Q2. What future works have the authors mentioned in the paper "Replication note: women's luxury products as signals to other women" ?
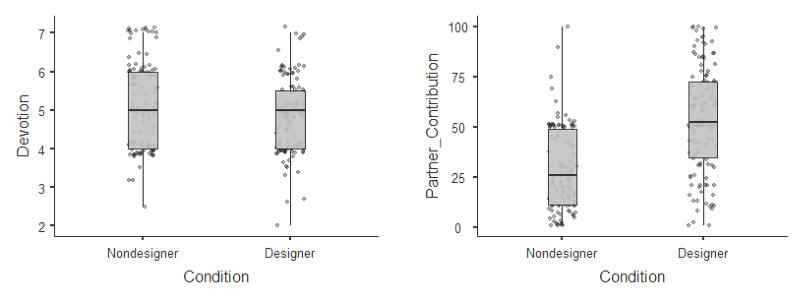
To eliminate this possibility, the authors conducted Study 2, a direct replication with designer ( vs. nondesigner ) products. One possibility is desirability bias. Another possibility is that women with luxury possessions were implicitly perceived to have materialistic traits, and the participants did not believe that the partner was devoted to a highly materialistic person. Future studies should further scrutinize the boundary conditions of the relationship between luxury products and partner devotion.