A fractional step method to compute a class of compressible gas–liquid flows
Jean-Marc Hérard,Olivier Hurisse +1 more
TLDR
In this article, the authors present some algorithms dedicated to the computation of numerical approximations of a class of two-fluid two-phase flow models and give the main properties of these models.About:
This article is published in Computers & Fluids.The article was published on 2012-02-15 and is currently open access. It has received 48 citations till now. The article focuses on the topics: Relaxation (approximation) & Uniqueness.read more
Figures
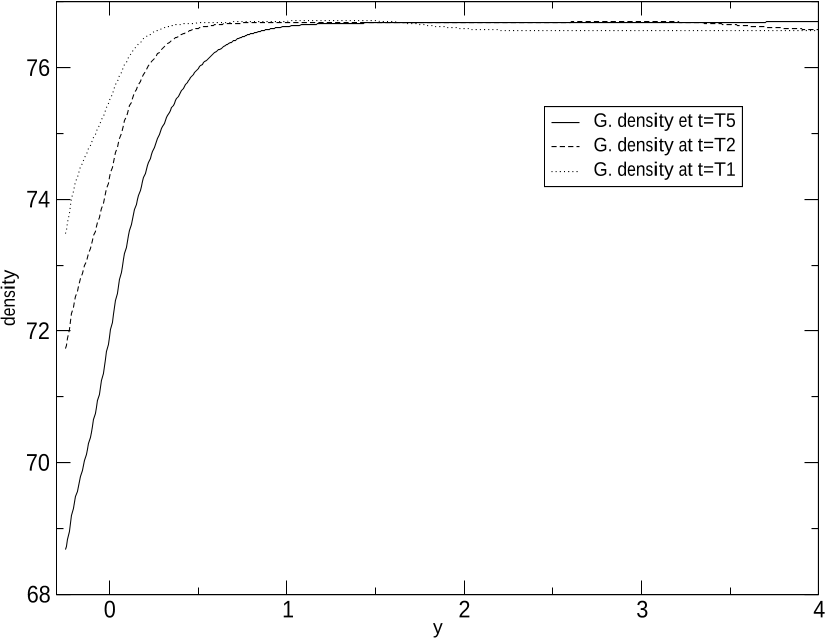
Figure 11: Heated wall: y-profile of the gas density ρg at three distinct times T = T1 (dotted line), T2 (dashed line), T5 (plain line), at: x = 2. The small cavity in the wall boundary corresponds to −0.25 < y < 0. 
Table 1: : Initial condition for the first Riemann problem and intermediate states. 
Figure 3: Approximate solution of the second Riemann problem obtained with 100000 cells and the exact solution (ex.) at time t = 1.4 10−4. Top left: liquid fraction, top right: pressures, bottom left: densities, bottom right: velocities. 
Figure 2: L1 norm of the error for the first Riemann problem. Plain lines: gas, dotted lines: liquid. Liquid mass fraction (crosses), velocities (squares), pressures (triangles), densities (circles). Meshes contain 500000, 250000, 50000, 5000, 500 and 50 regular cells. 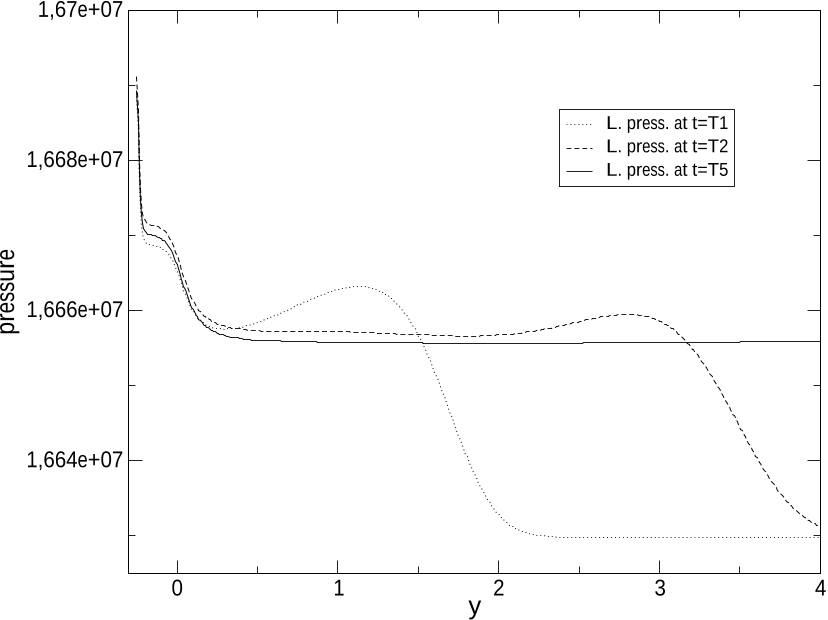
Figure 12: Heated wall: y-profiles of gas and liquid pressures Pg, Pl at three distinct times T = T1 (dotted line), T2 (dashed line), T5 (plain line), at: x = 2. The small cavity in the wall boundary corresponds to −0.25 < y < 0. 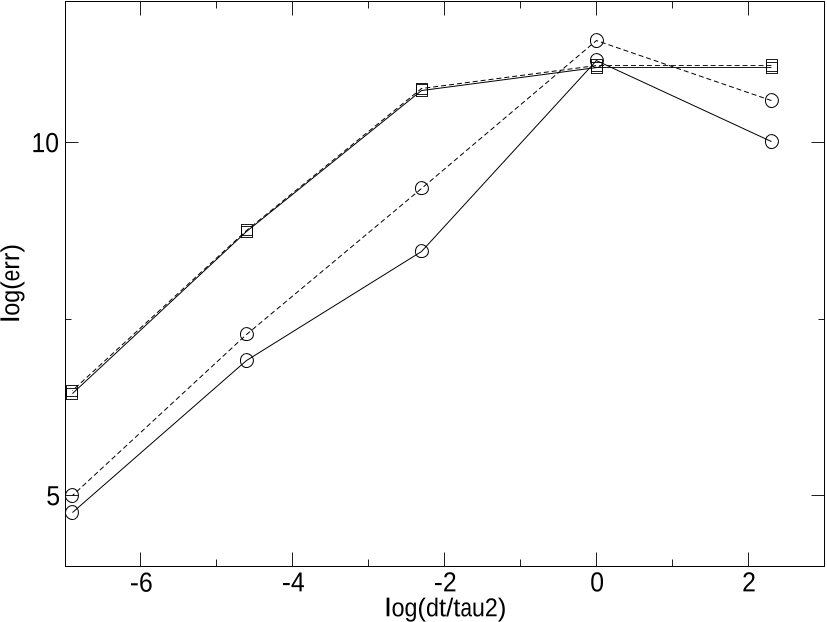
Figure 7: Pressure relaxation substep: measured L1 norm of the error for the liquid pressure (straight line) and the gas pressure (dotted line) at time T = 10−5 as a function of ∆t/τ2 = {10, 1, 10−1, 10−2, 10−3}. Implicit scheme (20) (circles) versus half-implicit scheme (squares).
Citations
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Numerical simulation of a compressible two-layer model: A first attempt with an implicit–explicit splitting scheme
TL;DR: This work is devoted to the numerical simulation of the compressible two-layer model developed in [16], an hyperbolic two-fluid two-pressure model dedicated to gas-liquid flows in pipes, especially stratified air-water flows.
Journal ArticleDOI
Various choices of source terms for a class of two-fluid two-velocity models
TL;DR: In this article, the authors propose different non-classical forms for the source terms of the Baer-Nunziato model, which are more linear with respect to the conservative variables.
Journal ArticleDOI
Simulation and preliminary validation of a three-phase flow model with energy
Hamza Boukili,Jean-Marc Hérard +1 more
TL;DR: The fractional step method proposed herein complies with the continuous entropy inequality, and implicit schemes that are considered to account for relaxation terms take their roots on the true relaxation process.
Journal ArticleDOI
Simulations of liquid-vapor water flows with non-condensable gases on the basis of a two-fluid model
Olivier Hurisse,Lucie Quibel +1 more
TL;DR: In this paper, an extension of the classical Baer-Nunziato two-fluid model is presented in order to account for the non-condensable gases, and a new algorithm is proposed here for the pressure relaxation effect.
Journal ArticleDOI
Adsorption in complex porous networks with geometrical and chemical heterogeneity
TL;DR: In this article, a simple algorithm to create 2D lattice-based models of porous deposits of preformed nanometric particles, by mimicking to some extent the physics of the actual deposition/aggregatio...
References
More filters
Journal Article
Finite difference methods for numerical computation of discontinous solutions of the equations of fluid dynamics
Finite difference method for numerical computation of discontinuous solutions of the equations of fluid dynamics
S. K. Godunov,I. Bohachevsky +1 more
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors proposed a method of characteristics used for numerical computation of solutions of fluid dynamical equations is characterized by a large degree of non standardness and therefore is not suitable for automatic computation on electronic computing machines, especially for problems with a large number of shock waves and contact discontinuities.
Book
Thermo-Fluid Dynamics of Two-Phase Flow
Mamoru Ishii,Takashi Hibiki +1 more
TL;DR: In this article, two-phase field equations based on time average are proposed. But they do not consider the effect of structural materials in a control volume on the two-fluid model.
Journal ArticleDOI
A two-phase mixture theory for the deflagration-to-detonation transition (ddt) in reactive granular materials
Melvin R. Baer,J.W. Nunziato +1 more
TL;DR: In this article, a two-phase mixture theory is presented which describes the deflagration-to-detonation transition (DDT) in reactive granular materials, based on the continuum theory of mixtures formulated to include the compressibility of all phases and the compaction behavior of the granular material.
Journal ArticleDOI
A Multiphase Godunov Method for Compressible Multifluid and Multiphase Flows
Richard Saurel,Rémi Abgrall +1 more
TL;DR: A new model and a solution method for two-phase compressible flows is proposed that provides reliable results, is able to compute strong shock waves, and deals with complex equations of state.
Related Papers (5)
A two-phase mixture theory for the deflagration-to-detonation transition (ddt) in reactive granular materials
Melvin R. Baer,J.W. Nunziato +1 more