Pushing using compliance
D. Nieuwenhuisen,A.F. van der Stappen,Mark H. Overmars +2 more
- pp 2010-2016
Reads0
Chats0
TLDR
This paper presents an approach based on the rapidly-exploring random tree (RRT) algorithm that, besides paths through the open space, exploits the power of compliance.Abstract:
This paper addresses the problem of maneuvering an object by pushing it through an environment with obstacles. Instead of only pushing the object through open spaces, we also allow it to use compliance, e.g. allowing it to slide along obstacle boundaries. The advantage of using compliance is twofold: compliance does not only extend the number of situations in which a push plan can be found, it also allows for simpler (i.e. less complicated) paths in many cases. Here, we present an approach based on the rapidly-exploring random tree (RRT) algorithm that, besides paths through the open space, exploits the power of complianceread more
Figures

Figure 4: The push range. The path of the object is shown by the dotted arrow. (a) The (counter clockwise) push range if no friction is assumed between the object and the obstacle. (b) The push range if there is friction between O and the obstacle. (c) The (clockwise) push range if O is pushed around an endpoint of an obstacle (no friction). (d) Pushing cannot continue because P is forced outside the push range by an obstacle. 
Figure 3: (a) An example of the compliant space CSro shown as the dotted lines. (b) The racetrack Rroγi of an obstacle γi. The position of O can be described by its compliant position. 
Figure 10: (a) A scene consisting of 4 obstacles. As can be seen from the compliant space CSro (the dotted lines), the top 3 obstacles form a compliant component while the bottom obstacle is a compliant component on its own. (b) Even though the two obstacles form a compliant component, the object runs into a dead-end. 
Table 1: Results of the experiments. 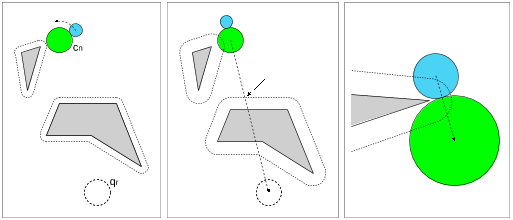
Figure 13: Ray shooting in the contact spaces. The rays are the dotted arrows. (a) A circular ray shoot in CSrp to collision check the contact transit. (b) A linear ray shoot in CSro to collision check the path of O. The arrow shows the point of collision. (c) A linear ray shoot in CSrp to collision check the wedges. 
Figure 19: (a) Experimentation scene. At the left the start configuration is shown, in the center the goal configuration. (b) An example of a final path, the dotted lines represent non-compliant path segments, the solid lines represent compliant path segments.
Citations
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Push-manipulation of complex passive mobile objects using experimentally acquired motion models
TL;DR: This work presents an experience-based push-manipulation approach that enables the robot to acquire experimental models regarding how pushable real world objects with complex 3D structures move in response to various pushing actions and demonstrates the superiority of the achievable planning and execution concept through safe and successful push- manipulation of a variety of passively mobile pushable objects.
Proceedings ArticleDOI
Automatic learning of pushing strategy for delivery of irregular-shaped objects
TL;DR: A learning-based approach for pushing objects of any irregular shape to user-specified goal locations by automatically collecting a set of data on how an irregular-shaped object moves given the robot's relative position and pushing direction.
Journal Article
Integer programming, lattices, and results in fixed dimension
TL;DR: In this article, various lattice basis reduction algorithms are used as auxiliary algorithms when solving integer feasibility and optimization problems, and three algorithms are described: binary search, a linear algorithm for a fixed number of constraints, and a randomized algorithm for different numbers of constraints.
Proceedings ArticleDOI
Achievable push-manipulation for complex passive mobile objects using past experience
TL;DR: The RRT algorithm is modified in such a way to use the recalled robot and object trajectories as building blocks to generate achievable and collision-free push plans that reliably transport the object to a desired 3 DoF pose.
Book ChapterDOI
Planning and Resilient Execution of Policies For Manipulation in Contact with Actuation Uncertainty
TL;DR: In this paper, a sampling-based motion planner is proposed for planning motion for robots with actuation uncertainty that incorporates contact with the environment and the compliance of the robot to reliably perform manipulation tasks.
References
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Orienting polygonal parts without sensors
TL;DR: It is shown that any polygonal part can be oriented without sensors by giving anO[n2 logn) algorithm for finding the shortest sequence of mechanical gripper actions that is guaranteed to orient the part up to symmetry in its convex hull.
Proceedings Article
Dynamic manipulation
Matthew T. Mason,Kevin M. Lynch +1 more
TL;DR: The design, control, and planning of dynamic manipulation is addressed, and an example of Dynamic manipulation, club-throwing using dynamic closure, is described.
Proceedings ArticleDOI
Augmenting RRT-planners with local trees
TL;DR: RRTLocTrees as mentioned in this paper augments RRT-planners with local trees to solve the narrow passage problem and explore several difficult regions in parallel, which has proved to be very effective for problems where the solution trajectory repeatedly has to pass difficult regions.
Proceedings ArticleDOI
Motion planning with uncertainty
TL;DR: How the open loop and closed loop plans can be viewed as optimal strategies in the framework of two-person, zero-sum, non-cooperative games is discussed.