Q2. How is the problem of finding shortest order picking tours in a warehouse solved?
In practice, the problem of finding order picking tours in a warehouse is mainly solved by the so-called S-shape heuristic in which order pickers move in a S-shape curve along the pick locations skipping the aisles where nothing has to be picked.
Q3. Why is the small peak for 3 aisles in the curve for the warehouse without cross aisles?
The small peak for 3 aisles in the curve for the warehouse without cross aisles, is due to the fact that at least one of the aisles has to be entered and left from the same side to ensure that the order picker ends his tour at the front of the warehouse.
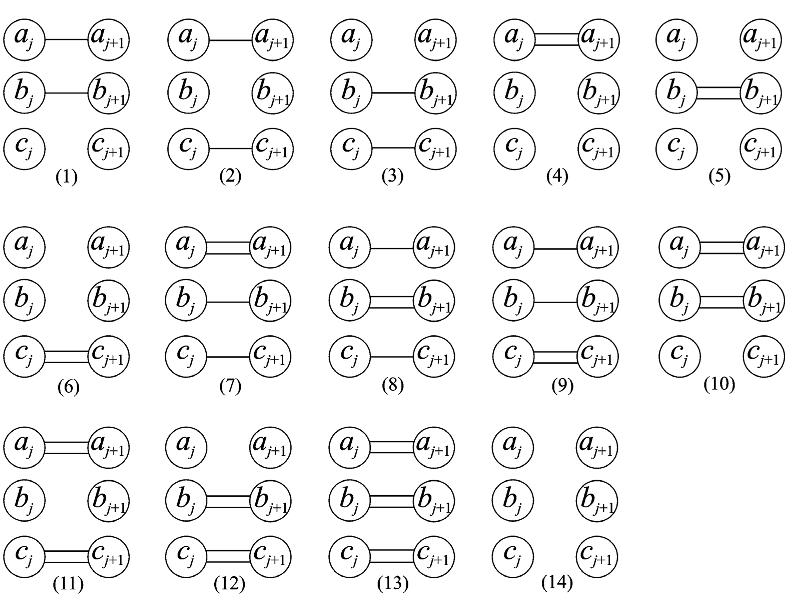
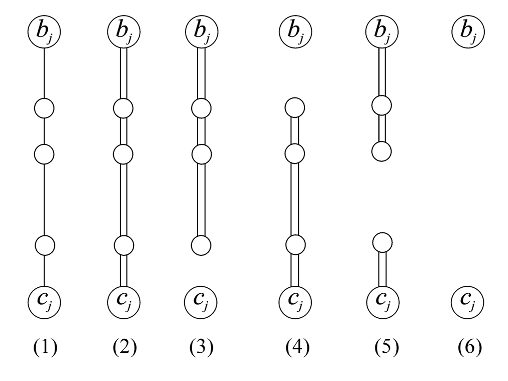
Q4. What is the length of a subgraph of the warehouse graph?
Let Yj be the subgraph of the warehouse graph consisting of vertices bj and cj together with all edges and vertices between bj and cj and define L+yj = L − j ∪ Yj .
Q5. What are the other activities that have to be performed?
Other order picking activities, like positioning the truck or crane at the pick location, picking items from the pick location and putting them onto a product carrier, have to be performed anyway.
Q6. How can the algorithm be used in warehouses with only one or two possibilities for aisle changing?
the algorithm can be used in warehouses with only one or two possibilities for aisle changing, by setting the appropriate distances between the aisles to infinity.