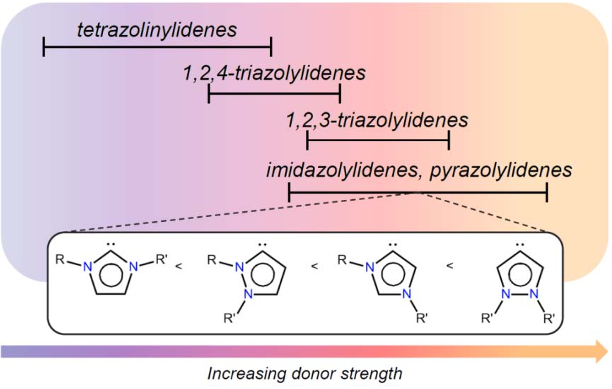
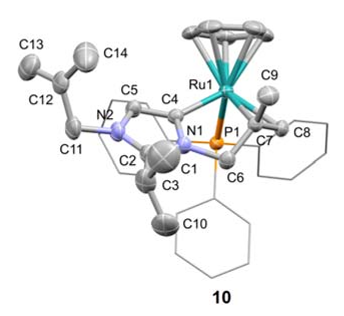
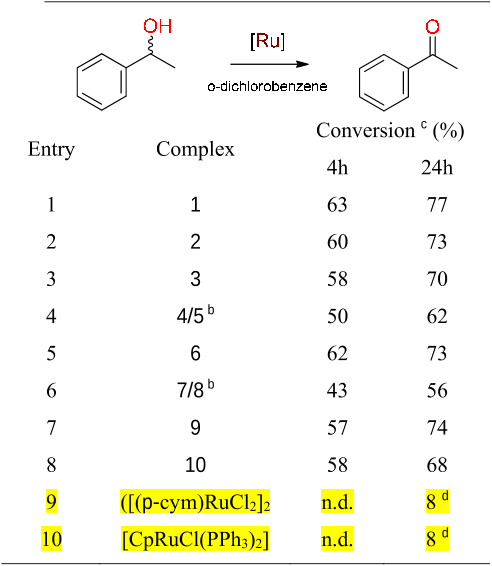
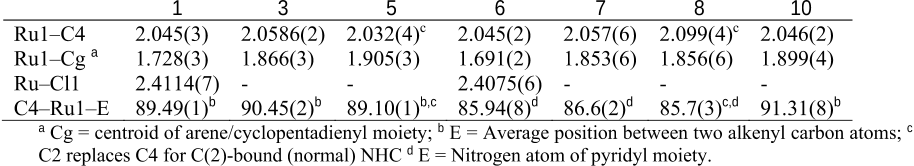Abstract: Metalation of a C2-methylated pyridylimidazolium salt with [IrCp*Cl2]2 affords either an ylidic complex, resulting from C(sp3)H bond activation of the C2-bound CH3 group if the metalation is performed in the presence of a base, such as AgO2 or Na2CO3, or a mesoionic complex via cyclometalation and thermally induced heterocyclic C(sp2)H bond activation, if the reaction is performed in the absence of a base. Similar cyclometalation and complex formation via C(sp2)H bond activation is observed when the heterocyclic ligand precursor consists of the analogous pyridyltriazolium salt, that is, when the metal bonding at the C2 position is blocked by a nitrogen rather than a methyl substituent. Despite the strongly mesoionic character of both the imidazolylidene and the triazolylidene, the former reacts rapidly with D+ and undergoes isotope exchange at the heterocyclic C5 position, whereas the triazolylidene ligand is stable and only undergoes H/D exchange under basic conditions, where the imidazolylidene is essentially unreactive. The high stability of the IrC bond in aqueous solution over a broad pH range was exploited in catalytic water oxidation and silane oxidation. The catalytic hydrosilylation of ketones proceeds with turnover frequencies as high as 6 000 h−1 with both the imidazolylidene and the triazolylidene system, whereas water oxidation is enhanced by the stronger donor properties of the imidazol-4-ylidene ligands and is more than three times faster than with the triazolylidene analogue.