A shape-constraint adversarial framework with instance-normalized spatio-temporal features for inter-fetal membrane segmentation
Alessandro Casella,Alessandro Casella,Sara Moccia,Dario Paladini,Emanuele Frontoni,Elena De Momi,Leonardo S. Mattos +6 more
TLDR
In this paper, a new deep learning framework for inter-fetal membrane segmentation on in-vivo fetoscopic videos is presented, which enhances existing architectures by encoding a novel (instance-normalized) dense block, invariant to illumination changes, that extracts spatio-temporal features to enforce pixel connectivity in time, and relying on an adversarial training, which constrains macro appearance.About:
This article is published in Medical Image Analysis.The article was published on 2021-02-19 and is currently open access. It has received 9 citations till now.read more
Figures

Figure 10: Sample frames in which the membrane is not present.Each frame was extracted from a video not used to train the network, as described in Sec. 3.4. The predicted segmentation is highlighted in yellow. 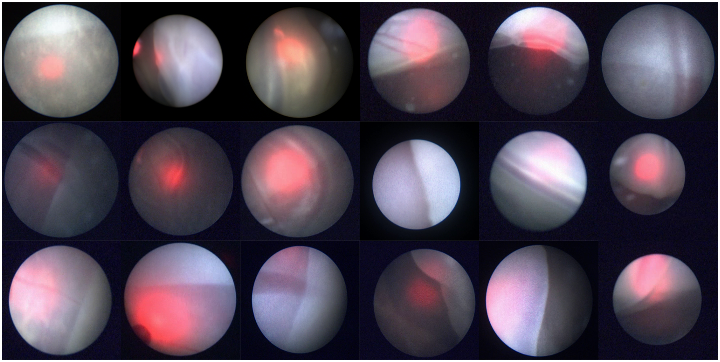
Figure 1: Sample frames from our dataset. The frames are extracted from intra-operative videos acquired in the actual surgical practice for Twin-to-Twin Transfusion Syndrome (TTTS). Each frame refers to a different video. Although video acquisition was performed with the same equipment, the frames present high variability, in terms of: (i) different membrane position, shape, tissue area in the field of view, contrast and texture, (ii) noise and blur, (iii) presence of amniotic fluid particles, (iv) vessels along the membrane equator, (v) different levels of illumination, (vi) presence of laser-guide light. 
Table 1: Architecture details for the (top) segmentor and (bottom) critic. The IN Conv3D and BN Conv3D refer to Instance Normalization - leaky ReLu - 3D Convolution and Batch Normalization - leaky ReLu - 3D Convolution, respectively. 
Figure 8: Sample results of inter-fetal membrane segmentation for three consecutive frames in a clip. Results are shown for the (second column) 2D adversarial framework and (third column) the proposed framework. The gold standard and segmentation prediction are highlighted in white and yellow, respectively. 
Table 4: Results of the sliding window configuration tested in E5, E6 in the ablation study. Segmentation Accuracy (Acc), Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC ) and Sensitivity (Sens) on the test set are reported in terms of mean ± standard deviation. The best results are highlighted in bold. 
Figure 5: Boxplot of performance comparison between E1, E2, E3, E4 in the ablation study and Casella et al. (2020). The comparison is shown in terms of Dice similarity coefficient (DSC ) for each fold. Black asterisks highlight significant differences between the different architectures (Mann–Whitney–Wilcoxon) (∗p < 0.05, ∗ ∗ p < 0.01, ∗ ∗ ∗p < 0.001).
Citations
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
A Review on Deep-Learning Algorithms for Fetal Ultrasound-Image Analysis
Maria Chiara Fiorentino,Francesca Pia Villani,Mariachiara Di Cosmo,Emanuele Frontoni,Sara Moccia +4 more
TL;DR: A detailed survey of the most recent work in the field can be found in this paper , with a total of 145 research papers published after 2017 and each paper is analyzed and commented on from both the methodology and application perspective.
Journal ArticleDOI
Artificial intelligence in the diagnosis of necrotising enterocolitis in newborns
Arkadiusz Sitek,Joanna Seliga-Siwecka,Szymon Płotka,Michał K. Grzeszczyk,Szymon Seliga,Krzysztof Wlodarczyk,Renata Bokiniec +6 more
TL;DR: A literature search on the use of AI in the diagnosis of NEC yielded 118 publications that were reduced to 8 after screening and checking for eligibility, and most publications showed promising results but no publications with evident clinical benefits were found.
Journal ArticleDOI
A deep learning approach to median nerve evaluation in ultrasound images of carpal tunnel inlet
Mariachiara Di Cosmo,Maria Chiara Fiorentino,Francesca Pia Villani,Emanuele Frontoni,Gianluca Smerilli,Emilio Filippucci,Sara Moccia +6 more
TL;DR: Wang et al. as discussed by the authors used Mask R-CNN with two additional transposed layers at segmentation head to accurately segment the median nerve directly on transverse US images, which achieved good performances both in median nerve detection and segmentation: Precision (Prec), Recall (Rec), Mean Average Precision (mAP) and Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC).
Journal ArticleDOI
FUN-SIS: a Fully UNsupervised approach for Surgical Instrument Segmentation
TL;DR: In this paper , a fully-unsupervised approach for binary Surgical Instrument Segmentation is proposed, which uses shape-priors as realistic segmentation masks of the instruments, not necessarily coming from the same dataset/domain as the videos.
Journal ArticleDOI
Computer‐assisted fetal laser surgery in the treatment of twin‐to‐twin transfusion syndrome: Recent trends and prospects
TL;DR: This review uncovers the literature on computer‐assisted software solutions focused on TTTS and evaluates the current maturity of technologies by the technology readiness level and enumerates the necessary aspects to bring these new technologies to clinical practice.
References
More filters
Proceedings ArticleDOI
Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition
TL;DR: In this article, the authors proposed a residual learning framework to ease the training of networks that are substantially deeper than those used previously, which won the 1st place on the ILSVRC 2015 classification task.
Book ChapterDOI
U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation
TL;DR: Neber et al. as discussed by the authors proposed a network and training strategy that relies on the strong use of data augmentation to use the available annotated samples more efficiently, which can be trained end-to-end from very few images and outperforms the prior best method (a sliding-window convolutional network) on the ISBI challenge for segmentation of neuronal structures in electron microscopic stacks.
Proceedings ArticleDOI
Densely Connected Convolutional Networks
TL;DR: DenseNet as mentioned in this paper proposes to connect each layer to every other layer in a feed-forward fashion, which can alleviate the vanishing gradient problem, strengthen feature propagation, encourage feature reuse, and substantially reduce the number of parameters.
Posted Content
Delving Deep into Rectifiers: Surpassing Human-Level Performance on ImageNet Classification
TL;DR: This work proposes a Parametric Rectified Linear Unit (PReLU) that generalizes the traditional rectified unit and derives a robust initialization method that particularly considers the rectifier nonlinearities.
Posted Content
Instance Normalization: The Missing Ingredient for Fast Stylization.
TL;DR: A small change in the stylization architecture results in a significant qualitative improvement in the generated images, and can be used to train high-performance architectures for real-time image generation.