A"zebrafish"reporter"line"reveals"immune"and"neuronal"expression"of"endogenous"
retrovirus."
!
Noémie! Hamilton
1,2
*,! Amy! Clarke
1
,! Hannah!Isles
1
,! Euan! Carson
1
,!Jean-Pierre!Levraud
3
,!
Stephen!A!Renshaw
1!
!
!
1.
!
The!Bateson!Centre,!Department!of!Infection,!Immunity!and!Cardiovascular!Disease,!
University!of!Sheffield,!Sheffield,!UK!
2.!The!Institute!of!Neuroscience,!University!of!Sheffield,!Sheffield,!UK!
3.!Macrophages!et!Développement!de!l’Immunité,!Institut!Pasteur,!CNRS!UMR3738,!25!
rue!du!docteur!Roux,!75015!Paris!!
!
*Corresponding!author:!n.m.hamilton@sheffield.ac.uk
!
"
Abstract"
"
Endogenous!retroviruses!(ERVs)!are!fossils!left!in!our!genome!from!retrovirus!infections!
of! the! past.! Their! sequences! are! part! of! every! vertebrate! genome! and! their! random!
integrations!are!thought!to!have!contributed!to!evolution.!Although!ERVs!are!mainly!kept!
silenced!by!the!host! genome,!they!are!found! a ctivated!in!mult iple!disease!stat es!such!as!
auto-in flammat ory! d isorders!and!neurological!diseases.!What!makes!defining!their!role!
in!health!and!diseases!challenging!is!the!numerous!copies!in!mammalian!genomes!and!
the! lack! of! tools! to! study! them.! In!this! study,! we! identified! 8! cop i es! of! the!zebrafish!
endogenous! retrovirus!(!"#$%).!We!created!and!characterised!the!first!&'(%&%)!ERV!reporter!
line!in!any!species.!Using!a!combination!of!live!imaging,!flow!cytometry!and!single!cell!
RNA!sequencing,!we!mapped!!"#$%!expression!to!early!T!cells! and!neurons.!Thus,!this!new!
tool!identified!tissues!expressing!ERV!in !zebrafish,!highlighting!a !p oten t ial!role!of!ERV!
during! brain! devel opment! and! strengthening! the! hypothesis! that! ERV! play! a! role! in!
immunity!and!neurological!diseases.!This!transgen ic!line!is!therefore!a!suitable!tool!to!
study!the!funct ion!of!ERV!in!health!and!diseases.!
"
Keywords"
Retroelement,!zebrafish,!endogenous!retrovirus,!reporter!line,!!"#$%,!LTR!
"
Funding"
This! work! has! been! supported! by! a! European! Leukodystrophy! Association! fellowship!
(ELA!2016-012F4)! to!NH,!an!MRC!Programme!Grant! (MR/M004864/1)!to!SAR! and!.!JPL!
is! supported! by! Agence! Nat ionale! de! la! R echerche! ( grant! ANR-16-CE20 -0002-03..!
Imaging!was!ca rried!out! i n!t he!Wolfson!Light!M i croscopy!Facility,!supported!by!an!MRC!
grant!( G0700091)!and!a!Wellcome!Trust!grant !(GR077544AIA).!!
"
Conflict"of"Interest"Statement"
The! authors!declare!that!the!research!was!conducted!in!the!absence!of!any!commercial!or!
financial!relationships !that!could!be!construed!as!a!potential!conflict!of!interest.!
!
!
"
"
"
"
"
"
.CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 International licenseperpetuity. It is made available under a
preprint (which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder, who has granted bioRxiv a license to display the preprint in
The copyright holder for thisthis version posted January 21, 2021. ; https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.01.21.427598doi: bioRxiv preprint

Introduction"
"
Over!40%!of!the!human!genome!comprises!endogenous!transposable!elements!capable!
of!recombination!and!disruption!of!genes!and!modification!of!their!expression!(Lander!et!
al.!2001).!Endogenous!retroviruses!(ERVs)!are!transposable!elements!originating!from!
old!integrations!of!retroviruses!so!successful!that!they!have!become!part!of!all!vertebrate!
genomes!st udied.!ERVs!replicate!autonomously!using!a!copy-and-pa ste!mechanism!and!
although!they! form!a!smaller!percentage!of! all!retroelements,!they!still!represent !8%!of!
the!human!genome!(Bourque!et!al.!2018;!Lander!et!al.!2001).! The!majority!of!known!ERVs!
have! lost! their! ability! to! replicate,! but! those! most! recently! acquired! still! h ave! intac t !
genomes! with!the!ability! to!produce!viral! RNA!and!particles.! However,!these! competent!
ERVs!are!under!strict!transcriptional!suppression!by!epigenetic! mechanisms!(Maksakova,!
Mager,! and! Reiss! 2008;! Rowe! et! al.! 2010;! Turelli! et! al.! 2014),! protecting! the! host!
organisms!against!potential!retroviral!insertions!and!viral!activities.!!!
!
Although!immobilised!by!mutations!or!transcriptiona lly!repressed,!ERVs!have!a!complex!
relationship!with!the!human!genome,!which!they!can!regulate!by!providing!cis-regulatory!
elements! to! surrounding! genes! and! by! lifting! their! transcriptionally! repressed! state.!
Through!these!mechanisms,!it!is!believed!that!transposable!elements!have!fuelled!some!
of! the! necessary!genetic!changes!for!evolution! (Feschotte!2008;!Kunarso!et!al.!2010).!!
*+',+-&'./,!an!ERV!envelope!gene! essential! for!the! vascularisation!of!the!placenta,! is! at!the!
origin! of! evolutionary! diversification! of! the! placenta! (Chuong! 2018;! Mi! et! al.! 2000).!
During!human!embryogenesis,!expression!of!specific!ERV!families!have!been!associated!
with!cell!identity!and!cell!pot ency!in!ea rly!stem!cells!(Göke!et!al.!2015).!Additionally,!ERV!
expression!has!been!reported!in!healthy!human!tissues!such!as!ovary!and!testis!for!ERV-
9! (Pi! et! al.! 2004),! pancreas! (Shiroma! et! al.! 2001),! breast! (Tavakolian,! Goudarzi,! and!
Faghihl oo!2019),! stomach! and! small! intestine! (Okahara!et!al.!2004).! Mainly! based! on!
transcriptional!studies,!the!expression!of!different!families!of!ERV!is!likely!to!be!extended!
to!more!tissues,!however!their!role!in!tissue!development!and!function!remains!largely!
unknown.!!
!
ERVs! have! been! linked! directly! and! indirectly! to! the! evolution! and! functioning! of! the!
immune!system.!Enhancer!regions!of!interferon!stimulated!genes!key!to!the!interferon!
pathway,!such!as!IRF1!and!STAT1,! were!found! i ntroduced! and!amplified!by!ERV! elements,!
with!the!human! inflammasome! failing!to!form! upon! the!deletion! of!a !subset! of!ERVs!
(Chuong,!Elde,!a nd! Feschotte!2 016) .!Ad aptive!immunity!also!benefits!from!the!presence!
of!ERVs.!Indeed,!ERV!peptide!recognition!is!used! in!T!cell !selection!to!optimise!antigen!
recognition! and! T! cells! have! a! higher! sensitivity! to! exogenous! virus! infection! when!
presented !with! ERV!peptides! during! their!initial!thymic!selection ! (Mandl! et! al.! 2013;!
Young!et!al.!2012).!The!human!ERV!(HERV)!envelope!gene!contains!immunosuppressive!
domains!that!reduce!the!Th1!response!during!pregnancy!and!therefore!promote!foetal!
development!(Knerr!et!al.! 2004;!Lokossou!et!al.! 2020).!The!role!of!ERVs!in!our!immune !
system,!particula rly!in!the!training!of!our!adap tive!immunity,!can!be!a!double-edge!sword!
as!ERVs!are!linked!to!a!range!of!different!disease!states,!including!autoimmunity.!!
!
Aberrant! expression! of! ERVs! contributes! to! multiple! pathologies.! ERVs! are! found! in!
abundance!in!multiple!forms!of!cancers!and!are!considered!tumour-promoting!fa ctors!
(extensively! reviewed! in! (Bermejo! et! al.! 2020).! The! pathology! of! auto-inflammatory!
diseases! has! also! been! strongly! associated! with! ERVs.! Syst emic! l upus! erythematosus!
(SLE)! is! an! autoimmune! disorder! with! increased! level! of! autoantigen! for! an! ERV!
(Jorgensen!et!al.!2014).! Recently,! one!of!the!murine! SLE! susceptibility!locus!was!i dentified!
as!a!key!suppressor!of!ERV!expression,!consolidating!the!role!of!ERVs!in!the!pathogenesis!
of!SLE!(Treger!et!al.!2019).!A!similar!disorder!is!Acardi-Goutieres!Syndrome!(AGS),!a !type!
1!interferonopathy!which!resembl es!congenital!cytome galovirus!infection!and!is!caused!
.CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 International licenseperpetuity. It is made available under a
preprint (which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder, who has granted bioRxiv a license to display the preprint in
The copyright holder for thisthis version posted January 21, 2021. ; https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.01.21.427598doi: bioRxiv preprint

by!mutation!in!several!genes!encoding!enzymes!responsible!for!nucleic!acid!metabolism!
(Crow!et!al.!2015).!Mutations!in!some!of!these! genes,!such! as!TREX1,!MDA5! and!ADAR1!
trigger!aberrant!presence!of!various!retroelements!and!the!upregulation!of!an!antiviral!
immune!response!(Ahmad!et!al.!2018 ;!Thomas!et!al.!2017).!Interestingly,!anti-reverse!
transcriptase!therapy!in!AGS!pa tients!can!decrease!the!IFN!response,!highl ighting!the!role!
of! aberrant! presence! of! ERVs! in!triggering!an!immune!response! (G.!Rice!et!al.!2018).!
Increased! expression! of! ERVs! has! been! found! in! brains! of! patient! suffering! from!
neurodegenerative!disea ses! such!as! Motor! Neuron!Disease!(Li! et!al.!2015)!and!multiple!
sclerosis!(Johnston!et!al.!2001;!Mameli!et!al.!2007).!Overexpression!of!a!human!ERV!in!
neurons!was!shown!to!be!neurotoxic,!suggesting!a!p otential!role!of!ERVs!in!t riggering!
neuronal!toxicity!(Li!et!al.!2015).!A!direct!link!to!the!pathology!of!these!disorders!has!yet!
to!be!made,!but!nonetheless!ERVs!appear!as!strong!causal!factors!for!autoimmune!and!
neurological!disorders.!
Although!ERV!enrichment!has!been!detected!in!neurological!pathol ogies,!little!is! known!
about!the!function!of!ERV!in!healthy!tissues.!The!exact!role!of!ERV!in!our!immune!system!
and!brain!pathologies!has!yet!to!be!understood!and!there!is!no!model!system!specifically!
looking! at!ERV!function!&'(%&%).!!Zebrafish! is!already!established!as!a!model!to!study!the!
immune! system,! with! significan t! homology! with ! mammals! in! innat e! and! ada ptive!
immunity! (Trede! e t!al.! 2004;! Renshaw! and!Trede! 2012).! The !genetic! tractability! and!
transparency!of!the!zebrafish! embryos!have!allowed!the!creation!of!transgenic!reporter!
lines,!some!of !which!have!elucidated!the!role!of!immune!cell!behaviour!&'(%&%)!(Renshaw!
et!al.!2006).!The!tractability!of!the!zebrafish!has!already!been!exploited!to!visualise!the!
expression!of!the!human!ERV-9!in!oocytes,!similarly!to!human!expression!(Pi!et!al.!2004).!
In! this! study,! we! used! the! zebrafish! as! a! tractable! in! vivo! model! to! characterise! the!
zebrafish!endogenous!retrovirus!( !"#$%).! We!identified! multiple! !"#$%! family! members,!
including!2!complete!genomes!!"#$%/0!and!!"#$%/1.!Using!the!tractability!of!the!zebrafish!
larvae! we! developed! a! reporter! line! for! !"#$%/0! and! imaged! for! the! first! time! ERV!
activation!in!healt hy!tissues! &'(%&%).!We!showed!that!!"#$%/0!is!expressed!in!the!thymus!
and! in! the! brain.! Colocalisation! analysis! and! single! cell! RNA! sequencing! revealed!
expression! of! !"#$%/0! specifica lly! in! T-cells,! suggesting! a! potential! role! for! ERV! in!
lymphocyte! development.! Brain! exp ression! of! ZFERV! appears! to! include! neuronal!
expression.!This!transgenic!line!can!be!used!as!a!tool!to!further!investigate!the!role!of!
ERVs!in!immunity!and!in!neurological!disorders.!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
.CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 International licenseperpetuity. It is made available under a
preprint (which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder, who has granted bioRxiv a license to display the preprint in
The copyright holder for thisthis version posted January 21, 2021. ; https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.01.21.427598doi: bioRxiv preprint
Results"
"
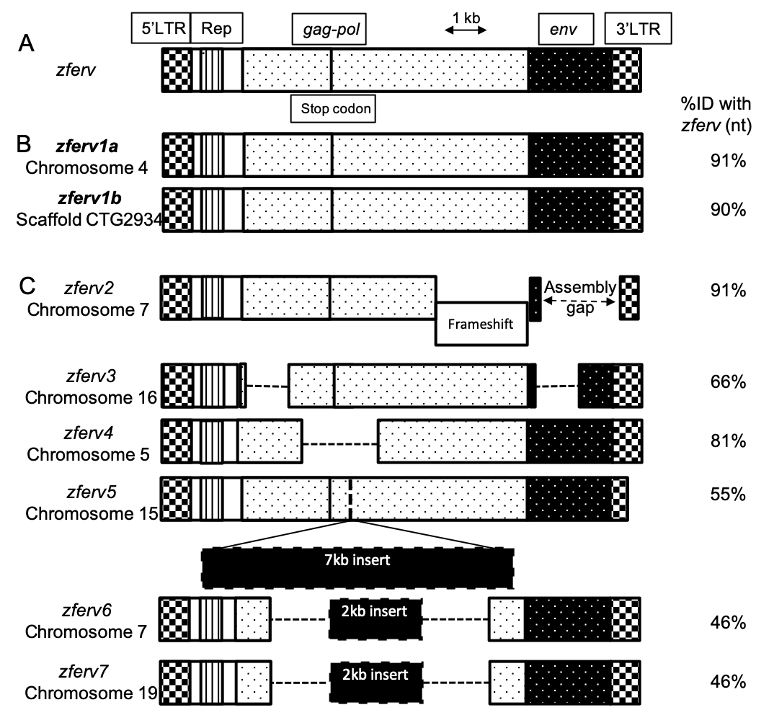
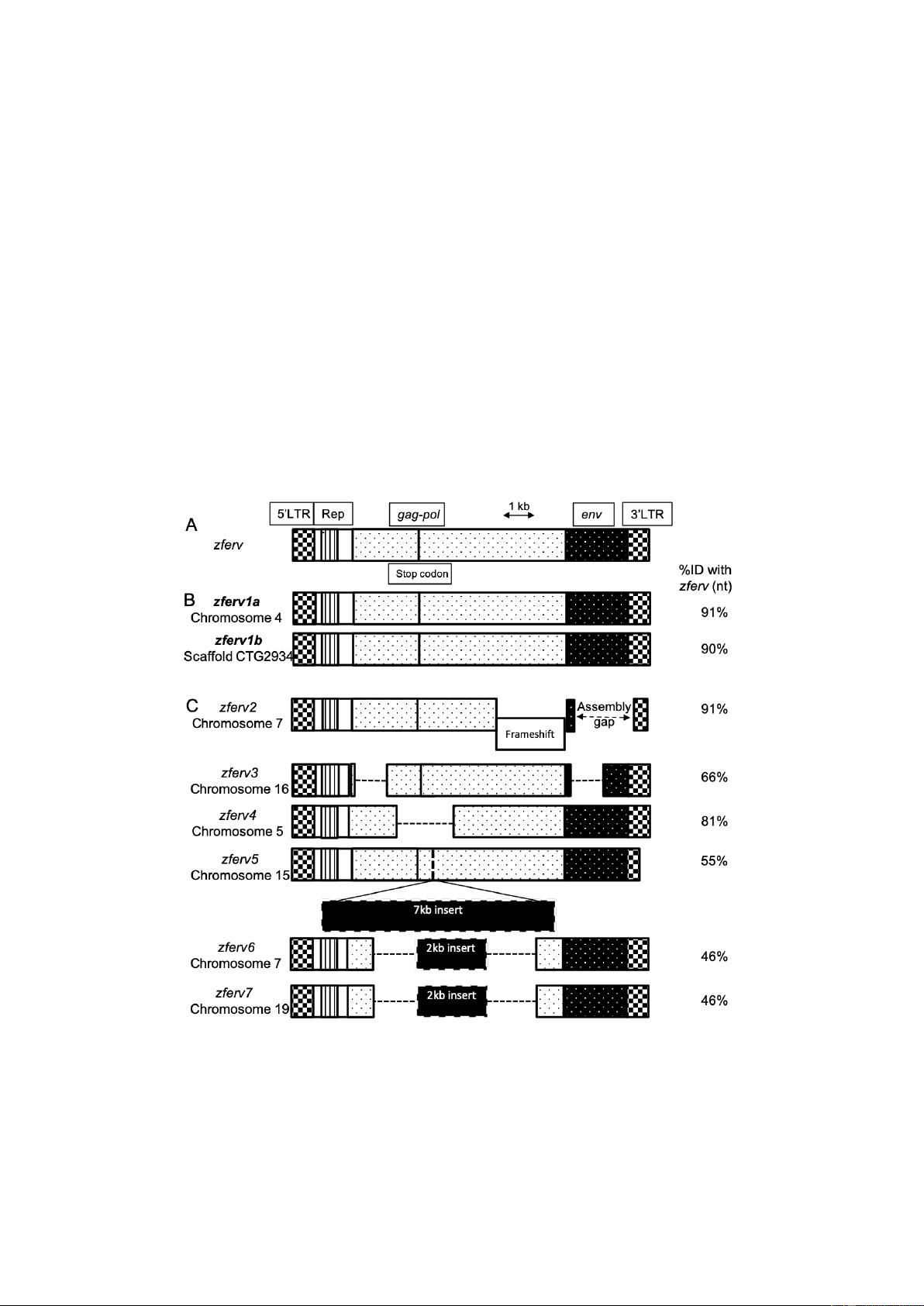
The"zebrafish"genome"contains"multiple"endogenous"retrovirus"integrations."
The!presence!of!an!ERV!in!zebrafish,!named!!"#$%,!has!been!reported!by!Shen!an d!Steiner!
while!screening!a!thymic!cDNA!library!(Shen!and!Steiner!2004)!(Figure"1A).!We!searched!
for!related!sequences!in!t he!most!recent!reference!zebrafish!genome!(GRCz11,!Tü!strain)!
using!BLASTN!searches,!with!the!original! !"#$%!sequence!as!a!query.!Limiting!ourselves!to!
sequences!flan ked!by!long!terminal!repeats! (LTRs)! on!both!sides,!we!retrieved!8 ! hits!
scattered!in! t he!zebra fish!genome,!but!n ot!t he! exact!!"#$%!sequence,!possibly! because!of!
strain! difference! ( Figure" 1+" Sup." Table" 1).! We! identified! 2 ! sequences! encoding!
apparently!fully!functional!ERVs,!with!91%!and!90%!identity!to!!"#$%,!that!we!respectively!
named !!"#$%/0!and!!"#$%/1!(Figure"1B).!These!t wo!ERVs!encode!almost!identical!proteins!
(95!to!97%!identity! at!the!amino-acid!level).! Their! LTRs! are!also!highly!simil a r!(95%!
identity! at! the! nucleot id e! level),! suggesting! that! t heir! promoters! probably! d rive!
expression!in!similar!cells.!An!additional!6!pseudo!!"#$%!genes!(here!call ed!!"#$%2!-!!"#$%3)!
were!identified!(Figure"1C),! !"#$%2!containing!a! frameshift,!!"#$%4!and! !"#$%5!with!large!
deletions! and! !"#$%6,! !"#$%7! and! !"#$%3! containing! a! large! insertion,! all! resulting! in! a!
degenerated!ERV!genome.!
!
!
Figure" 1.!Multiple" copies"of"zferv" are" present" in" the" zebra fish" genome.! A.! Diagram! of! the!
original!zferv!genome!found!by!Steiner!et!al.!used!as!a!r eference!for!nucleotide!identity!(ID%!nt)!
B.!Diagram! representing! the! two! closest! related! !"#$%! genome! found!in!most!recent!zebrafish!
genome!GRCz11,!name d!zferv1a!and!!"#$%/1.!C.!Diagram!of! 6!pseudo!zferv!genes!with!degenerated!
genome! (dotted! line! represents! insertions).! 5’-LTR:!5’!–Long! terminal! repeat,! Rep.:!Repetitive!
element,!gag-pol:!genes!encoding!the!polyprotein!and!reverse!transcriptase,!env:!envelope!gene.!
!
!
!
.CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 International licenseperpetuity. It is made available under a
preprint (which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder, who has granted bioRxiv a license to display the preprint in
The copyright holder for thisthis version posted January 21, 2021. ; https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.01.21.427598doi: bioRxiv preprint

zferv1a!is"actively"expressed"in"the"brain"and"in"the"thymus.!
!"#$%!expression!was!initially!found!in!the!thymus!at!5!days!post!fertilisation!(dpf)!using!
a!RNA!probe!against!the!envelope!(#'%)!gene!of!the!original!!"#$%!(Shen!and!Steiner!2004).!
To! verify! this! observation,! the! entire! !"#$%/0! genome! was! subcloned! from! a! fosmid!!
provided!by!the!Sanger!Center!and! we!used! this!sequence!to!create!an!&'( 8&-9!hybridisatio n!
(ISH)!RNA!probe!against!the!envelope!gene!(#'%)!of!!"#$%/0.!ISH!p erformed!on!a !time!
course! starting! from! 2! cell-stage! embryos! from! the! '0,$#! strain! con firmed! that! the!
strongest!signal! appeared!at!5dpf!(Figure"2).!At!5dpf,!the!thymus!was!strongly!labelled!
(Figure" 2A-B),! similarly! to! what! was! previously! reported! (Shen! and! Steiner! 2004).!
Individual!labelled!cells!were!visible!around!the!thymus!following!the!branchial!arches!
and!around!the!ear!(Figure"2B).!Additionally,!we!identified!a!clear!signal!of!the!#'%!probe!
in!the!brain!(Figure!2A,!2C)!and!the!spinal!cord!(Figure!2A).!!
!
!
Figure" 2:"Reporter"line"for"zferv1a"recapitulates"endogenous"expression.!A.!Expression!of!the!
envelope! gene!(#'%)!by!&'(8&-9(hybridisation!from!2-cell!stage!until!5dpf.!Black!box!highlighting!
strong!expression!around!the!thymus,!black!arrows!highlighting!brain!and!spinal!cord!expression.!
Scale!bar! 500µm.! B.!Zoomed!image!on! the ! thymus!area,!single!positive!cells! are!visible ! in! the!
vicinity!of! the! thymus! around! the! ear! (white! arrowheads)! and! alongside! the! branchial! arches!
(white!arrows).!Scale!bar!70µm.!C.!Dorsal!view!of!#'%!expression!in!the!brain!at!5dpf.!Scale!bar!
100µm.!!
!
!
zferv1a"reporter"line"recapitulates"endogenous"expression.!
To!follow!the!expression!of!the!zebrafish!endogenous!retrovirus!we!identified!as!!"#$%/0,!
we!took!a!transgenic!approach!ta king!adva ntage!of!the!promoter!activity!of!retroviral!
LTR.!We!used!the!5’!viral!promoter!:-$6!from!!"#$%/0!to!drive!GFP!expres sion!by!Gateway!
recombination!(Figure"3A).!Injected!embryos!showing! expression!in!their!thymus!were!
raised!and!screened!in!adulthood!for!germline!transmission.!We!observed!a!strong!and!
consistent!GFP!expression!in!the!thymus!at!5dpf!in!F1!and!F2!larvae!(Figure"3B)!from!
.CC-BY-NC-ND 4.0 International licenseperpetuity. It is made available under a
preprint (which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder, who has granted bioRxiv a license to display the preprint in
The copyright holder for thisthis version posted January 21, 2021. ; https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.01.21.427598doi: bioRxiv preprint