Q2. What future works have the authors mentioned in the paper "Disentangling the impact of securitization on bank profitability" ?
There are some opportunities to extend the current analysis in different dimensions. Additionally, further analysis can be done to investigate the impact of different types of securitization, including ABS or MBS, on bank profitability.
Q3. What is the main explanatory variable for the variation in bank profitability?
The outstanding amount of securitization is used as the main explanatory variable for explaining the variation in bank profitability.
Q4. What is the expected effect of the size of a bank on its profitability?
The bank size is expected to positively affect its profitability due to the economies of scale or the ability of large banks to lend more.
Q5. What does Loutskina argue that reduces the cost of funding?
Loutskina (2011) argues that the availability of securitization as an internal source of funds reduces the sensitivity of the bank cost of funding to the availability of other external sources of funds such as traditional liquid funds and deposits.
Q6. What is the main reason why banks securitize?
Jones (2000) finds that banks securitize, among other reasons, to diversify funding sources, reduce the costs of external financing through debt and deposits, and accordingly to reduce the overall cost of funding.
Q7. What are the main components of the securitization relationship?
Their results show that bank risk, cost of funding, liquidity and regulatory capital work as transmission channels in the securitizationprofitability relationship.
Q8. What is the origin of mortgage loans in the US?
In the US, securitization origins go back to the early 1970s, when Government National Mortgage Association (Ginnie Mae) started to sell mortgage loans (Ibanez and Scheicher, 2012).
Q9. What are the variables used to measure the liquidity of a bank?
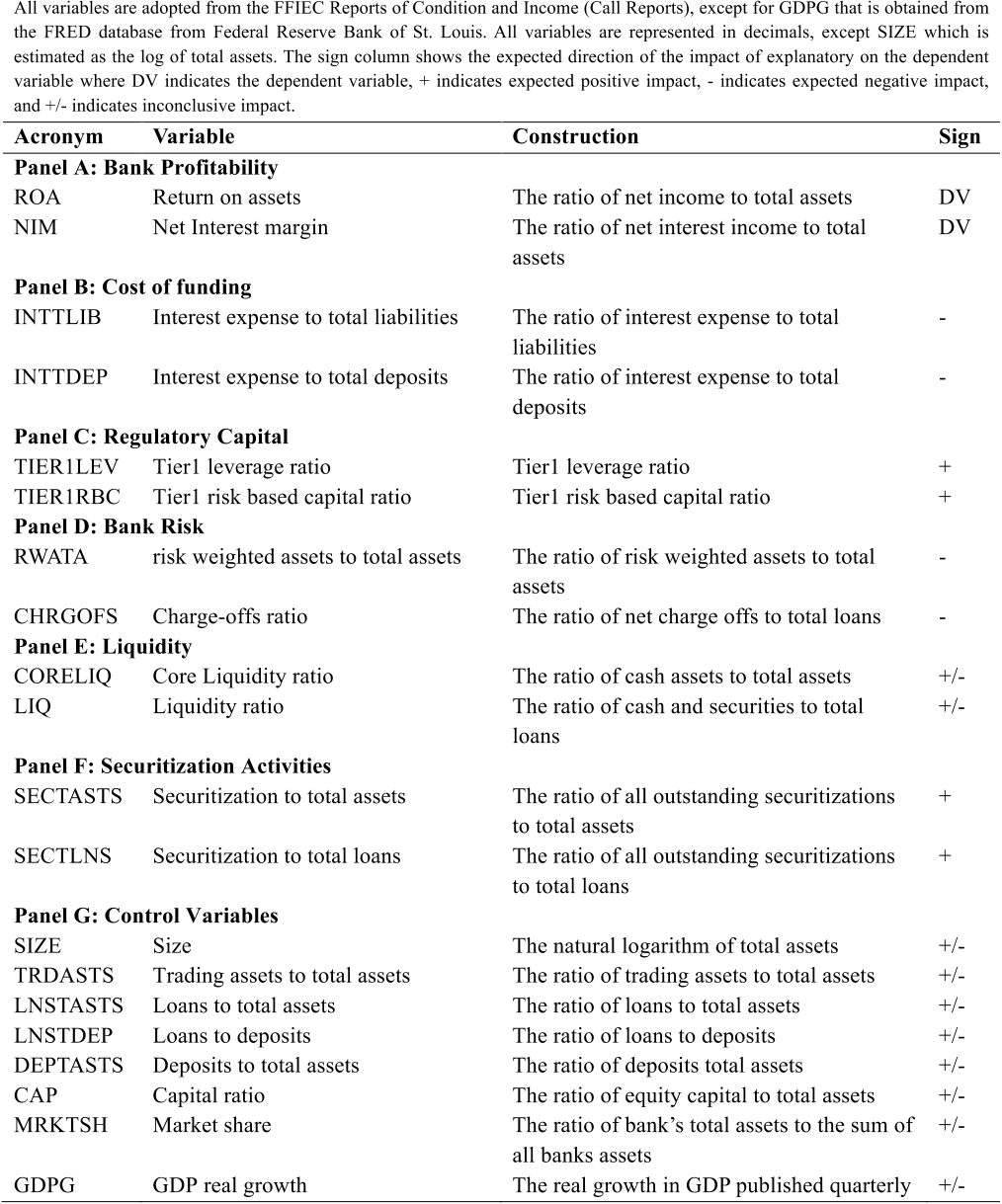
To measure the on-balance sheet liquidity of the bank, a widely-used measure is core liquidity ratio (CORELIQ) which is estimated as the ratio of cash to total assets, and the liquidity ratio (LIQ) which is estimated as the ratio of cash and securities to total assets.
Q10. How do the authors estimate the relationship between securitization and profitability?
The authors estimate the model with clustered standard errors at the bank level, which enables us to use within-bank variations to estimate the parameters of the relationship between securitization and profitability.
Q11. What is the empirical framework used to test the different relationships?
their empirical framework is based on a Structural Equations Modeling (SEM) approach that can simultaneously test the different relationships comprised in the proposed empirical model.
Q12. What was the perception of the US banking system until mid-2007?
until mid-2007 it was widely perceived that the US banking system was sound and performing well, particularly because banks capital holdings and profitability appeared to be high and at record levels.
Q13. What did the increase in foreclosures and defaults in mortgages mean for the US banking industry?
The increased number of foreclosures and defaults in mortgages led to a decline in the value of securitized assets and reduced investors’ appetite for such securities and accordingly problems within the US banking industry (Gerardi et al., 2008).
Q14. What is the average deviation of the risk-weighted assets to total assets ratio?
With respect to bank risk measures, panel D shows that risk-weighted assets to total assets ratio has a high standard deviation of 0.270 compared to 0.021 of the charge-offs ratio.
Q15. What are the main channels through which securitization affects bank profitability?
In so doing, the authors argue that the impact of securitization on bank profitability is transmitted through four main channels, namely bank risk, cost of funding, liquidity and regulatory capital.
Q16. What is the effect of securitization on bank risk?
On the other hand, securitization may increase bank risk due to the increase in risk taking and recourse or other seller-provided credit enhancements (Higgins and Mason, 2004).
Q17. How does the model estimate the percentage of indirect effect?
In this regard, the authors follow the method applied by Iacobucci (2008) to estimate the percentage of indirect effect using the estimated indirect and direct path coefficients as follows:34 = 678 9:7678 9:7 1 6; (8)where km is the indirect effect that is transmitted through mediator m as a percentage of total effect.
Q18. What is the next step in testing the hypothesized mediation model?
The next step in testing the hypothesized mediation model is to construct and test a model that incorporates all the four proposed mediators at the same time.
Q19. What is the final step in analyzing the theoretical mediation model?
The final step in analyzing the theoretical mediation model is computing the percentage contribution of each mediator in explaining the variation in bank profitability.