Morphological response to river engineering and management in alluvial channels in Italy
Nicola Surian,Massimo Rinaldi +1 more
Reads0
Chats0
TLDR
In this article, the authors reviewed all existing published studies and available data, and aimed to reconstruct a general outline of the main channel adjustments that have occurred in Italian rivers during the past 100 years.About:
This article is published in Geomorphology.The article was published on 2003-03-01 and is currently open access. It has received 580 citations till now. The article focuses on the topics: Channel pattern & Fluvial.read more
Figures

Fig. 5. Trends of average channel width in the braided reach of the Piave River (the reach is 115 km long). Channel width was measured along 94 transects on historical maps and aerial photographs (modified from Surian, in press). 
Fig. 3. Channel narrowing along the Brenta River: (A) topographic map (I.G.M.) of 1887; (B) aerial photograph of 1999. Besides narrowing, decrease in intensity of braiding, increase in channel sinuosity and change in channel pattern (from braided to wandering) have taken place during the last century. 
Fig. 4. Trends of bed-level adjustments. (A) Po River: minimum annual river stage at the gauging station of Cremona (modified from Lamberti and Schippa, 1994). (B) Arno River in the Lower Valdarno reach: changes in bed bottom elevation obtained from longitudinal profiles and cross sections of different years (modified from Rinaldi and Simon, 1998). Horizontal hatched line: trend of stable (dynamic equilibrium) conditions before incision; continuous curves: fitting exponential decay functions. 
Table 3 (continued ) 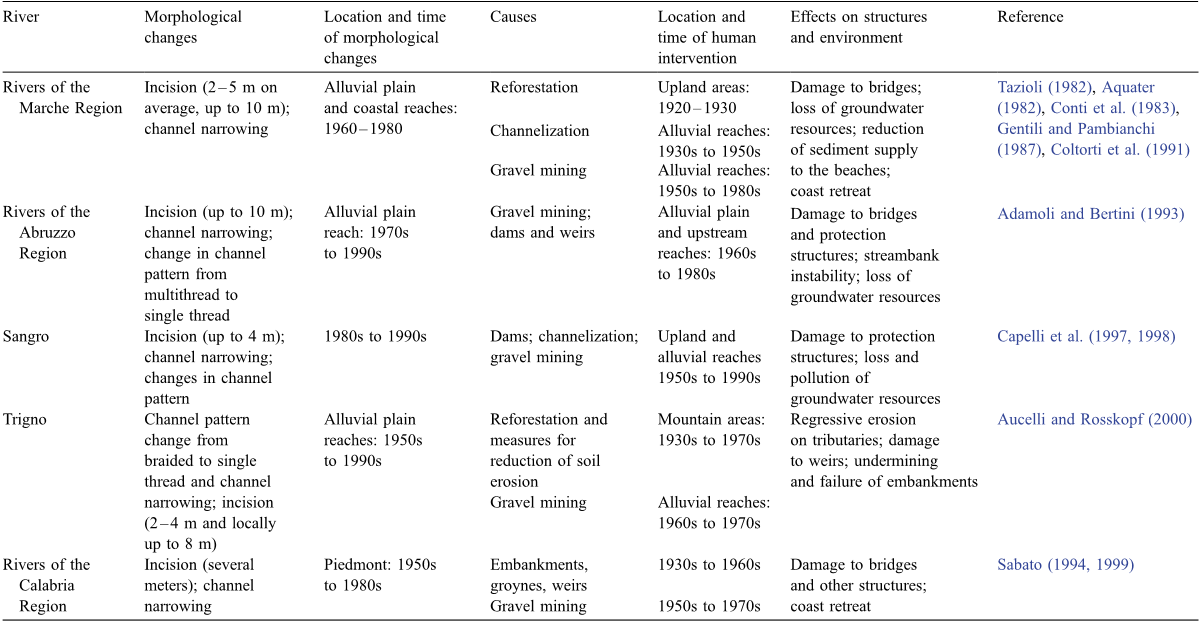
Table 2 Recent channel adjustments in Italian rivers and relative causes and effects 
Fig. 2. Channel incision along the Arno River in the Lower Valdarno–Pisa Plain reach. (A) Example of typical change in cross section, with limited bed lowering from 1936 to 1954, and intense incision from 1954 to 1978. Total bed level lowering from 1844 to 1978 was 6.3 m. (B) Bridge 2 km upstream of the previous section, with exposed piles due to the incision.
Citations
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
Long-term river management legacies strongly alter riparian forest attributes and constrain restoration strategies along a large, multi-use river.
Philippe Janssen,John C. Stella,B. Räpple,Charles-Robin Gruel,Gabrielle Seignemartin,Bernard Pont,Simon Dufour,Hervé Piégay +7 more
TL;DR: To enhance the functionality of these human-made ecosystems, restoration strategies should target the reconnection of dike fields to the river by dismantling part of the dikes to promote lateral erosion, forest initiation and community succession, as well as increasing minimum flows in channels to improve connection with groundwater.
Journal ArticleDOI
Enhancing sediment flux control and natural hazard risk mitigation through a structured conceptual planning approach
TL;DR: In this paper, a structured design workflow is proposed to enhance sediment flux control and hazard risk mitigation in such heavily modified alpine streams, with the overall aim of enhancing sediment flux management and hazard mitigation.
Dissertation
Dynamique des flux sédimentaires et des éléments métalliques en lien avec l’exploitation courante et exceptionnelle d’un barrage hydroélectrique
TL;DR: In this paper, an etude of terrain of 19 mois a l amont and a laval de l’ouvrage a ete effectuee en conditions courantes and evenementielles d'exploitation.
Human impacts on fluvial systems in the Mediterranean region (Invited paper for Binghamton Symposium
TL;DR: The long history of substantial human impacts on the landscape of the Mediterranean region, and their effects on fluvial systems, is documented in this article, where the importance of analysing the connectivity within different land units and of the spatial position of human activity within a catchment is illustrated.
References
More filters
Journal ArticleDOI
PROFILE: Hungry Water: Effects of Dams and Gravel Mining on River Channels
TL;DR: Management of sand and gravel in rivers must be done on a regional basis, restoring the continuity of sediment transport where possible and encouraging alternatives to river-derived aggregate sources.
OtherDOI
Downstream effects of dams on alluvial rivers.
G.P. Williams,M.G. Wolman +1 more
TL;DR: In this paper, the authors describe changes in mean channel-bed elevation, channel width, bed-material sizes, vegetation, water discharges, and sediment loads downstream from 21 dams constructed on alluvial rivers.
Journal ArticleDOI
A model of channel response in disturbed alluvial channels
TL;DR: In this article, the adjustment of channel geometry and phases of channel evolution are characterized by six process-oriented stages of morphologic development, premodified, constructed, degradation, threshold, aggradation, and restabilization.
Journal ArticleDOI
Riparian vegetation and island formation along the gravel‐bed Fiume Tagliamento, Italy
Angela M. Gurnell,Geoffrey E. Petts,David M. Hannah,Barnaby P.G. Smith,Peter J. Edwards,Johannes Kollmann,James V. Ward,Klement Tockner +7 more
TL;DR: In this paper, a conceptual model of island development is proposed which integrates the interactions between large woody debris and vegetation, geomorphic features, sediment calibre and hydrological regime.
Related Papers (5)
Causes of 20th century channel narrowing in mountain and piedmont rivers of southeastern France
Frédéric Liébault,Hervé Piégay +1 more