Morphological response to river engineering and management in alluvial channels in Italy
Nicola Surian,Massimo Rinaldi +1 more
Reads0
Chats0
TLDR
In this article, the authors reviewed all existing published studies and available data, and aimed to reconstruct a general outline of the main channel adjustments that have occurred in Italian rivers during the past 100 years.About:
This article is published in Geomorphology.The article was published on 2003-03-01 and is currently open access. It has received 580 citations till now. The article focuses on the topics: Channel pattern & Fluvial.read more
Figures

Fig. 5. Trends of average channel width in the braided reach of the Piave River (the reach is 115 km long). Channel width was measured along 94 transects on historical maps and aerial photographs (modified from Surian, in press). 
Fig. 3. Channel narrowing along the Brenta River: (A) topographic map (I.G.M.) of 1887; (B) aerial photograph of 1999. Besides narrowing, decrease in intensity of braiding, increase in channel sinuosity and change in channel pattern (from braided to wandering) have taken place during the last century. 
Fig. 4. Trends of bed-level adjustments. (A) Po River: minimum annual river stage at the gauging station of Cremona (modified from Lamberti and Schippa, 1994). (B) Arno River in the Lower Valdarno reach: changes in bed bottom elevation obtained from longitudinal profiles and cross sections of different years (modified from Rinaldi and Simon, 1998). Horizontal hatched line: trend of stable (dynamic equilibrium) conditions before incision; continuous curves: fitting exponential decay functions. 
Table 3 (continued ) 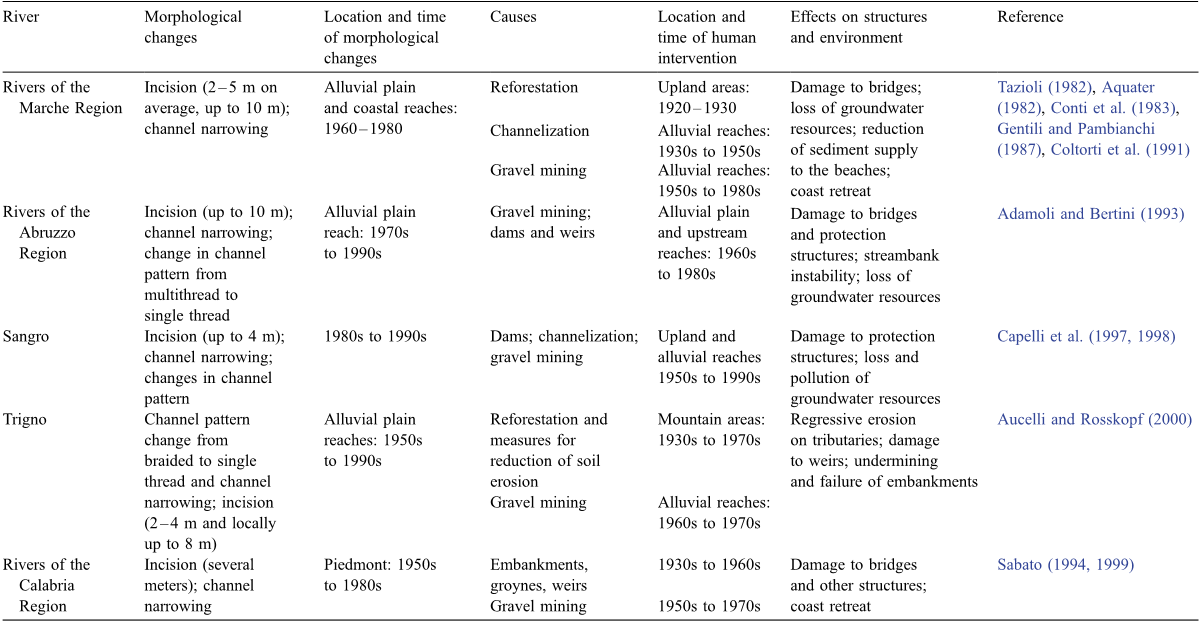
Table 2 Recent channel adjustments in Italian rivers and relative causes and effects 
Fig. 2. Channel incision along the Arno River in the Lower Valdarno–Pisa Plain reach. (A) Example of typical change in cross section, with limited bed lowering from 1936 to 1954, and intense incision from 1954 to 1978. Total bed level lowering from 1844 to 1978 was 6.3 m. (B) Bridge 2 km upstream of the previous section, with exposed piles due to the incision.
Citations
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Climate change and the world's river basins: anticipating management options
Margaret A. Palmer,Margaret A. Palmer,Catherine Reidy Liermann,Christer Nilsson,Martina Flörke,Joseph Alcamo,P. Sam Lake,Nick Bond +7 more
TL;DR: In this article, the authors project river discharge under different climate and water withdrawal scenarios and combine this with data on the impact of dams on large river basins to create global maps illustrating potential changes in discharge and water stress for dam-impacted and free-flowing basins.
Journal ArticleDOI
The human role in changing river channels
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors consider the human role in changing river channels and propose a model to understand the relationship between changes at channel, reach, and network scales, with the most extreme effects produced by building activity and urbanisation.
Journal ArticleDOI
Human influence and the changing geomorphology of Mediterranean deltas and coasts over the last 6000 years: From progradation to destruction phase?
TL;DR: In this article, the authors explore the interactions between geosystems and the human environment, and identify anthropogenic signatures in clastic coastal sedimentary archives, including base-level deltaic and estuarine sedimentary sinks, to understand the life cycle of these deltas.
Journal ArticleDOI
Sediment mining in alluvial channels: physical effects and management perspectives
TL;DR: In this paper, a review of a number of documented case studies from various countries and a detailed analysis of sediment exploitation from five rivers in Italy and Poland is presented, where the authors discuss alluvial river response to extensive sediment mining.
Journal ArticleDOI
Human impacts on fluvial systems in the Mediterranean region
TL;DR: The long history of substantial human impacts on the landscape of the Mediterranean region, and their effects on fluvial systems, is documented in this paper, where the importance of analysing the connectivity within different land units and of the spatial position of human activity within a catchment is illustrated.
References
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
River response to channel regulation: Case study of the Raba river, Carpathians, Poland
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors examined the response of a gravel-bed stream following narrowing and straightening of its channel and found that the change from a slow and relatively steady degradation in the lower reaches to separate degradation events in the higher reaches is attributed to the differential rate of headcut retreat and to the control exerted by mid-channel bars upon the rate of river-energy dissipation.
Journal ArticleDOI
Channel incision, gravel mining and bedload transport in the Rhône river upstream of Lyon, France (“canal de Miribel”)
TL;DR: The Miribel canal is a former arm of the Rhone embanked between 1848 and 1857 over a length of 18 km to improve navigation at low discharges.
Journal ArticleDOI
Channel bed adjustment along mine-affected rivers of northeast Tasmania
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors measured the degradation rate of the Ringarooma and George Rivers between 1875 and 1984 and found that degradation followed the same pattern as aggradation.
Journal ArticleDOI
Evolution of mid‐channel bars in a braided river and complex response to reservoir construction: an example from the middle Hanjiang River, China
TL;DR: In this paper, the development of mid-channel bars in a braided river, as controlled by channel boundary conditions; runoff and sediment load, as well as reservoir construction, was investigated.
Human impact on sediment yield and channel dynamics in the Arno River basin (central Italy)
Paolo Billi,Massimo Rinaldi +1 more
TL;DR: In this paper, a comparison of many cross-sections spanning a period of more than one century was made to identify the dominant channel changes and the relationship between vertices and lateral adjustments.
Related Papers (5)
Causes of 20th century channel narrowing in mountain and piedmont rivers of southeastern France
Frédéric Liébault,Hervé Piégay +1 more