The Nature of Credit Constraints and Human Capital
Reads0
Chats0
TLDR
This paper developed a human capital model with borrowing constraints explicitly derived from government student loan (GSL) programs and private lending under limited commitment, which helps explain the persistent strong positive correlation between ability and schooling in the U.S., as well as the rising importance of family income for college attendance.Abstract:
We develop a human capital model with borrowing constraints explicitly derived from government student loan (GSL) programs and private lending under limited commitment. The model helps explain the persistent strong positive correlation between ability and schooling in the U.S., as well as the rising importance of family income for college attendance. It also explains the increasing share of undergraduates borrowing the GSL maximum and the rise in student borrowing from private lenders. Our framework ofiers new insights regarding the interaction of government and private lending as well as the responsiveness of private credit to economic and policy changes.read more
Figures

Table 3: Baseline Model Parameters 
Figure 4: dU , hU , hX , and hG for high wealth individuals (w > w̄) 
Figure 3: dU , hU , hX , and hG for low wealth individuals (w ≤ w̄) 
Figure 8: ‘Year 2000’ GSL and Private Lending Constraints 
Figure 9: Private Borrowing (‘Year 2000’) 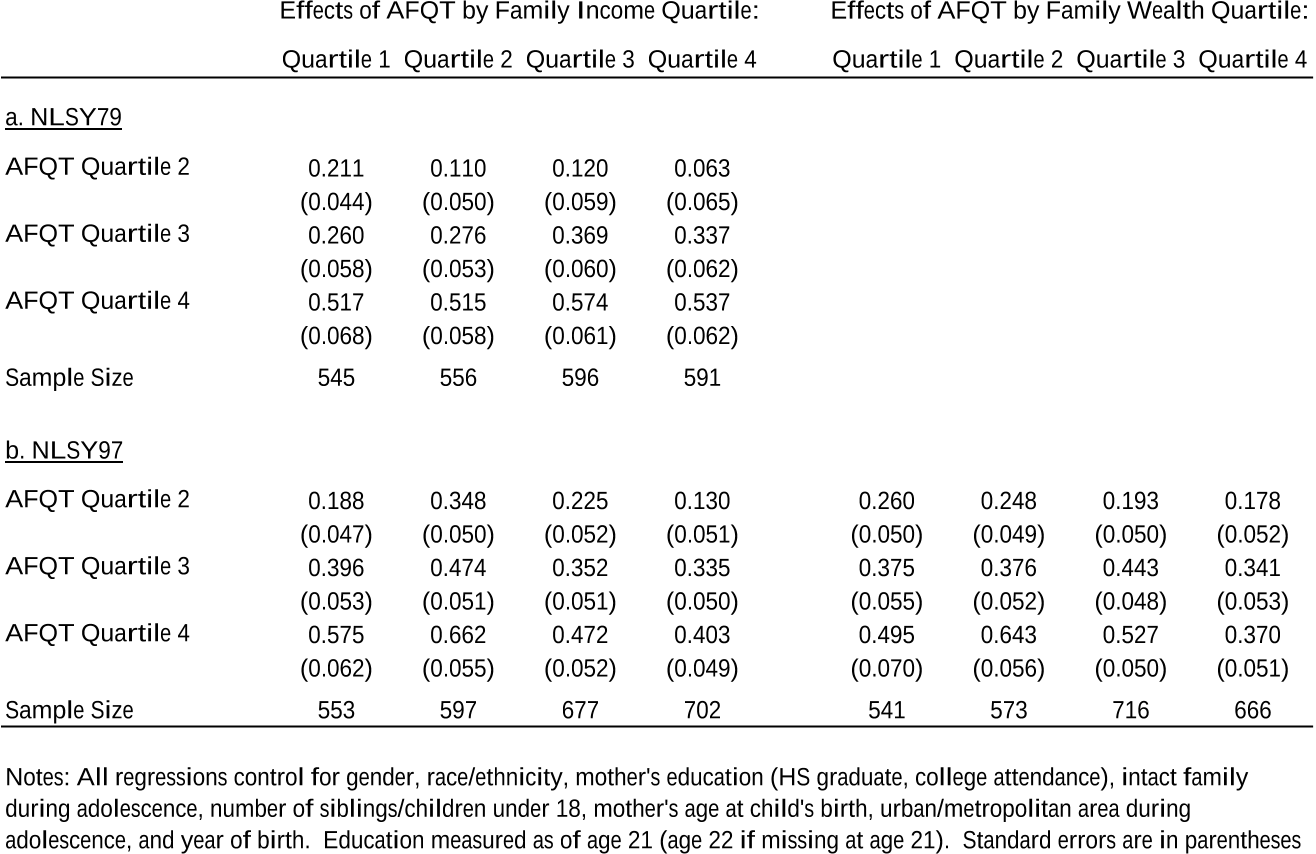
Table 2: Estimated Effects of AFQT on College Attendance by Family Income and Wealth (NLSY79 and NLSY97)
Citations
More filters
DissertationDOI
Essays on inequality and human capital
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors developed a heterogeneous life-cycle model of human capital accumulation to analyze individual college and borrowing decisions and found that increases in the college wage premium and college costs are important factors in generating the sharp rise in loans and particularly the increase in the fraction of borrowers and borrowing amounts.
Essays in Public Economics and International Trade
Abstract: FOR KAUFFMAN FOUNDATION ESSAYS IN PUBLIC ECONOMICS AND INTERNATIONAL TRADE
Posted Content
The Dropout Option in a Simple Model of College Education
Ali K. Ozdagli,Nicholas Trachter +1 more
TL;DR: This paper presented a simple dynamic model of education where students are uncertain about their ability to accumulate human capital in college, and students are faced with exams that motivate them to update their beliefs.
Posted Content
Models Of Development Of Labour Productivity Forecast
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors focused on relations mathematical calculation, they underpinned the forecasts of labor productivity, and they sought and failed to provide essential elements posed forecast labor productivity in order to predict labor productivity.
Journal ArticleDOI
Subsidizing heterogeneous higher education systems
Limor Hatsor,Itzhak Zilcha +1 more
References
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
The Production of Human Capital and the Life Cycle of Earnings
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors provide a framework for the understanding of many aspects of observed behavior regarding education, health, occupational choice, mobility, etc., as rational investment of present resources for the purpose of enjoying future returns.
Book ChapterDOI
Changes in the Wage Structure and Earnings Inequality
Lawrence F. Katz,David H. Autor +1 more
TL;DR: In this article, the authors present a framework for understanding changes in the wage structure and overall earnings inequality, emphasizing the role of supply and demand factors and the interaction of market forces and labor market institutions.
ReportDOI
Interpreting the evidence on life cycle skill formation
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors formalize the concepts of self-productivity and complementarity of human capital investments and use them to explain the evidence on skill formation, and provide a theoretical framework for interpreting the evidence from a vast empirical literature, for guiding the next generation of empirical studies, and for formulating policy.
Journal ArticleDOI
Life Cycle Schooling and Dynamic Selection Bias: Models and Evidence for Five Cohorts of American Males
TL;DR: This article examined the statistical model used to establish the empirical regularity and the intuitive behavioral interpretation often used to rationalize it, and showed that the implicit economic model assumes myopia and that the intuitive interpretive model is identified only by imposing arbitrary distributional assumptions onto the data.
Related Papers (5)
The Evidence on Credit Constraints in Post-Secondary Schooling†
Pedro Carneiro,James J. Heckman +1 more