Q2. What is the role of p53 suppressor tumor gene in cancer?
It is known that the p53 suppressor tumor gene has a key role in stress cellular response, to preserve genome stability, and it is universally recognized as a human cancer marker when it is mutated.
Q3. What is the role of the DEC1 protein in causing squamous cell?
Overexpression of the DEC1 Protein InducesSenescence In Vitro and Is Related to Better Survival in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.
Q4. What is the AA genotype of the ADH1B R48H gene?
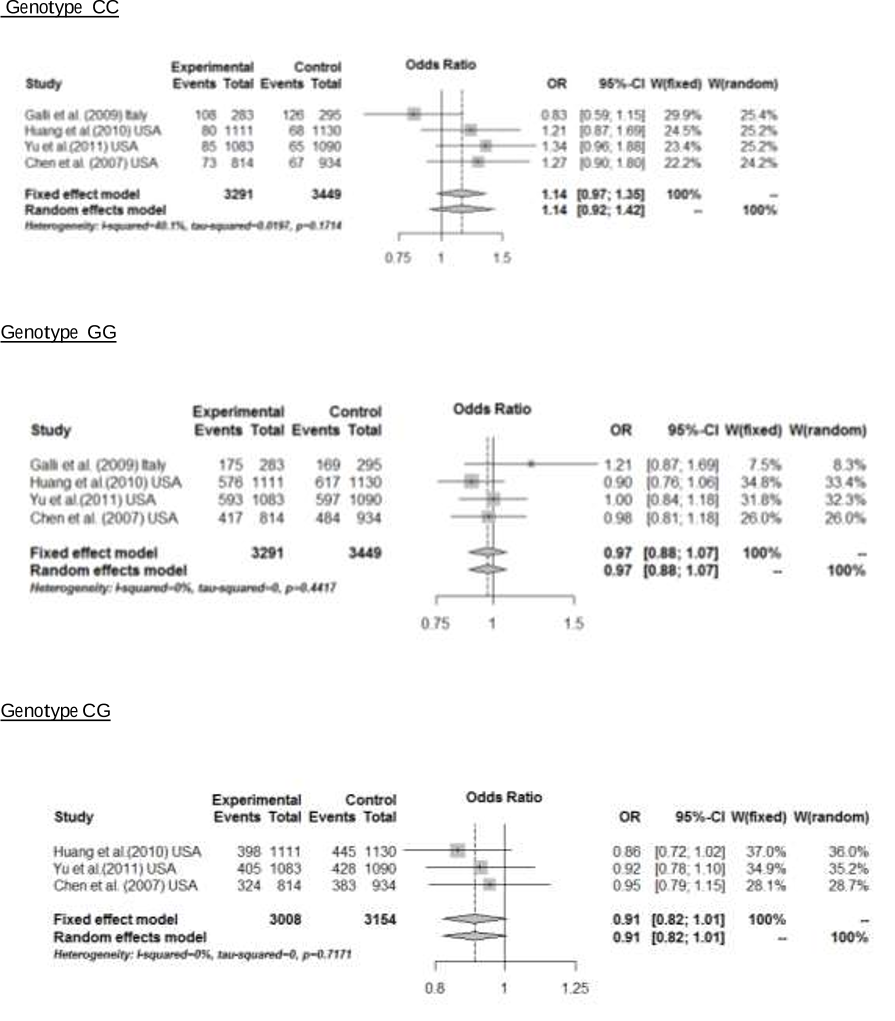
59 The AA genotype of the ADH1B R48H gene encodes an enzyme that is about 40 times more active than the enzyme encoded by AG and GG genotypes.
Q5. What is the significance of the evaluation of diagnostic markers?
The evaluation of diagnostic markers such as symptoms and genetic tests helps to increase the sensitivity or specificity of the determination of the presence/absence of malignancy.
Q6. Who have observed inflammatory infiltrate in epithelial dysplasia?
Authors such as Piva et al. 48 have observed inflammatory infiltrate in epithelial dysplasia with overexpression of NFKB and TNF-α, establishing a connection between the cancer and inflammation.
Q7. What is the significance of the allele G of CRYAB C-802G?
61,62 Research by Su et al. 62 showed that allele G of CRYAB C-802G is correlated to breast cancer risk, and could be useful as a clinical marker for its early detection.
Q8. What are the main features of the model proposed in this paper?
the model proposed in this paper could fit models 1, 2, and 3 because it considers such epigenetic events as inflammation, mutational compounds such as tobacco and alcohol, and genomic stability and the cell cycle regulation process.
Q9. What databases were used for the systematic review and meta-analysis?
The authors conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of case-control studies from the MEDLINE, Scopus, Cochrane, and CancerLit databases between January 2007 and January 2013.
Q10. What are the main factors that affect the incidence of cancer?
3,29 Cancer is a complex pathology, and its incidence and survival index are closely related to social, cultural and socio-economic determinants of health.
Q11. What is the role of alanine in the squamous cell carcinoma?
Pradhan S, Nagashri MN, Gopinath KS, Kumar A.Expression profiling of CYP1B1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma: counter intuitive down regulation in tumors.
Q12. What is the gene that encodes glutathioneStransferase Mu 1?
This gene encodes glutathioneStransferase Mu 1, which is critical to detoxification and the removal of electrophilic carcinogens.
Q13. What is the definition of a risk polymorphism?
The identification of a predictive model of risk polymorphisms could help in early diagnosis, and in understanding disease recurrence and/or progression in the subset of patients.
Q14. What was the search strategy used to identify grey literature?
A search was made of combined electronic databases, and the bibliographies of all selected papers were searched to identify grey literature.