Kinetic-energy induced smoothening and delay of epitaxial breakdown in pulsed-laser deposition
Byungha Shin,Michael J. Aziz +1 more
Reads0
Chats0
TLDR
In this paper, the effect of kinetic energy of depositing species from flux pulsing during pulsed-laser deposition (PLD) on surface morphology evolution of Ge(001) homoepitaxy at low temperature was isolated.Abstract:
We have isolated the effect of kinetic energy of depositing species from the effect of flux pulsing during pulsed-laser deposition (PLD) on surface morphology evolution of Ge(001) homoepitaxy at low temperature $(100\phantom{\rule{0.2em}{0ex}}\ifmmode^\circ\else\textdegree\fi{}\mathrm{C})$. Using a dual molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) PLD chamber, we compare morphology evolution from three different growth methods under identical experimental conditions except for the differing nature of the depositing flux: (a) PLD with average kinetic energy $300\phantom{\rule{0.3em}{0ex}}\mathrm{eV}$ (PLD-KE); (b) PLD with suppressed kinetic energy comparable to thermal evaporation energy (PLD-TH); and (c) MBE. The thicknesses at which epitaxial breakdown occurs are ranked in the order $\mathrm{PLD}\text{\ensuremath{-}}\mathrm{KE}g\mathrm{MBE}g\mathrm{PLD}\text{\ensuremath{-}}\mathrm{TH}$; additionally, the surface is smoother in PLD-KE than in MBE. The surface roughness of the films grown by PLD-TH cannot be compared due to the early epitaxial breakdown. These results demonstrate convincingly that kinetic energy is more important than flux pulsing in the enhancement of epitaxial growth, i.e., the reduction in roughness and the delay of epitaxial breakdown.read more
Figures
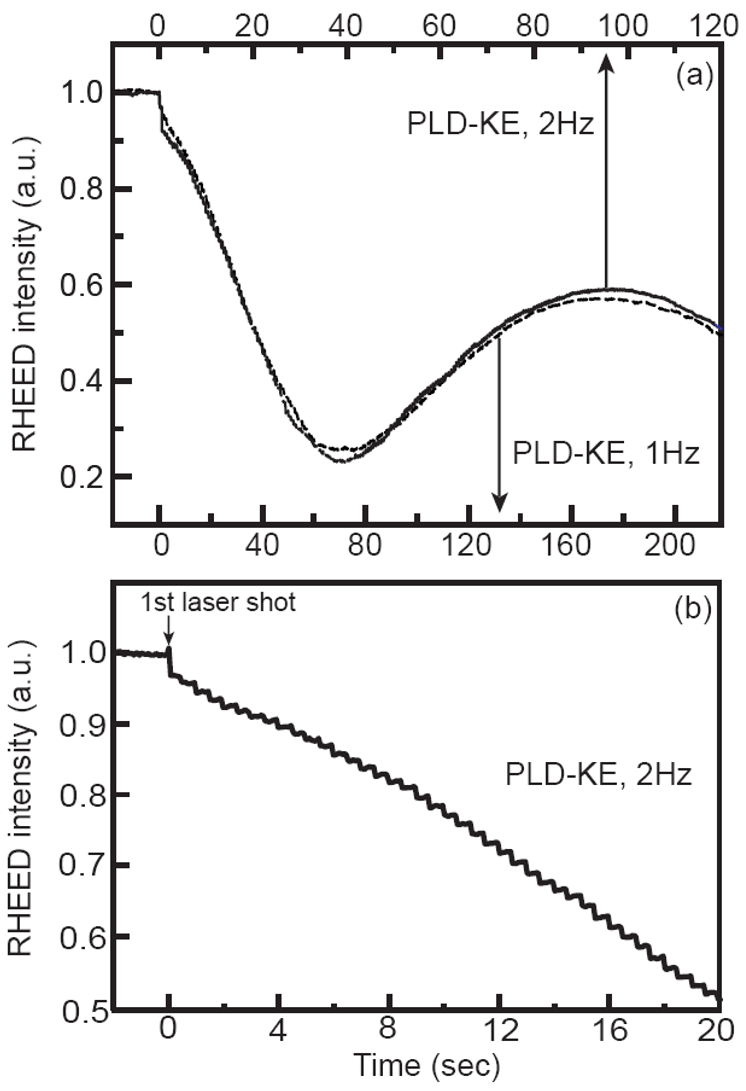
Fig. 4. (a) RHEED specular intensity variations during PLD-KE with 1 Hz (dashed line) and 2 Hz (solid line) of repetition rate while keeping instantaneous flux the same in both cases. Time axes are adjusted such that intensity minima and maxima for both cases are aligned at the same positions on abscissa. (b) First 20 seconds of RHEED intensity variation of PLD-KE with 1 Hz from (a). Modulations from individual laser pulses are visible. 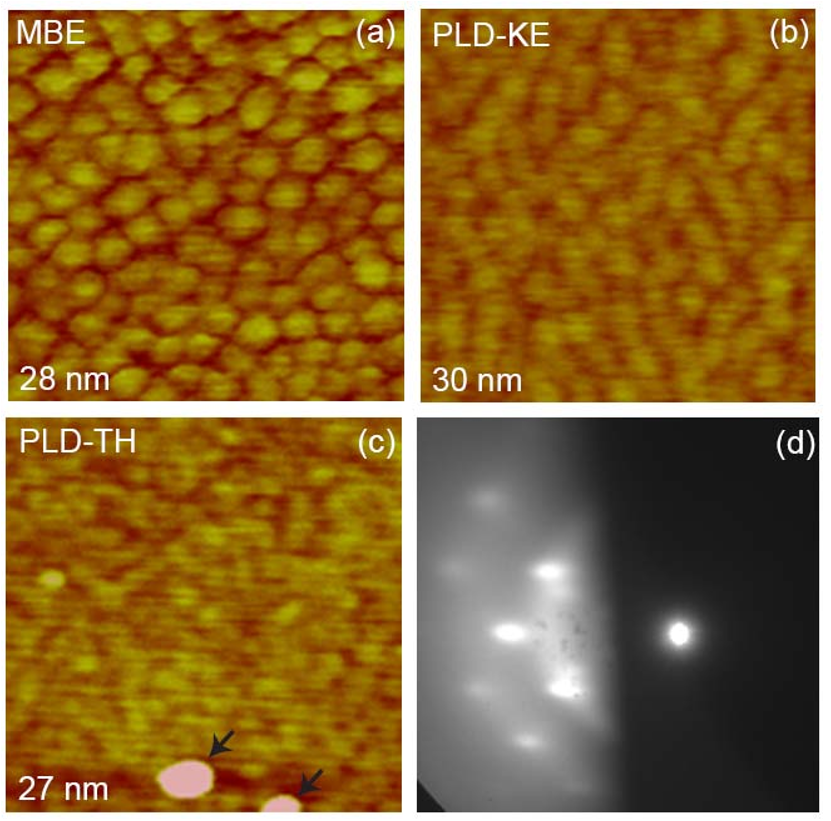
Fig. 2. (Color online) AFM images of films grown at 100 °C by (a) MBE, (b) PLD-KE, and (c) PLD-TH, and (d) RHEED pattern taken from surface shown in (c). Scan size and vertical scale of (a) – (c) are 0.25 x 0.25 μm2 and 5 nm, respectively. Thickness of films in (a) – (c) is shown in the left bottom corner of each image. 
Table I. Epitaxial thickness of PLD-KE, PLD-TH, and MBE at 100 °C and 150 °C. In the case of PLD-KE, the thickest samples – 270 nm at 100 °C and 410 nm at 150 °C – are still fully epitaxial.
Citations
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Recent advances in pulsed-laser deposition of complex oxides
Hans M. Christen,Gyula Eres +1 more
TL;DR: Detailed growth kinetics results are discussed, which illustrate that 'true' layer-by-layer (LBL) growth can only be approached, not fully met, even though many characterization techniques reveal interfaces with unexpected sharpness.
Journal ArticleDOI
Film Growth Mechanisms in Pulsed Laser Deposition
TL;DR: In this article, a comparison of growth morphology evolution for pulsed laser deposition and thermal deposition in the same dual-use chamber under identical thermal, background, and surface preparation conditions, and varying the kinetic energy by varying the laser fluence or using an inert background gas was made.
Journal ArticleDOI
Impact of the interplay between nonstoichiometry and kinetic energy of the plume species on the growth mode of SrTiO 3 thin films
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors studied the pulsed laser deposition of homoepitaxial SrTiO3 thin films in different deposition regimes in order to elucidate the possibility to promote two-dimensional growth by increasing the kinetic energy of the oncoming particles.
Journal ArticleDOI
Pulsed laser deposition of nanoparticle films of Au
TL;DR: In this paper, Nanosecond pulsed laser deposition (PLD) has been used to grow nanoparticle films of Au on Si and sapphire substrates, and the equivalent solid density thickness was measured with a quartz crystal monitor and the ion flux was measured using a time-of-flight Langmuir probe.
Journal ArticleDOI
Evolution of InGaAs quantum dot molecules
TL;DR: In this paper, the formation and evolution process of self-assembled InGaAs quantum dot molecules (QDMs) is studied in terms of configuration, volume, and types of QDMs.
References
More filters
Journal Article
Comparison of Morphology Evolution of Ge(001) Homoepitaxial Films Grown by Pulsed Laser Deposition and Molecular Beam Epitaxy
TL;DR: In this paper, a dual molecular-beam epitaxy (MBE)-pulsed laser deposition (PLD) ultrahigh vacuum chamber was used to compare Ge(001) homoepitaxial growth morphology in PLD and MBE.
Journal ArticleDOI
Role of Cluster Transient Mobility in Pulsed Laser Deposition-Type Growth Kinetics
E. Vasco,J. L. Sacedón +1 more
TL;DR: The ballistic motion of kinetically hyperthermal clusters on corrugated potential energy surfaces is studied by molecular dynamics simulations to explain the enhancement of growth kinetics by pulsed laser deposition.
Journal ArticleDOI
Epitaxial Si(001) grown at 80–750 °C by ion‐beam sputter deposition: Crystal growth, doping, and electronic properties
TL;DR: In this article, an epitaxial undoped and Sb-doped Si films were grown on Si(001) substrates at temperatures between 80 and 750°C by ultrahigh-vacuum Kr+−ion-beam sputter deposition (IBSD).
Journal ArticleDOI
Enhancement of low‐temperature critical epitaxial thickness of Si(100) with ion beam sputtering
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors have grown an ion beam sputtered Si epitaxially on Si(100) at substrate temperatures between 390 and 480 K. At lower T, they observed an abrupt transition to amorphous growth at a critical thickness, he, which exhibited an Arrhenius dependence on T.
Journal ArticleDOI
Unconventional MBE strategies from computer simulations for optimized growth conditions
TL;DR: In this paper, the influence of step edge diffusion and desorption on MBE growth was investigated using kinetic Monte-Carlo simulations of the solid-on-solid (SOS) model.
Related Papers (5)
Role of Cluster Transient Mobility in Pulsed Laser Deposition-Type Growth Kinetics
E. Vasco,J. L. Sacedón +1 more