Communications
2015; 3(2): 35-41
Published online July 23, 2015 (http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/com)
doi: 10.11648/j.com.20150302.12
ISSN: 2328-5966 (Print); ISSN: 2328-5923 (Online)
A Technique for Improving Telecommunications Planning
Based on Indices of Growth
Thomas Kokumo Yesufu, Anthony Olutope Fakeye
Department of Electronic and Electrical Engineering, Obafemi Awolowo University, Ile-Ife, Nigeria
Email address:
thomas_yesufu@yahoo.com (T. K. Yesufu), anthonyolutope@gmail.com (A. O. Fakeye)
To cite this article:
Thomas Kokumo Yesufu, Anthony Olutope Fakeye. A Technique for Improving Telecommunications Planning Based on Indices of Growth.
Communications. Vol. 3, No. 2, 2015, pp. 35-41. doi: 10.11648/j.com.20150302.12
Abstract:
Subscribers’ indices of growth are essential for planning and ensuring the rapid pursuit of best practices by
telecommunication systems in Nigeria. Based on network principles and the established process of telecommunications
planning, a questionnaire was developed and administered to 300 stakeholders that were randomly selected from existing
subscriber communities across Nigeria. Subsequently, a Java software application for the analysis and planning of
telecommunication systems was developed using Netbeans Integrated Design Environment (IDE) for its Rapid Application
Development (RAD). It was found that Nigerian telecommunication planning fell below expectations despite the high
teledensity in Nigeria, and had 60% of the necessary user participation, 49% degree of communication, and 63% of demand-
driven services. Subsequently, a mobile application software system was developed such that the participation of subscribers in
the planning process was enlisted via a short message service (SMS) that uses a typical SMS delivery system for sorting out
spurious messages. By continuously linking the planning of telecommunications to subscribers’ indices of growth, the software
would improve reliability, effectively shorten the feedback loop for timely and accurate decision-making, reveal the magnitude
of acceptance of telecommunication services, and thereby bring about seamless network integration, technologically and on the
applications and service levels.
Keywords:
Telecommunication Planning, Feedback, Network Reliability, Decision Support Systems, Quality of Service
1. Introduction
Telecommunications is the engine of economic growth
with which all peoples can get connected seamlessly in
order to become a “global village”. This scenario makes
telecommunication a current national priority both in terms
of sustaining the rapid growth of subscribers as well as
improving on the existing telecommunication systems (e.g.,
NCC, 2011; ITU, 2011). Accordingly, a modern
telecommunication infrastructure is not only important for
domestic growth but also needed to connect domestic
market of commodities as well as credit with international
commodity and financial markets, this would develop the
smooth flow of foreign investment, positive value of net
exports, increase the value addition in GDP of an economy
etc.
With the advancement of telecommunication services, a
new market mechanism, low cost structure and expanded
value chain of firms is possible. On the other hand in
developing countries, the average price of agricultural
commodities is higher in other areas than in the areas where
there are no facilities to communicate (Bayes et al, 1999).
As the telecommunication capabilities of a country evolve
the relevant statistical measures appropriate to assessing
national performance change. No single measure is entirely
satisfactory in gauging performance. In addition
researchers and policy makers invariably face difficulties in
finding uniform data. Problems in this area can range from
definitional differences to a lack of uniform data collection
and management (Patridge, 1992).
Today’s telecommunication industry in Nigeria is
focusing on a way to improve their products and services as
well as sustaining the growth of subscribers (Adegbemi et
al., 2012). In view of this, most telecommunications service
providers are taking a critical look at their business
intelligence through network-inspired planning. Access to
information obviously marks the beginning of a good
telecommunication plan that focuses on sustainable

economic development, improved quality of life and the
attendant reduction of risks in hu
man activities and
development.
A telecommunication service is expected to grow in
demand, increase provider-user interactio
n and absorb new
streams of innovations whilst focusing on the required
depth of impact and future developments. There is no
gainsaying the fact that this expectation
telecommunication planning, which includes the collection
and analysis
of suitable data for timely and accurate
decision-making.
Planning relies heavily on available data
for analysis and decision making. The current trend
indicates that telecommunication planning is mostly based
on theoretical facts, assumed view of “experts
Telecommunication planning involves processes,
procedures, framework and guidelines that translate into
action(s).
This approach to telecommunication planning can
therefore be viewed as a set of tasks required for enhancing
appropriate decisions fo
r an effective action plan. In view
of this, a
low teledensity, inadequate quality of service,
fraudulent messaging, questionable subscriber participation
and provider/subscriber communications are some of the
consequences of inadequate planning. The probl
tele-
density, lack or minimal services suited for local socio
economic activities, questionable services performance and
minimal/absence of user centric planning approach inspired
the need to develop an improved technique. Consequently,
that will make the
planning of telecommunication system
to
fulfill the necessary and sufficient technological
requirements such as the physical connectivity between the
operators and the subscribers, the procedures for reliable
transfer of information and the qua
lity of service.
work
will address these consequences, and subsequently
evaluate the indices of growth in a telecommunication
system and then develop
a method for planning a mobile
telecommunication system, which will however be
benchmarked with the e
xisting methods for planning
telecommunication systems.
2. Theoretical Development
The Nigerian telecoms market offers a clear and exciting
opportunity for many telecom operators. This market is
highly deregulated with the NCC lice
nsing a wide variety
of telecom
s operators. This market has moved from zero to
hero in just under few years and is now considered a
leading opportunity for both telecom operators and
equipment suppliers.
The eight steps of the structured
planning process are illustrated in the Fig
with an Implementation Plan, must be presented to the
organization’s managers for decision making (Pietrasiewicz,
2000).
Communications 2015; 3(2): 35-41
economic development, improved quality of life and the
man activities and
A telecommunication service is expected to grow in
n and absorb new
streams of innovations whilst focusing on the required
depth of impact and future developments. There is no
gainsaying the fact that this expectation
relies heavily on
telecommunication planning, which includes the collection
of suitable data for timely and accurate
Planning relies heavily on available data
for analysis and decision making. The current trend
indicates that telecommunication planning is mostly based
on theoretical facts, assumed view of “experts
”, etc.
Telecommunication planning involves processes,
procedures, framework and guidelines that translate into
This approach to telecommunication planning can
therefore be viewed as a set of tasks required for enhancing
r an effective action plan. In view
low teledensity, inadequate quality of service,
fraudulent messaging, questionable subscriber participation
and provider/subscriber communications are some of the
consequences of inadequate planning. The probl
ems of low
density, lack or minimal services suited for local socio
economic activities, questionable services performance and
minimal/absence of user centric planning approach inspired
the need to develop an improved technique. Consequently,
planning of telecommunication system
s
fulfill the necessary and sufficient technological
requirements such as the physical connectivity between the
operators and the subscribers, the procedures for reliable
lity of service.
This
will address these consequences, and subsequently
evaluate the indices of growth in a telecommunication
a method for planning a mobile
telecommunication system, which will however be
xisting methods for planning
The Nigerian telecoms market offers a clear and exciting
opportunity for many telecom operators. This market is
nsing a wide variety
s operators. This market has moved from zero to
hero in just under few years and is now considered a
leading opportunity for both telecom operators and
The eight steps of the structured
planning process are illustrated in the Fig
. 1. This solution,
with an Implementation Plan, must be presented to the
organization’s managers for decision making (Pietrasiewicz,
Fig. 1. Telecom/IT planning steps
adapted from Pietrasiewicz (
Fig. 2.
A block diagram of the business model.
The present ICT industry indicates that
and applications are going to change radically in the future.
The future evolution of mobile applications and services
means seamless integration,
the applications
and service level
solut
ions for users. The attractiveness of mobile
applications and services in the future relies heavily on
comprehensive fulfillment of user needs. The c
situation in telecom
s is going to change in the countries
where the mobile markets are maturing
will make the traditional business models of mobility less
attractive. Companies need to seek turnkeys to new
sustainable business models, since many of the models in
36
adapted from Pietrasiewicz (
2000).
A block diagram of the business model.
The present ICT industry indicates that
mobile services
and applications are going to change radically in the future.
The future evolution of mobile applications and services
both technologically and on
and service level
, towards more attractive
ions for users. The attractiveness of mobile
applications and services in the future relies heavily on
comprehensive fulfillment of user needs. The c
ompetitive
s is going to change in the countries
where the mobile markets are maturing
and the competition
will make the traditional business models of mobility less
attractive. Companies need to seek turnkeys to new
sustainable business models, since many of the models in

37 Thomas Kokumo Yesufu and Anthony Olutope Fakeye: A Technique for Improving Telecommunications Planning
Based on Indices of Growth
use will become obsolete by focusing on a profit-based
feedback on the industry’s promotion (Fig. 2). At the same
time, telecom companies’ interests in integrating users and
their needs more tightly in the development processes have
increased by focusing on a growth-based feedback on the
industry’s acceptability and reliability. Fig. 3 shows that
new business opportunities are in the area of integrated
mobile application and service development, which takes
users’ overall needs more closely into account (Edelmann
and Koivuneimi 2004; and Kunz and Black, 1999).
Fig. 3. New opportunities’ development model.
Reliability is the ability of an item to perform a function
acceptable to the user without failure under stated conditions
for a stated period. Telecommunication system planning is
concerned with the design and maintenance of large network
at a reasonable cost in order to deliver high capacity and
speed. In telecommunication systems, the network design
problem is challenging engineering and a mathematical one,
even when all the sites behave in the mode for which the
system is designed, all links are in the mode for which the
network is designed and all links provide the level of service
expected. The concept of reliability depicts the probability of
a system to have an expected performance over a time
interval, so the reliability of a system depends on its
configuration and the reliability of its components. In real
life, however, through human faults, design faults,
operational faults, environmental factors, or random wear out,
sites and links do not always function correctly. The
telecommunication planner must therefore address the
reliability issue (Colbourn, 2009). The reason for all these is
to establish a feedback that would make planning approaches
to yield value added services and also impact positively on
the environment.
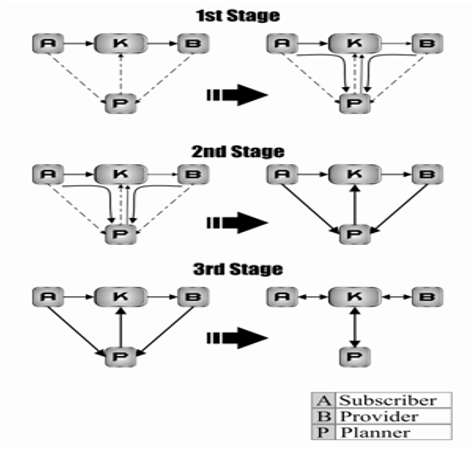
Connectivity links a provider to a node, and from there,
possibly, through other nodes to some final end-user
(subscriber) destination with which the initiating end-user
wants to communicate. There would seem to be two
interpretations of this definition. First, the equipment, both
switching and transmission facilities, are available to set up a
path from, say, Point A to Point B; assuming A and B to be
user end-points. The second interpretation would be that not
only are the circuits available but that they are connected and
ready to pass information or are in the information passing
mode. At this juncture, the end-users are assumed to be
telephone users, and the path that is set up may be for speech,
text, video, data, etc. Fig. 4 describes a flow diagram of a
planner (P) establishing a link between a subscriber (A) and
a provider (B).
Fig. 4. Stages for integrating planning with online subscriber and provider
participation.
It can be deduced that performance of a planning exercise
relies heavily on the likely unpredictable decision maker(s),
even though the actions contained in a plan are felt and
experienced. Since the decision makers are the key players
(K) that agreed to implement the action plan, the task of
easier and good decision making is a major approach to
improving planning and this can be indicated with the
following indices of growth:
2.1. Participation
This generally means having all involved to be represented
in the decision making process. This allowed issues to be
considered from different points of view but with the
knowledge of parties involved to serve as a guide to a
concise and effective solution. Since, expectedly, any
decision taken without the contribution of involved parties
will not reflect a truly acceptable solution.
2.2. Demand-Driven
This depicts that the felt effect of decision plays a lot in
evaluating planned actions as actions which satisfies the
desirable environment in all its ramifications will
undoubtedly be considered adequate or vice versa. However,
for such desirable acceptance, it is most often demand driven.
Therefore, performance will be considered based on the
yearnings of the patrons of telecommunication services.
2.3. Service Quality
The performance of any telecommunication system can be
verified based on its service quality. Service, on the other

hand,
is generally used to describe something offered to the
end-users of any network such as end-to-
end commu
or client-
server applications. If a network is inaccessible, the
service is clearly questionable. Different people see quality
of service as different concepts because various and
ambiguous quality of service problems exist. The users of a
network
service have the tendency of judging the quality of
service based on the frequency of failures of the network
more than its overall success in delivering information in a
consistent and reliable manner. The ambiguity within the
quality of service yields d
ifferent possible solutions to
various problems, which leaves somewhat of schism in the
networking industry on the issue of quality of service.
Quality of service,
as perceived by customers/subscribers
actually the level of satisfaction derived from
telecommunication network. As such, a very well planned
system will most likely have as its result a widely acceptable
service quality and a badly planned system will most likely
be providing unsatisfactory service quality.
2.4. Communication
The most effective technique for re
solving issues is
communications. T
herefore, for clearer understanding of
issues before decision makers without prejudice and for
better understanding of telecommunications environment, a
communication platform must be in place.
3. Experimental Procedure
Fig. 3 informed the use of the
field survey
determine the knowledge, practice and results of
telecommunication planning in Nigeria.
sampling the opinion of telecommunication use
practitioners.
Data collection for the execution of th
was carried out
through the administration of a structured
questionnaire to 300 respondents connected with the
activities of telecommunication organizations
develop an improved
technique for plann
telecommunication system.
The structured questions employed
identified performance indicators of
telecommunications
networks. The questions of the survey were
extracting information: on the mentioned per
indicators from existing systems
as shown in Fig.
perspective will attempt to evaluate separate platforms
presented by existing systems for observing the environment
and also how effective a
re these platforms, the degree of
attention paid to subscribers’
participation and level
reliability. The
questionnaire was randomly administered to
the six geo-
political zones in the country. The targeted
audience for the circulation was primarily subscribers and
providers of telecommunication services
states visited were Osun, Lagos, Kastina, Enugu, Anambra,
Federal Capital Terri
tory Kano, Bayelsa, Delta and Benue. A
breakdown of the results from the survey carried out
tabulated
using descriptive statistics to cover
Service Quality, Demand-
Driven, and Degree of
Communications 2015; 3(2): 35-41
is generally used to describe something offered to the
end commu
nication
server applications. If a network is inaccessible, the
service is clearly questionable. Different people see quality
of service as different concepts because various and
ambiguous quality of service problems exist. The users of a
service have the tendency of judging the quality of
service based on the frequency of failures of the network
more than its overall success in delivering information in a
consistent and reliable manner. The ambiguity within the
ifferent possible solutions to
various problems, which leaves somewhat of schism in the
networking industry on the issue of quality of service.
as perceived by customers/subscribers
, is
actually the level of satisfaction derived from
using a certain
telecommunication network. As such, a very well planned
system will most likely have as its result a widely acceptable
service quality and a badly planned system will most likely
solving issues is
herefore, for clearer understanding of
issues before decision makers without prejudice and for
better understanding of telecommunications environment, a
field survey
in this paper to
determine the knowledge, practice and results of
telecommunication planning in Nigeria.
This involved
sampling the opinion of telecommunication use
rs and
Data collection for the execution of th
e survey
through the administration of a structured
questionnaire to 300 respondents connected with the
activities of telecommunication organizations
in order to
technique for plann
ing a
centered on the
telecommunications
networks. The questions of the survey were
aimed at
extracting information: on the mentioned per
formance
as shown in Fig.
5. This
perspective will attempt to evaluate separate platforms
presented by existing systems for observing the environment
,
re these platforms, the degree of
participation and level
s of
questionnaire was randomly administered to
political zones in the country. The targeted
audience for the circulation was primarily subscribers and
in Nigeria. The
states visited were Osun, Lagos, Kastina, Enugu, Anambra,
tory Kano, Bayelsa, Delta and Benue. A
breakdown of the results from the survey carried out
were
using descriptive statistics to cover
Participation,
Driven, and Degree of
Communication, which have been identified as the
benchmarks for existing planning techniques
The response
s obtained from the survey,
performance indicators
shown in
for software development.
The software
participatory planning technique with
capability was
developed using Netbeans IDE (integrated
Design environment) for its RAD (Rapid Application
D
evelopment) feature, which assist
development. In addition,
the use of
(JDK) brings about ease
in the
solutions.
Fig. 5.
Perspectives against performance indicators
4. R
esults and Discussion
The technique applied for this analysis is based on
descriptive analysis
in which the votes of respondents were
counted and the percentage of votes against a performance
indicator was calculated based on votes against number of
circulated questionnaire. In
respondents were sampled. However, results from the
questionnaire of each respondent were classified based on
performance indicators i.e. each performance indicator has a
38
Communication, which have been identified as the
benchmarks for existing planning techniques
.
s obtained from the survey,
as against the
shown in
Fig. 5, created a pathway
The software
for an SMS-based
participatory planning technique with
anti-spamming
developed using Netbeans IDE (integrated
Design environment) for its RAD (Rapid Application
evelopment) feature, which assist
s in quick software
the use of
Java Development Kit
in the
deployment of these software
Perspectives against performance indicators
.
esults and Discussion
The technique applied for this analysis is based on
in which the votes of respondents were
counted and the percentage of votes against a performance
indicator was calculated based on votes against number of
circulated questionnaire. In
all, 200 (two hundred)
respondents were sampled. However, results from the
questionnaire of each respondent were classified based on
performance indicators i.e. each performance indicator has a

39 Thomas Kokumo Yesufu and Anthony Olutope Fakeye: A Technique for Improving Telecommunications Planning
Based on Indices of Growth
100% (hundred percent) score for the total expected response
while the actual response depicts the factual score from the
environment in percentage. Assertions were made based on
the magnitude of scores percentage of the respondents.
From the data collected and analyzed, Tables 1 – 4 were
created. In Table 1, it is observed that telecommunication
organizations’ planning activities lacked the required
participation of all stakeholders. Table 2 shows that the
subscriber services were of low quality. Furthermore, Table 3
revealed that most of the services provided were not
demand-driven. With this repine, it is clear that
communication exists between providers and subscribers but
with a high rate of non-reliance on such platforms; hence, the
degree of communication is questionable as shown in Table 4.
Table 1. Participation.
S/N ACTIVITIES RESPONDENTS (%)
1
Claimed indirect or direct
involvement in planning
20
2
Interest are not particularly
represented
35
3 Interest particularly represented 15
4 No involvement in planning 26
5 Indecisive 4
TOTAL
100
Table 2. Service quality.
S/N ACTIVITIES RESPONDENTS (%)
1
Responded to unacceptable service
downtime
63
2 Responded to Crosstalk 10
3 Responded to High Tariffs 6
4 Responded to indifferent 12
5 Responded to satisfactory services 9
TOTAL
100
Table 3. Demand driven.
S/N ACTIVITIES RESPONDENTS (%)
1 Responded to unknown application 65
2 Responded to basic services 25
3 Responded to understand service 10
TOTAL
100
Table 4. Degree of communication.
S/N ACTIVITIES RESPONDENTS (%)
1 Do not rely on forum/for a 49
2 Relies on Operator’s fora 21
3 Relies on Customer Service 30
TOTAL
100
Fig. 6. Flow chart of the participatory technique.
Fig. 7. Flow chart of an Anti-Spam technique.