subplate.
Journal ArticleDOI
Present Kinematic Regime and Recent Seismicity of Gulf Suez, Egypt
TL;DR: In this article, the authors computed recent seismicity and present kinematic regime in the northern and middle zones of Gulf of Suez as inferred from moment tensor settlings and focal mechanism of local earthquakes that happened in this region.
References
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Global Positioning System constraints on plate kinematics and dynamics in the eastern Mediterranean and Caucasus
Simon McClusky,S. Balassanian,Aykut Barka,Coskun Demir,Semih Ergintav,Ivan Georgiev,O. Gurkan,Michael W. Hamburger,K. Hurst,Hans-Gert Kahle,Kim A. Kastens,G. Kekelidze,Robert W. King,V. Kotzev,Onur Lenk,Salah Mahmoud,A. Mishin,M. Nadariya,A. Ouzounis,Demitris Paradissis,Yannick Peter,M. Prilepin,Robert Reilinger,I. Sanli,H. Seeger,A. Tealeb,M. N. Toksoz,G. Veis +27 more
TL;DR: In this article, the authors present and interpret GPS measurements of crustal motions for the period 1988-1997 at 189 sites extending east-west from the Caucasus mountains to the Adriatic Sea and north-south from the southern edge of the Eurasian plate to the northern edge of Africa.
Journal ArticleDOI
Geological evolution of the tethys belt from the atlantic to the pamirs since the LIAS
J. Dercourt,L.P. Zonenshain,L. E. Ricou,V. G. Kazmin,X. Le Pichon,A. L. Knipper,C. Grandjacquet,I.M. Sbortshikov,J. Geyssant,Claude Lepvrier,D.H. Pechersky,J. Boulin,Jean-Claude Sibuet,L. A. Savostin,O. Sorokhtin,M. Westphal,Mikhail L. Bazhenov,J. P. Lauer,B. Biju-Duval +18 more
TL;DR: In this article, the evolution of the Tethys belt from the Pliensbachian (190 Ma) to the Tortonian (10 Ma) is depicted at 1 20,000,000 scale.
Journal ArticleDOI
GPS constraints on Africa (Nubia) and Arabia plate motions
TL;DR: In this article, the authors used continuously recording GPS and survey-mode GPS (SGPS) observations to determine Euler vectors for relative motion of the African (Nubian), Arabian and Eurasian plates.
Journal ArticleDOI
Plate tectonics of the Mediterranean region.
TL;DR: The seismicity and fault plane solutions in the Mediterranean area show that two small rapidly moving plates exist in the Eastern Mediterranean, and such plates may be a common feature of contracting ocean basins.
Journal ArticleDOI
Estimating regional deformation from a combination of space and terrestrial geodetic data
TL;DR: In this article, an approach for efficiently combining different types of geodetic data to estimate time-dependent motions of stations in a region of active deformation is discussed. But the work is limited to the case of finite constraints and stochastic perturbation of parameters.
Related Papers (5)
GPS constraints on continental deformation in the Africa-Arabia-Eurasia continental collision zone and implications for the dynamics of plate interactions
Robert Reilinger,Simon McClusky,Philippe Vernant,Shawn Lawrence,Shawn Lawrence,Semih Ergintav,R. Cakmak,Haluk Ozener,Fakhraddin Kadirov,Ibrahim Guliev,Ruben Stepanyan,Merab Nadariya,Galaktion Hahubia,Salah Mahmoud,K. Sakr,Abdullah ArRajehi,Demitris Paradissis,A. Al-Aydrus,Mikhail Prilepin,Tamara Guseva,Emre Evren,Emre Evren,Andriy Dmitrotsa,S. V. Filikov,Francisco Gomez,R. Al-Ghazzi,Gebran N. Karam +26 more