Identifying FDI spillovers
TLDR
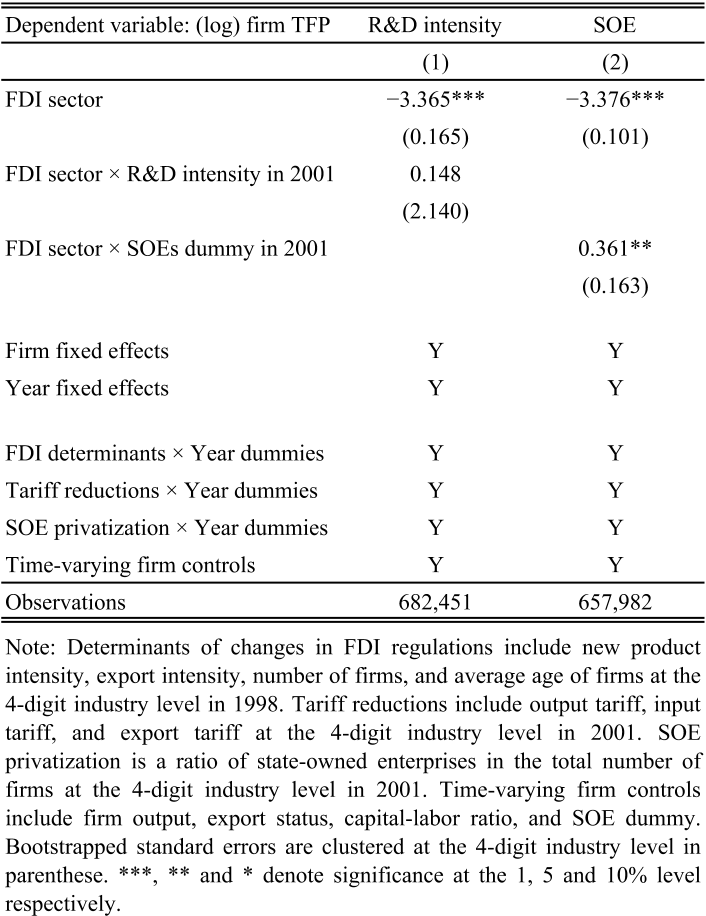
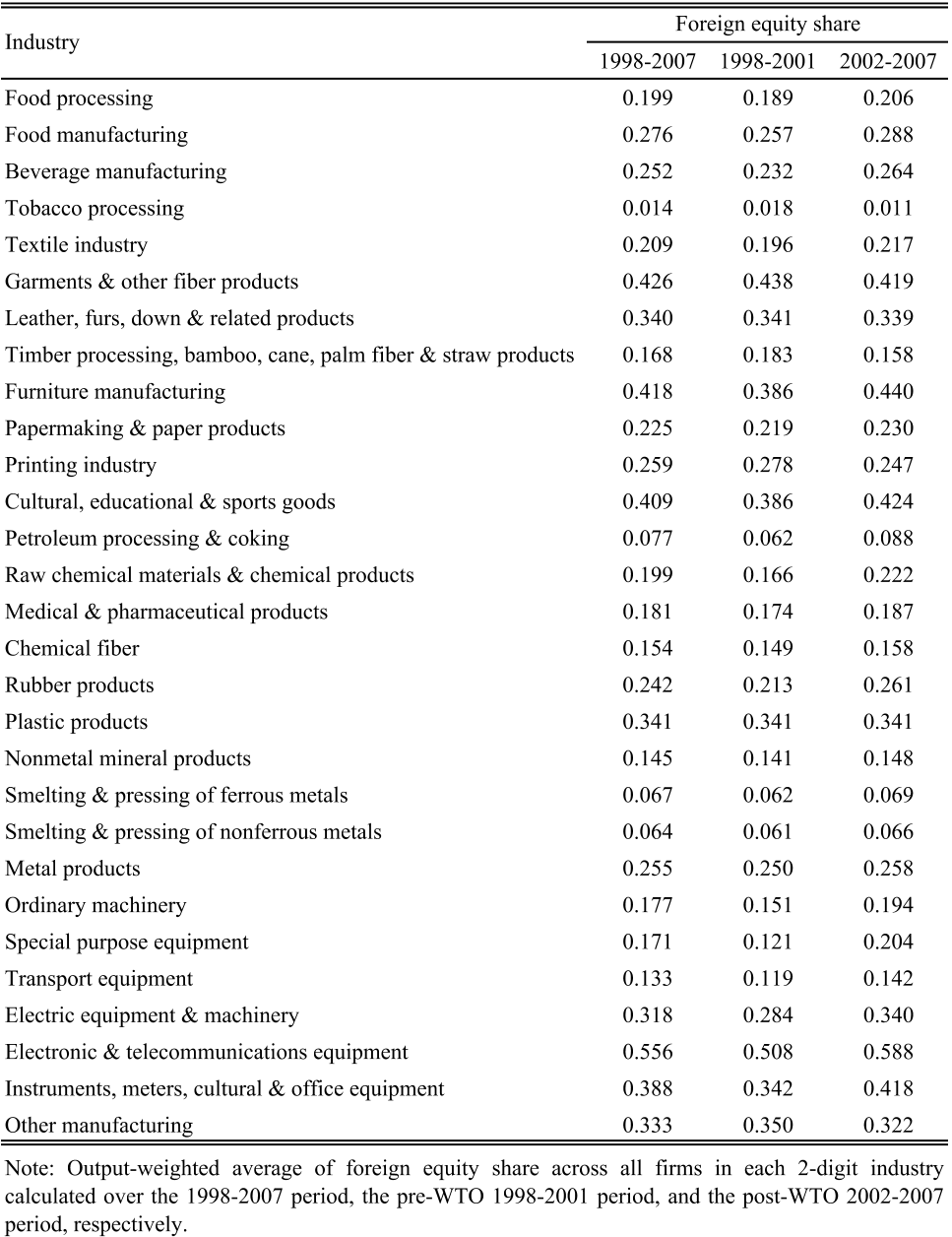
In this paper, the authors improved on the strategy used in the literature to identify the spillover effect of horizontal foreign direct investment (FDI) by taking advantage of the plausibly exogenous relaxation of FDI regulations on China's World Trade Organization accession at the end of 2001.About:
This article is published in Journal of International Economics.The article was published on 2017-07-01 and is currently open access. It has received 281 citations till now. The article focuses on the topics: Spillover effect & Foreign direct investment.read more
Figures
Citations
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Low-carbon city pilot and carbon emission efficiency: Quasi-experimental evidence from China
Yantuan Yu,Ning Zhang +1 more
TL;DR: In this paper, the causal effect of low-carbon city pilot (LCCP) policy on carbon emission efficiency (CEE) was identified and a general nonconvex metafrontier data envelopment analysis model was developed to calculate CEE.
Journal ArticleDOI
Green spillovers of outward foreign direct investment on home countries: Evidence from China's province-level data
TL;DR: Wang et al. as mentioned in this paper examined empirically the reverse spillovers of China's OFDI on its domestic green development, and found that the relationship between OFDI, absorptive capability, environmental regulation stringency, and green economic growth are robust to multiple econometric methods and alternative proxies for threshold variables.
Repository
Is housing still the business cycle? Perhaps not
TL;DR: This article showed that residential investment led GDP under a wide range of specifications, while non-residential investment did not, and showed that the increasing stringency of local land use policy had interfered with the ability of the Federal Reserve to use housing as an instrument on monetary policy.
Journal ArticleDOI
Greening the career incentive structure for local officials in China: Does less pollution increase the chances of promotion for Chinese local leaders?
Mingqin Wu,Xun Cao +1 more
TL;DR: Li et al. as mentioned in this paper examined the effect of local environment regulation outcomes, i.e., local pollution, on leaders' chances of promotion, and found that those who are able to reduce air pollution are more likely to be promoted.
References
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Testing for horizontal and vertical foreign investment spillovers in China, 1998–2007
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors show that foreign investment originating outside of Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan has positive effects on individual firm level productivity, while foreign investment from HKMT firms does not.
Posted Content
Convergence to the Law of One Price Without Trade Barriers or Currency Fluctuations
TL;DR: In this paper, an upper bound estimate of the rate of convergence to purchasing power parity was provided using a panel of 51 prices from 48 cities in the United States, and they investigated some potentially serious biases induced by i.i.d. measurement errors in the data and found their estimates to be robust to these potential biases.
Journal ArticleDOI
Is China different? A meta-analysis of the effects of foreign direct investment on domestic firms
TL;DR: The authors performed a meta-analysis on a sample of 67 country-specific studies yielding 137 observations that have gauged the link between FDI and measures of economic growth, finding that the impact of FDI is, on average, more positively significant for China than for the full sample of countries, but that the difference between China and other transition economies is less clear.
Journal ArticleDOI
Do Foreign Firms Crowd Out Domestic Firms? Evidence from the Czech Republic
TL;DR: The authors analyzes the impact of foreign presence on growth and survival of domestic firms, and analyzes whether the crowding out effect is dynamic, i.e., domestic firms cut production over time as foreign firms grow, or a static effect realized upon foreign entry into the industry.
Journal ArticleDOI
Imperfect factor mobility and the distribution of income
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors investigated the degree of labor mobility in a two-good model in which the "degree of labour mobility" is measured by the elasticity of a convex input transformation curve and the existence of such a transformation curve is justified by a model where individual workers have differing relative and absolute efficiencies in different industries.
Related Papers (5)
Do Domestic Firms Benefit from Direct Foreign Investment? Evidence from Venezuela
Brian J. Aitken,Ann Harrison +1 more