Identifying FDI spillovers
TLDR
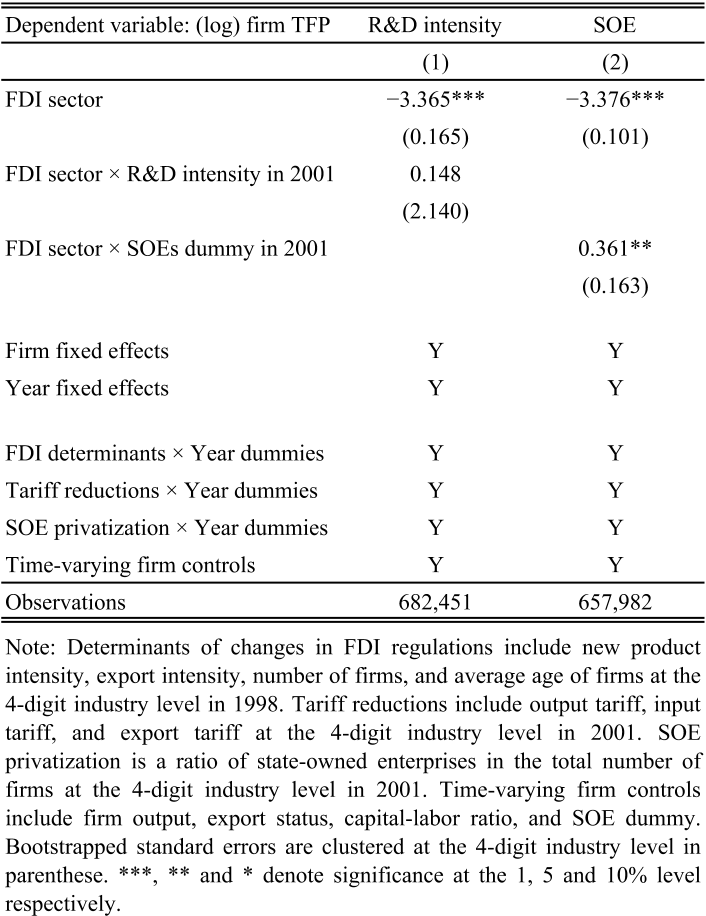
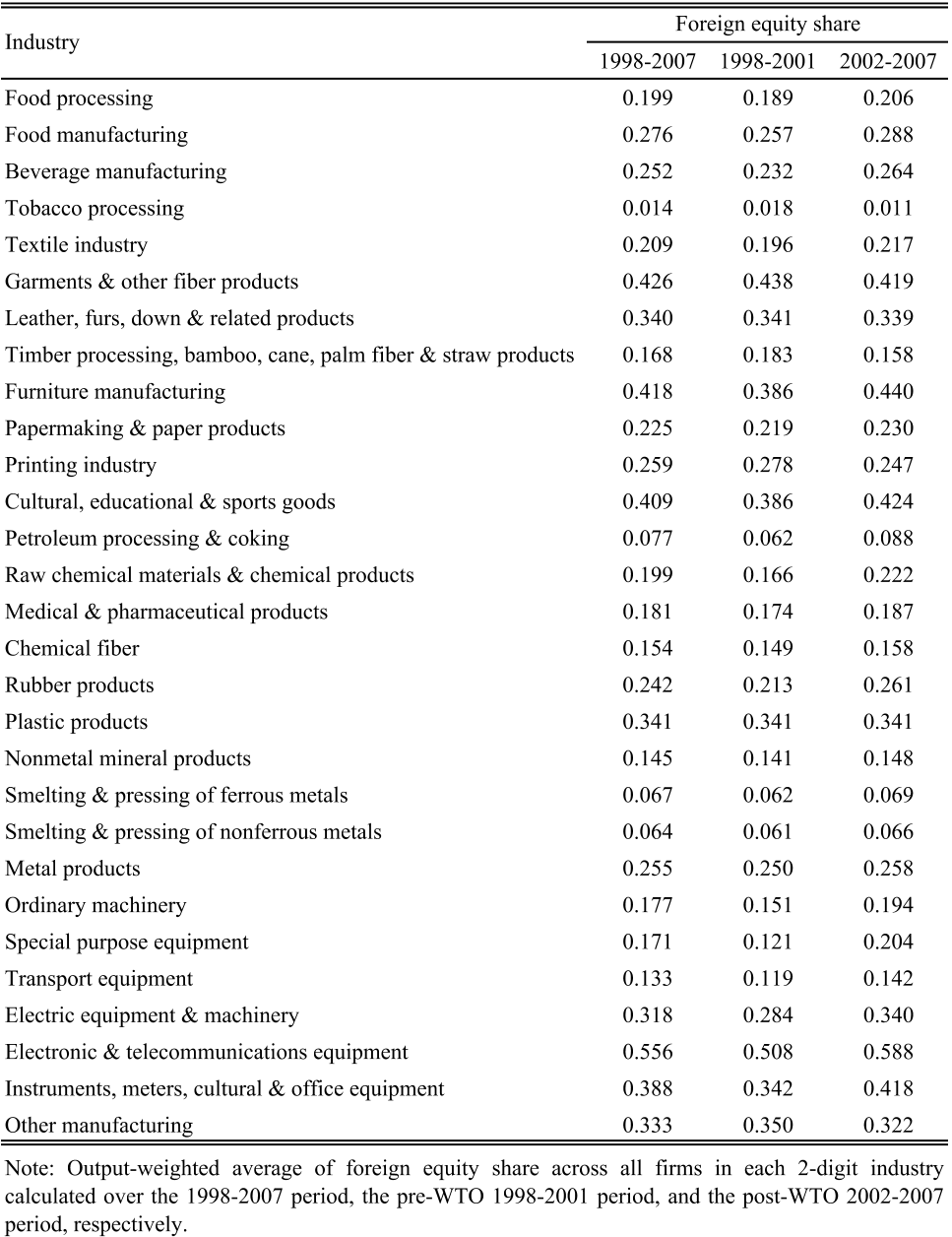
In this paper, the authors improved on the strategy used in the literature to identify the spillover effect of horizontal foreign direct investment (FDI) by taking advantage of the plausibly exogenous relaxation of FDI regulations on China's World Trade Organization accession at the end of 2001.About:
This article is published in Journal of International Economics.The article was published on 2017-07-01 and is currently open access. It has received 281 citations till now. The article focuses on the topics: Spillover effect & Foreign direct investment.read more
Figures
Citations
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Foreign influence, control, and indirect ownership: Implications for productivity spillovers
TL;DR: In this article, the authors revisited the historical distinction between control and influence by the foreign owner and defined "controlled" foreign firms as those with a foreign ultimate owner holding 50% or more of voting shares.
Journal ArticleDOI
Import competition and the gender gap in labor force participation: Evidence from China
TL;DR: Wang et al. as discussed by the authors found that import competition enlarges the gender gap in labor force participation in China during 1990 and 2005, and that the magnitude of the gender-differential effects of import competition grows by age, and peaks for people aged 46-50.
Posted Content
A Review of the Literature on Productivity Impacts of Global Value Chains and Foreign Direct Investment: Towards an Integrated Approach
TL;DR: In this paper, an integrated approach of incorporating the insightful perspective of GVC studies into the empirical approach of FDI studies will likely lead to more meaningful empirical findings that may reveal, in greater depth, the mechanisms underlying the productivity improvements of local enterprises in developing countries.
Journal ArticleDOI
Estimating and testing the multicountry endogenous growth model
TL;DR: In this article, the authors estimate Cobb-Douglas production functions that parameterize unobserved total factor productivity as a global technology process interacted with country-specific absorptive capacities, and show that an enhancement in absorptive capacity raises a country's long-run productivity level but not its growth rate.
Posted Content
International Technology Transfer and Domestic Innovation: Evidence from the High-Speed Rail Sector in China
Yatang Lin,Yu Qin,Zhuan Zie +2 more
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors exploit the large-scale introduction of high-speed railway (HSR) technology into China in 2004 as a natural experiment to address the question of how the transfer of advanced technology spur innovation in developing countries.
References
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
How Much Should We Trust Differences-In-Differences Estimates?
TL;DR: In this article, the authors randomly generate placebo laws in state-level data on female wages from the Current Population Survey and use OLS to compute the DD estimate of its "effect" as well as the standard error of this estimate.
Journal ArticleDOI
The Impact of Trade on Intra-Industry Reallocations and Aggregate Industry Productivity
TL;DR: This paper developed a dynamic industry model with heterogeneous firms to analyze the intra-industry effects of international trade and showed how the exposure to trade will induce only the more productive firms to enter the export market (while some less productive firms continue to produce only for the domestic market).
Posted Content
The Impact of Trade on Intra-Industry Reallocations and Aggregate Industry Productivity
TL;DR: In this paper, a dynamic industry model with heterogeneous firms is proposed to explain why international trade induces reallocations of resources among firms in an industry and contributes to a welfare gain.
Posted Content
The Dynamics Of Productivity In The Telecommunications Equipment Industry
George S Olley,Ariel Pakes +1 more
TL;DR: In this article, the authors developed an estimation algorithm that takes into account the relationship between productivity on the one hand, and both input demand and survival on the other, guided by a dynamic equilibrium model that generates the exit and input demand equations needed to correct for the simultaneity and selection problems.
Posted Content
R&D Spillovers and the Geography of Innovation and Production
TL;DR: In this paper, the spatial distribution of innovation activity and the geographic concentration of production are examined, using three sources of economic knowledge: industry R&D, skilled labor, and the size of the pool of basic science for a specific industry.
Related Papers (5)
Do Domestic Firms Benefit from Direct Foreign Investment? Evidence from Venezuela
Brian J. Aitken,Ann Harrison +1 more