Q2. How many samples are enlarged to obtain a SNR142?
a white Gaussian noise is added on the response to obtain a SNR¼2 and the signal duration is enlarged 10 times (i.e. one million samples) while keeping the same speed variation.
Q3. What is the efficient indicator for the assessment of CS2 sources in rotating machine?
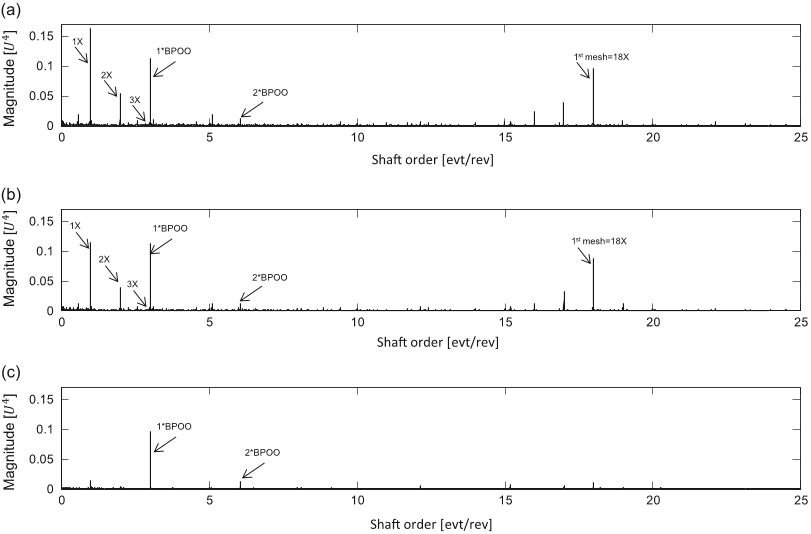
In vibration analysis of rotating machine, the squared envelope spectrum (SES) is one of the most efficient indicators for the assessment of CS2 sources which are typical symptoms of damage in rolling element bearing faults [35].
Q4. What is the reason for the high error in the second?
According to Eq. (20), the high error in the former is due to the low number of cycles associated with the regime, while the high error in the second is due to the high mean instantaneous power.
Q5. What is the flow-chart of this method?
The flow-chart of this method is provided in Fig. 4.Since all signals are finite-length in practice, the asymptotic conditions in the GSA definition (see Eq. (15) cannot be met, resulting in a bias and variance of the raw estimator.
Q6. What is the Fourier coefficient of the response at a given instant?
In this case, the Fourier coefficients of the response at a given instant are principally dependent on the operating speed at that instant, as well as past and future instances of the speed profile.
Q7. What is the KDE method for smoothing the GSA?
In this context, the kernel density estimation (KDE) method—also termed the Parzen–Rosenblatt window method—provides a non-parametric solution for an efficient smoothing operation [29,30].
Q8. What are the two parameters that govern the bias of the estimator?
there are two parameters that govern the bias, namely the speed resolution, δω, and the second derivative of the actual GSA with respect to speed.
Q9. How is the effect of the transmission path in rotating machines modeled?
A natural way to model the effect of the transmission path in rotating machines is by exciting a single degree-of-freedom (dof) system by a constant-amplitude chirp.
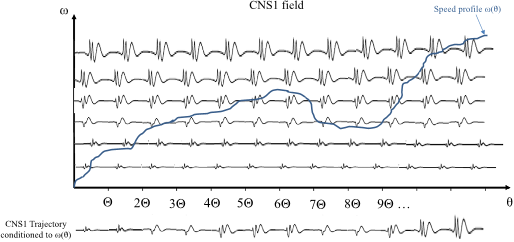
Q10. What is the speed profile of a finite-length CNS signal?
In details, the speed profile is divided into a predefined set of speed intervals called regimes defined by their central frequency ωr and the speed resolution δω.
Q11. How can the GSA be relaxed in the general case?
In particular, it has been assumed that the speed variations are slower than the signal cycle; although this condition seems reasonable in several applications, it can easily be relaxed in the general case by averaging portions of signal smaller than cycles.
Q12. What is the heaviside function used to enforce the system causality?
with A¼ 10; ξ¼ 0:05; ωn ¼ 2π 200, ωd ¼ωnffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi1 ξ2q, and ~U tð Þ the Heaviside function used to enforce the system causality.