Credit Constraints, Heterogeneous Firms and International Trade
Reads0
Chats0
TLDR
This article examined the detrimental consequences of financial market imperfections for international trade and developed a heterogeneous-firm model with countries at different levels of financial development and sectors of varying financial vulnerability.Abstract:
This paper examines the detrimental consequences of financial market imperfections for international trade. I develop a heterogeneous-firm model with countries at different levels of financial development and sectors of varying financial vulnerability. Applying this model to aggregate trade data, I study the mechanisms through which credit constraints operate. First, financial development increases countries' exports above and beyond its impact on overall production. Firm selection into exporting accounts for a third of the trade-specific effect, while two thirds are due to reductions in firm-level exports. Second, financially advanced economies export a wider range of products and their exports experience less product turnover. Finally, while all countries service large destinations, exporters with superior financial institutions have more trading partners and also enter smaller markets. All of these effects are magnified in financially vulnerable sectors. These results have important policy implications for less developed economies that rely on exports for economic growth but suffer from poor financial contractibility.read more
Figures

Table 10. Economic Significance: Predicted vs. Actual Trade Growth 
Table 9. Economic Significance: Comparative Statics 
Table 5. Financial Development and Firm-Level Exports 
Figure 3. The Productivity Cut-off for Exporting 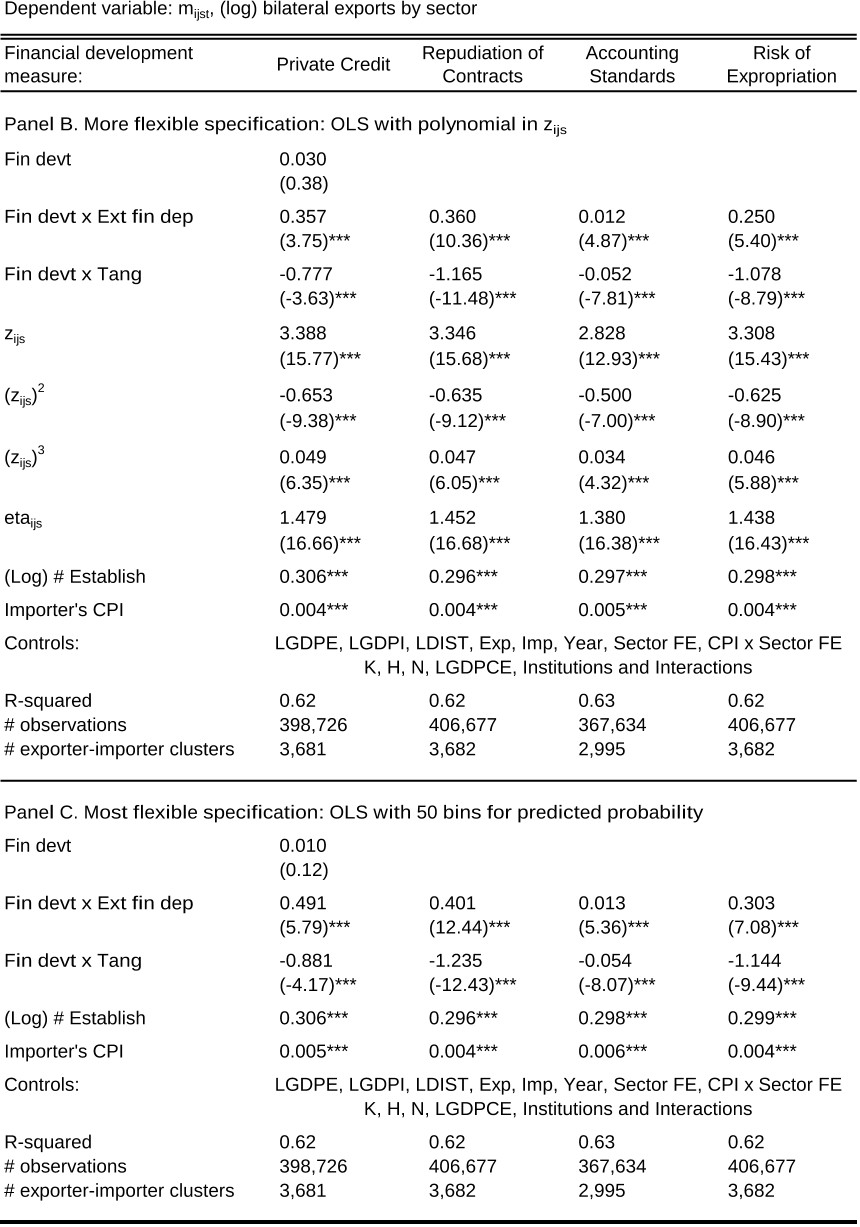
Table 5. Financial Development and Firm-Level Exports 
Table 1. Export Patterns in the Data
Citations
More filters
Posted Content
Estimating Trade Flows: Trading Partners and Trading Volumes
TL;DR: In this paper, the impact of trade frictions on trade flows can be decomposed into the intensive and extensive margins, where the former refers to the trade volume per exporter and the latter referred to the number of exporters.
Journal ArticleDOI
Finance and Development: A Tale of Two Sectors †
TL;DR: This article developed a model co-determining aggregate total factor productivity (TFP), sectoral TFP, and scales across industrial sectors and found that financial frictions disproportionately affect TFP in tradable sectors where production requires larger costs.
Posted Content
Exports and Financial Shocks
Mary Amiti,David E. Weinstein +1 more
TL;DR: In this article, a causal link between the health of banks providing trade finance and growth in a firm's exports relative to its domestic sales is established, suggesting that trade finance accounts for about one-third of the decline in Japanese exports in the financial crises of the 1990s.
Journal ArticleDOI
Off the Cliff and Back? Credit Conditions and International Trade During the Global Financial Crisis
TL;DR: This article studied the collapse of international trade flows during the global financial crisis using detailed data on monthly US imports and showed that credit conditions were an important channel through which the crisis affected trade volumes, by exploiting the variation in the cost of capital across countries and over time.
Journal ArticleDOI
The Empirics of Firm Heterogeneity and International Trade
Andrew B. Bernard,Andrew B. Bernard,Andrew B. Bernard,J. Bradford Jensen,J. Bradford Jensen,Stephen J. Redding,Peter K. Schott,Peter K. Schott,Peter K. Schott +8 more
TL;DR: A review of empirical evidence on firm heterogeneity in international trade can be found in this article, where a first wave of empirical findings from micro data on plants and firms proposed challenges for existing models of international trade and inspired the development of new theories emphasizing firm heterogeneity.
References
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Why Some Firms Export
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors present a dynamic model of the export decision by a profit-maximizing dynamic model using ap anel of U.S. manufacturing plants, and test for the role of plant characteristics, spillovers from neighboring exporters, entry costs and government export promotion expenditures.
BookDOI
A new database on financial development and structure
TL;DR: In this article, the authors introduce a new database of indicators of financial development and structure across countries and over time, which unifies a variety of indicators that measure the size, activity, and efficiency of financial intermediaries and markets.
Posted Content
Relationship-Specificity, Incomplete Contracts, and the Pattern of Trade
TL;DR: This paper found that countries with good contract enforcement specialize in the production of goods for which relationship-specific investments are most important, and that contract enforcement explains more of the pattern of trade than physical capital and skilled labor.
Journal ArticleDOI
Plants and Productivity in International Trade
Andrew B. Bernard,Andrew B. Bernard,Andrew B. Bernard,Jonathan Eaton,Jonathan Eaton,J. Bradford Jensen,J. Bradford Jensen,Samuel Kortum,Samuel Kortum +8 more
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors reconcile international trade theory with findings of enormous plant-level heterogeneity in exporting and productivity, and fit the model to bilateral trade among the United States and its 46 major trade partners, and see how well it can explain basic facts about U.S. plants: (i) productivity dispersion, (ii) the productivity advantage of exporters, (iii) the small fraction who export, and (iv) a small fraction of revenues from exporting among those that do).
Posted Content
The Case of the Missing Trade and Other Mysteries
TL;DR: The Heckscher-Ohlin-Vanek (HOV) theorem, which predicts that countries will export products that are made from factors in great supply, performs poorly as mentioned in this paper.