Q2. What are the future works mentioned in the paper "The impact of supply chain integration on performance: a contingency and configuration approach" ?
While their study makes a significant contribution to the SCI literature and has important implications for practice, there are some limitations and opportunities for future studies. Because integration between customers, suppliers and manufacturers is developed over time, it will be fruitful for future research to examine the evolution of SCI patterns in a longitudinal fashion. Second, because the data were only collected from manufacturers, future studies can broaden their scope by collecting data from all supply chain partners, including suppliers, manufacturers and customers. Future research should examine cross-cultural differences in the relationship between SCI and performance.
Q3. How did the authors obtain a representative sample?
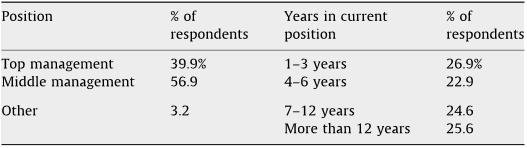
To obtain a representative sample, the authors used the Yellow Pages of China Telecom in each of the four mainland China cities and the directory of the Chinese Manufacturers Association in Hong Kong as their sampling pool.
Q4. What did Devaraj et al. (2007) find?
Devaraj et al. (2007) found that customer integration did not have a significant direct effect on operational performance, but only moderated the effect of supplier integration on operationalperformance.
Q5. What is the way to assess the common method bias?
To further assess common method bias, confirmatory factor analysis was applied to Harman’s single-factor model (Sanchez and Brock, 1996).
Q6. What is the average variance for each construct?
The estimates for the average variance extracted (AVE) were higher than 0.50 for four constructs, and 0.46 for the fifth construct.
Q7. What was the third step of the analysis?
The third step assessed the relationship between two- and three-way interactions of internal, customer and supplier integration and operational or business performance, in order to determine whether there was a moderating effect.
Q8. What is the relationship between supplier integration and operational performance?
Supplier integration may not contribute to operational performance directly, but instead interacts with customer integration in improving operational performance, reflecting the importance of manufacturers’ integration with both downstream and upstream supply chain partners.