Credit Constraints, Heterogeneous Firms and International Trade
Reads0
Chats0
TLDR
This article examined the detrimental consequences of financial market imperfections for international trade and developed a heterogeneous-firm model with countries at different levels of financial development and sectors of varying financial vulnerability.Abstract:
This paper examines the detrimental consequences of financial market imperfections for international trade. I develop a heterogeneous-firm model with countries at different levels of financial development and sectors of varying financial vulnerability. Applying this model to aggregate trade data, I study the mechanisms through which credit constraints operate. First, financial development increases countries' exports above and beyond its impact on overall production. Firm selection into exporting accounts for a third of the trade-specific effect, while two thirds are due to reductions in firm-level exports. Second, financially advanced economies export a wider range of products and their exports experience less product turnover. Finally, while all countries service large destinations, exporters with superior financial institutions have more trading partners and also enter smaller markets. All of these effects are magnified in financially vulnerable sectors. These results have important policy implications for less developed economies that rely on exports for economic growth but suffer from poor financial contractibility.read more
Figures

Table 10. Economic Significance: Predicted vs. Actual Trade Growth 
Table 9. Economic Significance: Comparative Statics 
Table 5. Financial Development and Firm-Level Exports 
Figure 3. The Productivity Cut-off for Exporting 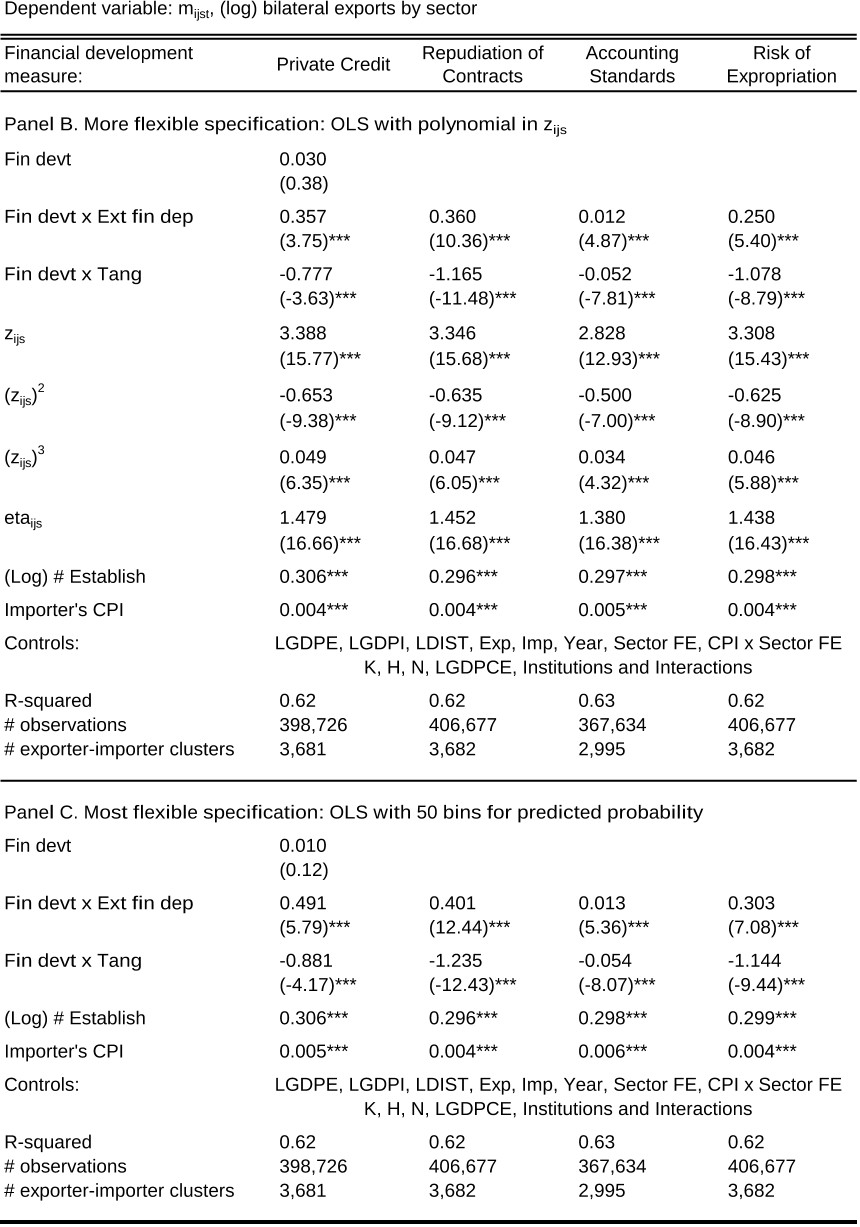
Table 5. Financial Development and Firm-Level Exports 
Table 1. Export Patterns in the Data
Citations
More filters
Posted Content
Financial Frictions and Export Dynamics
TL;DR: This paper studied the relationship between firm export dynamics and financial constraints in a small open economy model and found that financial constraints can largely explain the decreasing hazard rate and the increasing export volume of new exporters.
Posted Content
Labor Market Frictions as a Source of Comparative Advantage, with Implications for Unemployment and Inequality
TL;DR: In this article, the impact of trade on unemployment and inequality is studied, combining this approach with labor market frictions and worker heterogeneity, providing a framework for studying the effect of trade.
Posted Content
Trade Intermediation, Financial Frictions, and the Gains from Trade
TL;DR: In this article, a heterogeneous firm model of international trade with trade intermediation and financial frictions is developed, and the model finds strong empirical support in firm-level data on indirect exports for 118 countries as well as country level data on entrepA´t trade through Hong Kong for over 50 countries.
Posted Content
Markups and Productivity under Heterogeneous Financial Frictions
TL;DR: In this article, the authors incorporate heterogeneous financial frictions in a setting of monopolistically competitive firms with endogenous markups, and show how heterogeneity in access to finance explains part of the dispersion of prices and markups.
Journal ArticleDOI
Skills, population aging, and the pattern of international trade
Ke Gu,Andrey Stoyanov +1 more
TL;DR: In this article, the authors find evidence for a significant negative effect of population aging on comparative advantage of a country in industries that are intensive in skill adaptability of labor force, in both the cross-sectional and dynamic panel data sets.
References
More filters
Posted Content
Law and Finance
Rafael La Porta,Rafael La Porta,Florencio Lopez de Silanes,Florencio Lopez de Silanes,Andrei Shleifer,Andrei Shleifer,Robert W. Vishny,Robert W. Vishny +7 more
TL;DR: This paper examined legal rules covering protection of corporate shareholders and creditors, the origin of these rules, and the quality of their enforcement in 49 countries and found that common law countries generally have the best, and French civil law countries the worst, legal protections of investors.
Journal ArticleDOI
Law and Finance
TL;DR: In this article, the authors examined legal rules covering protection of corporate shareholders and creditors, the origin of these rules, and the quality of their enforcement in 49 countries and found that common-law countries generally have the strongest, and French civil law countries the weakest, legal protections of investors, with German- and Scandinavian-civil law countries located in the middle.
Journal ArticleDOI
The Impact of Trade on Intra-Industry Reallocations and Aggregate Industry Productivity
TL;DR: This paper developed a dynamic industry model with heterogeneous firms to analyze the intra-industry effects of international trade and showed how the exposure to trade will induce only the more productive firms to enter the export market (while some less productive firms continue to produce only for the domestic market).
Journal ArticleDOI
Finance and Growth: Schumpeter Might Be Right
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors examined a cross-section of about 80 countries for the period 1960-89 and found that various measures of financial development are strongly associated with both current and later rates of economic growth.
ReportDOI
Financial Dependence and Growth
Raghuram G. Rajan,Raghuram G. Rajan,Raghuram G. Rajan,Luigi Zingales,Luigi Zingales,Luigi Zingales +5 more
TL;DR: This paper examined whether financial development facilitates economic growth by scrutinizing one rationale for such a relationship; that financial development reduces the costs of external finance to firms, and found that industrial sectors that are relatively more in need of foreign finance develop disproportionately faster in countries with more developed financial markets.