GPS evidence for northward motion of the Sinai Block: Implications for E. Mediterranean tectonics
Reads0
Chats0
TLDR
In this article, an elastic block model constrained by the GPS results that is consistent with the regional tectonics and allows us to estimate slip rates for Sinai bounding faults, including the Gulf of Aqaba-southern Dead Sea fault system, is presented.About:
This article is published in Earth and Planetary Science Letters.The article was published on 2005-09-30 and is currently open access. It has received 119 citations till now. The article focuses on the topics: Strike-slip tectonics.read more
Figures
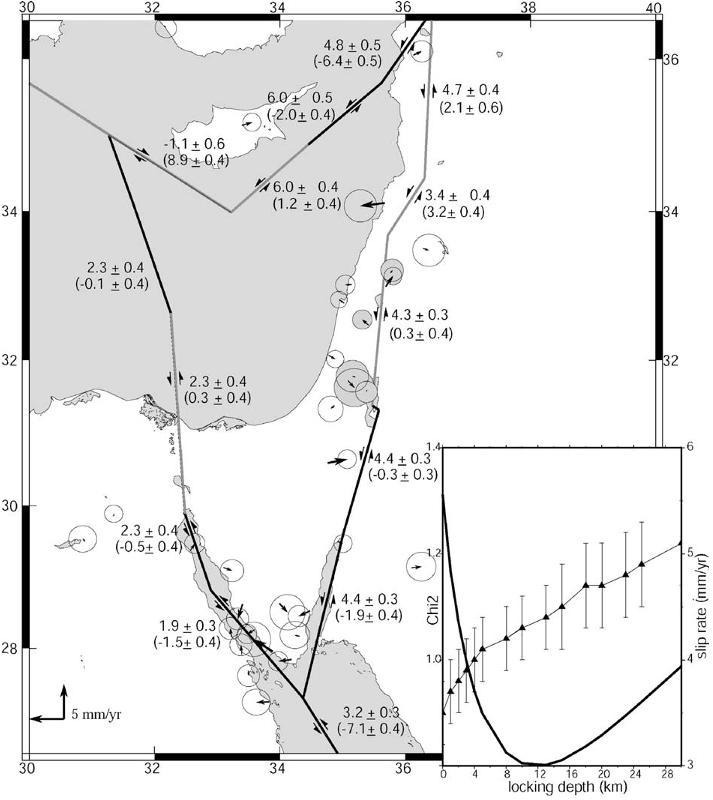
Fig. 3. Elastic block model for the Sinai area showing GPS residual velocities (given in Table 1) for the model described in the text. Faults are vertical and assigned locking depths of 15 km except for the Gulf of Aqaba/Dead Sea fault system that has a locking depth of 13 km, and the western Cyprus Arc that has a 308 dip down to the NE. Residuals are well within the uncertainties for the velocity determinations. Numbers show fault strike slip and fault-normal slip rates and 1-sigma formal uncertainties (fault normal component in brackets; negative for left lateral and extension). Slip rates are averages along each segment. Light modeled faults indicate segments with fault-normal shortening, and dark extension. Inset shows a plot of the local Chi*2 computed from sites close to the fault (shaded error ellipses indicate sites used to estimate fault locking depth) and estimated fault strike slip rate as a function of the locking depth for the Dead Sea fault. The best fit is for a 13 km locking depth and a strike slip rate of 4.3 mm/yr. 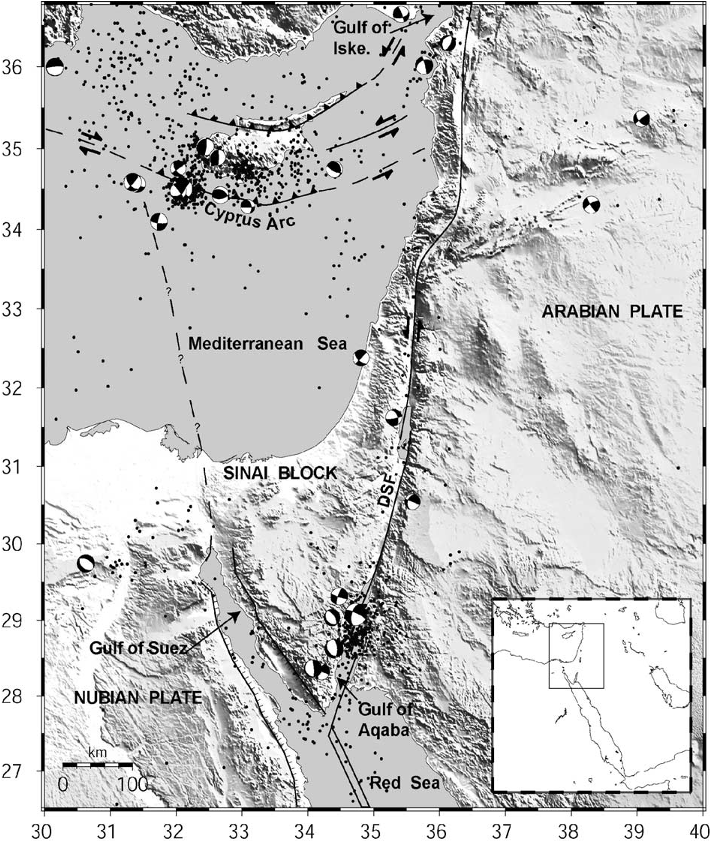
Fig. 1. Topographic (SRTM30) and tectonic map of the Sinai and surrounding region. Dots show seismicity (NEIC), focal mechanisms are from Harvard CMT. Inset shows location of study area within the context of the eastern Mediterranean. DSF=Dead Sea fault, Gulf of Iske.=Gulf of Iskenderum. 
Table 2 Euler vectors relative to Eurasia and 1-sigma uncertainties estimated from this study 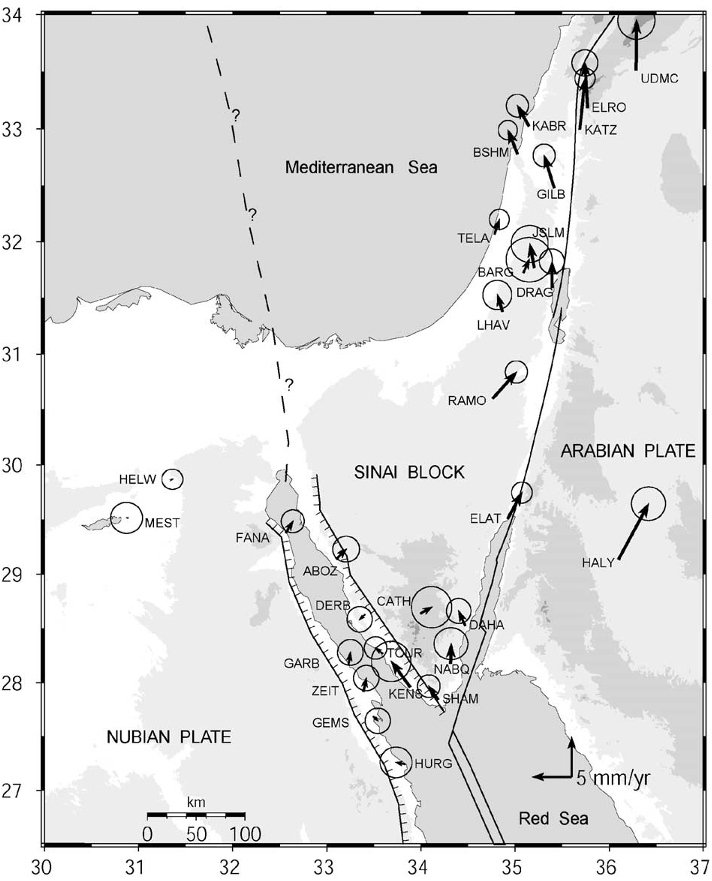
Fig. 2. Simplified tectonic map of the Sinai and surrounding regions show Lines with tick-marks are normal faults, ticks on downthrown block, doubl are given in Table 1. 
Table 1 GPS velocities in an Africa (Nubia)-fixed reference frame and 1-sigma uncertainties for sites shown in Fig. 2
Citations
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
GPS constraints on continental deformation in the Africa-Arabia-Eurasia continental collision zone and implications for the dynamics of plate interactions
Robert Reilinger,Simon McClusky,Philippe Vernant,Shawn Lawrence,Shawn Lawrence,Semih Ergintav,R. Cakmak,Haluk Ozener,Fakhraddin Kadirov,Ibrahim Guliev,Ruben Stepanyan,Merab Nadariya,Galaktion Hahubia,Salah Mahmoud,K. Sakr,Abdullah ArRajehi,Demitris Paradissis,A. Al-Aydrus,Mikhail Prilepin,Tamara Guseva,Emre Evren,Emre Evren,Andriy Dmitrotsa,S. V. Filikov,Francisco Gomez,R. Al-Ghazzi,Gebran N. Karam +26 more
TL;DR: In this article, an elastic block model was developed to constrain present-day plate motions (relative Euler vectors), regional deformation within the interplate zone, and slip rates for major faults.
Journal ArticleDOI
A geodetic plate motion and Global Strain Rate Model
TL;DR: The Global Strain Rate Model (GSRM v.2.1) as mentioned in this paper is a new global model of plate motions and strain rates in plate boundary zones constrained by horizontal geodetic velocities.
Journal ArticleDOI
Present-day kinematics of the Mediterranean: A comprehensive overview of GPS results
TL;DR: In this article, a geodetic horizontal velocity field consistent at the scale of the Mediterranean and the surrounding Alpine belts is derived to discuss the boundary conditions around each major deforming area in the Mediterranean, to describe the main patterns of motion and deformation, to critically review the existing kinematics models and to finally point out the main unresolved kinematic questions.
Journal ArticleDOI
The angular velocities of the plates and the velocity of Earth's centre from space geodesy
Donald F. Argus,Richard G. Gordon,Michael Heflin,Chopo Ma,Richard J. Eanes,Pascal Willis,Pascal Willis,W. Richard Peltier,Susan Owen +8 more
TL;DR: In this article, a set of relative plate angular velocities, called GEODVEL (for GEODesy VELocity) is presented, which is based on the estimation of the position of the Earth's center and the assignment of sites to plates.
Journal ArticleDOI
The southernmost margin of the Tethys realm during the Mesozoic and Cenozoic: Initial geometry and timing of the inversion processes
Dominique Frizon de Lamotte,Camille Raulin,Nicolas Mouchot,Jean-Christophe Wrobel-Daveau,Christian Blanpied,Jean-Claude Ringenbach +5 more
TL;DR: The existence of synchronous geodynamic events from one end of the system to the other, although they do not have the same meaning, is emphasized in this article, where two of them are particularly important: the Campanian-Santonian (C-S) event corresponds to obduction and exhumation of high pressure-low-temperature metamorphic rocks around the Arabian promontory, inversion along the margins of the East Mediterranean basins, and lithosphere buckling in the Atlas system (Maghreb and adjacent Sahara platform).
References
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Marine geologic evidence for a Levantine-Sinai plate, a new piece of the Mediterranean puzzle
Jean Mascle,Jean Benkhelil,Gilbert Bellaiche,Tiphaine Zitter,J.M. Woodside,Lies Loncke,Prismed Ii Scientific Party +6 more
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors infer that this tectonic belt might correspond to an offshore extension of the Gulf of Suez rift system, which is the western boundary of a Levantine-Sinai microplate, locked between the major Arabia and Africa plates and the Anatolian-Aegean microplate.
Journal ArticleDOI
Pattern of mantle thinning from subsidence and heat flow measurements in the Gulf of Suez: Evidence for the rotation of Sinai and along-strike flow from the Red Sea
TL;DR: In this paper, a combined analysis of tectonic subsidence, heat flow and uplift data for the Gulf of Suez is presented. But the results show significant differences along the length of the rift.
Related Papers (5)
GPS constraints on continental deformation in the Africa-Arabia-Eurasia continental collision zone and implications for the dynamics of plate interactions
Robert Reilinger,Simon McClusky,Philippe Vernant,Shawn Lawrence,Shawn Lawrence,Semih Ergintav,R. Cakmak,Haluk Ozener,Fakhraddin Kadirov,Ibrahim Guliev,Ruben Stepanyan,Merab Nadariya,Galaktion Hahubia,Salah Mahmoud,K. Sakr,Abdullah ArRajehi,Demitris Paradissis,A. Al-Aydrus,Mikhail Prilepin,Tamara Guseva,Emre Evren,Emre Evren,Andriy Dmitrotsa,S. V. Filikov,Francisco Gomez,R. Al-Ghazzi,Gebran N. Karam +26 more