Q2. What are the useful features of the context-based modeling algorithm?
Their experiments suggest that the context aspect of their algorithm improves recognition performance by about 6% and that the most useful contextual features are coplanarity and orthogonality.
Q3. What is the first phase of the BIM process?
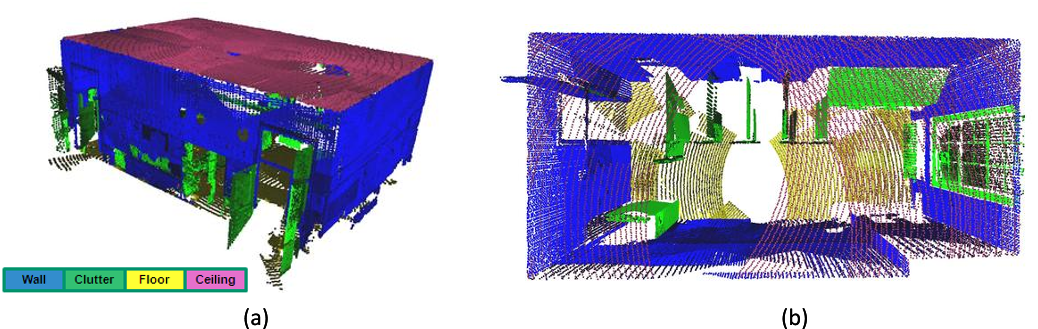
In the first phase, planar patches are extracted from the point cloud and a context-based machine learning algorithm is used to label the patches as wall, ceiling, floor, or clutter.
Q4. What is the purpose of the detailed surface modeling phase of the algorithm?
The detailed surface modeling phase of the algorithm operates on each planar patch produced by the contextbased modeling process, detecting the occluded regions and regions within openings in the surface.
Q5. What is the purpose of the algorithm?
A learning algorithm is used to encode the characteristics of opening shape and location, which allows the algorithm to infer the shape of an opening even when it is partially occluded.
Q6. What is the common problem in the BIM pipeline?
The authors are currently working on completing the points-to-BIM pipeline by implementing an automated method to convert the surface-based representation produced by their algorithm into a volumetric representation that is commonly used for BIMs.
Q7. What is the way to detect openings in unoccluded surfaces?
Detecting openings in unoccluded surfaces can be achieved by analyzing the data density and classifying low density areas as openings.
Q8. What is the purpose of the classifier?
The classifier uses local features computed on each patch in isolation as well as features describing the relationship between each patch and its nearest neighbors.
Q9. What are the main purposes of building information models?
These models, which are generally known as building information models (BIMs), are used for many purposes, including planning and visualization during the design phase, detection of mistakes made during construction, and simulation and space planning during the management phase.
Q10. What is the result of this process?
The result of this process is a compact model of the walls, floor, and ceiling of a room, with each patch labeled according to its type.
Q11. What are the challenges of building modeling algorithms?
Building modeling algorithms are frequently demonstrated on simple examples like hallways that are devoid of furniture or other objects that would obscure the surfaces to be modeled.