Q2. What are the future works in "Analysis and optimization of temperature distribution in carbon fiber reinforced composite materials during microwave curing process" ?
Future studies will be carried out to identify the relationship between several physical mechanisms in microwave curing to get a better temperature distribution and establish the standard process specifications.
Q3. What is the physical mechanism of microwave curing?
The physical mechanism of microwave curing includes the natural heat convection of air inthe microwave oven, heat conduction inside the composite material and the directly heating action of microwave.
Q4. What was the result of the composite curing cycle?
Using the vacuum pressure technology and ceramic tooling, the composite samples achieved lower cost in manufacturing and better performance.
Q5. What is the reason why Bogetti and Gillespie reported that the complex gradients of temperature?
Bogetti and Gillespie (1992) reported that the complex gradients of temperature in thickness direction of composite laminates may cause serious process-induced residual stress and deformation.
Q6. What is the effect of the microwave on the surface of composites?
Under the action of an electromagnetic field, the temperature at the surface of carbon fiberreinforced composites is lower than the target temperature, no matter for what kinds of composite laminates.
Q7. What is the effect of microwave curing on the reaction rates of carbon fiber reinforced composites?
Boey and Yap (2001) reported that microwave curing was more effective than conventional heating in enhancing the reaction rates during cross-linking by testing different curing agents in curing.
Q8. What is the condition to be satisfied to get such a Bragg reflected wavelength?
The condition to be satisfied to get such a Bragg reflected wavelength is known as Bragg condition and is given by Grattan and Meggitt (1997) as: 2B nD (1)
Q9. What are the thickness values of composite laminates?
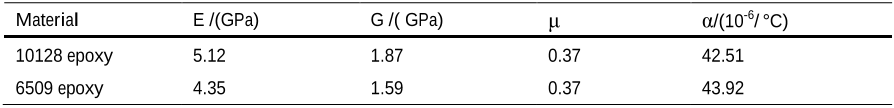
The thickness values of composite laminates are 4.5, 7.5 and 22.5mm, corresponding to sample #1, sample #2 and sample #3 respectively.
Q10. What are the important dwell stages?
The most important dwell stages were studied to analysis the temperature distribution influenced by ply orientation and thickness.
Q11. What is the definition of a periodic perturbation of the refractive index?
A periodic perturbation of the refractive index can be formed along the fiber length through the change of reflection wavelength influenced by the physical or mechanical characteristics of the grating area.
Q12. What are the two main solutions for the temperature distribution of composite laminates?
Based on the analysis, in order to uniform the temperature distribution of compositelaminates, different solutions need to be applied.
Q13. What is the reason why composites are becoming so popular?
For the above reason, alternative processing technologies, such as microwave curingtechnologies have been developed to form composite structures and provide a uniform temperature distribution.
Q14. How was the vacuum pressure used in the microwave cured composites?
Considering the previous work, the 0.09Mpa vacuum pressure was provided when heating from 100 °C or 90 °C to the end of heat preservation.
Q15. What was the curing cycle of the composite laminates?
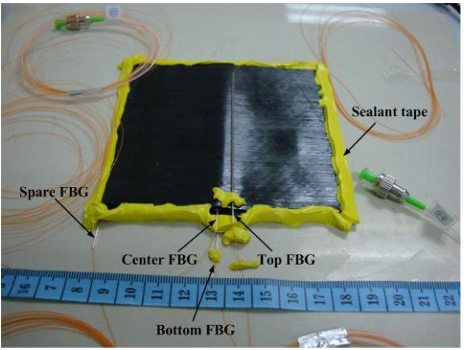
The composite laminates were laid up on a ceramic tooling coated with release agent and the edge areas were covered by sealant tapes.