Q2. What is the effect of between-person variance on subject-level internal consistency?
When withinperson variance is high relative to total variance, subject-level internal consistency will be closer to 0 (i.e., between-person variance is likely too low, given within-person variance, for examining individual differences).
Q3. What is the way to exclude participants with internal consistency?
Subject-level internal consistency can be used to exclude participants with internalconsistency that is too low for an intended purpose.
Q4. What is the advantage of computing split-half internal consistency over coefficient alpha?
An advantage of computing split-half internalconsistency over coefficient alpha (i.e., Cronbach’s alpha) is that all available ERP scores are used in its estimation, while the estimation of coefficient alpha requires each participant to have the same number of trials.
Q5. What can be the main reason for the use of data quality estimates?
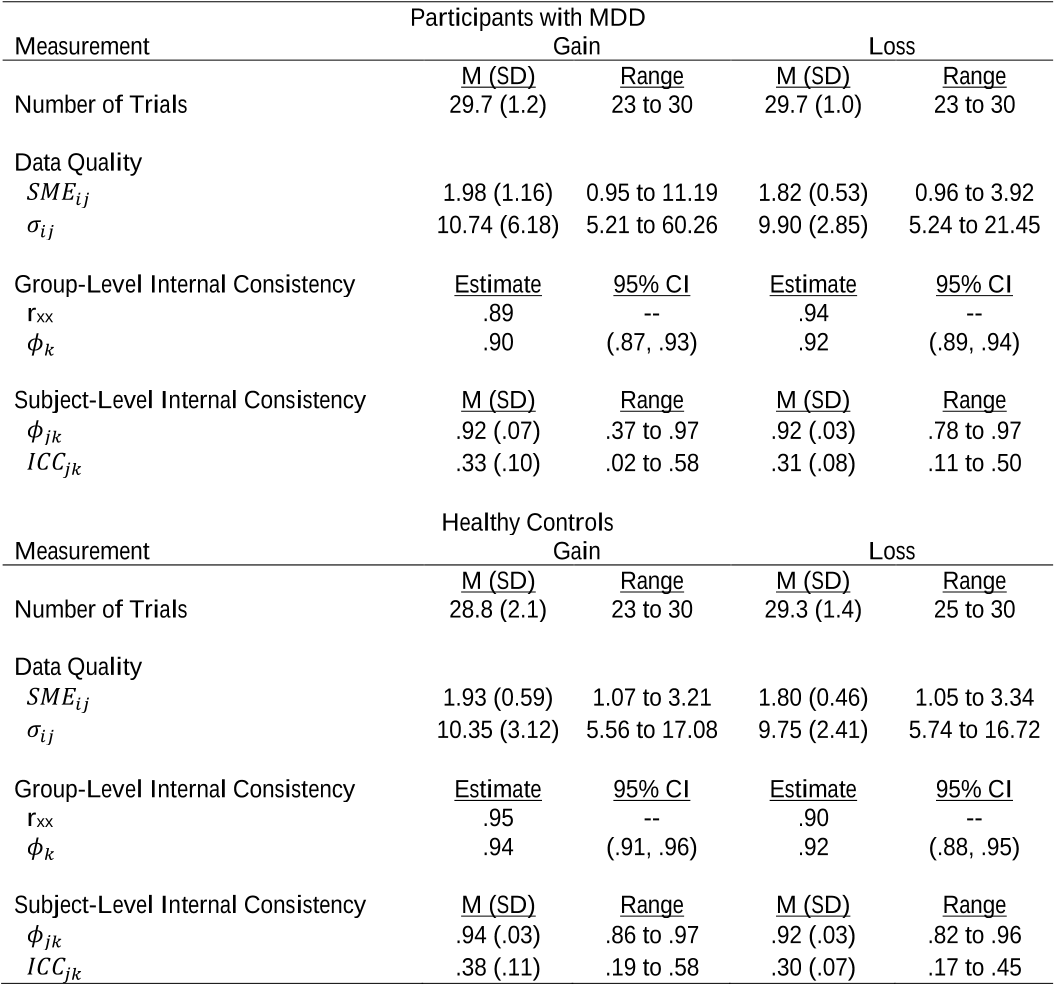
Although data quality estimates provide little useful information to justify comparingindividual differences with external correlates, they can help to justify the data quality is high enough to compare between-condition and between-group differences.
Q6. What is the ERA toolbox for assessing test-retest reliability?
Usinggeneralizability theory and the ERP Reliability Analysis (ERA) Toolbox for assessing test-retest reliability of ERP scores Part 1: Algorithms, framework, and implementation.
Q7. what is the formula for estimating subject-level internal consistency?
The formula for estimating subject-level internal consistency is an extension of the dependability formula from Equation 2.𝜙𝑗𝑘 = 𝜎𝑝2𝜎𝑝 2 +𝜎𝑖𝑗𝑘 2𝑛𝑖𝑗𝑘 ⁄(Eq. 3)Subject-level dependability for a given person, j, from a group, k, (𝜙𝑗𝑘) is computed as function of between-person variance (𝜎𝑝 2), person-specific between-trial variance (𝜎𝑖𝑗𝑘 2 ), and the personspecific number of included trials (𝑛𝑖𝑗𝑘).
Q8. What is the way to estimate the internal consistency of a sample?
If a researcher wishes to operate within the classical test theory framework, the average of randomly resampled5 split-half internal consistency coefficients could be estimated to characterize ERP score internal consistency (see Clayson et al., 2021).
Q9. What is the disadvantage of using split-half internal consistency?
Estimates from generalizability theory can overcome this disadvantage by using ERPscores from all trials in the estimation of internal consistency, which removes the sampling error endemic to selecting an approach to split the data (Baldwin, Larson, & Clayson, 2015; Carbine et al., in press; Clayson, Carbine, et al., in press; Clayson & Miller, 2017a, 2017b).